Abstract
Purpose
To derive the temperature response of the basic unit of the electromagnetic calorimeter of the high energy cosmic-radiation detection (HERD) facility.
Method
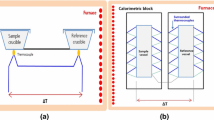
Tested a method to measure HERD calorimeter cell (HCC) light yield using an ultraviolet Light-Emitting Diode with a wavelength of 300 nm, and established an experimental setup and tested the light yield of the HCC at different temperatures in a thermal chamber.
Results and conclusions
The result showed that the signal amplitudes variation of the HCC reached up to 10.2% with temperature ranging from 0 to 60 °C, if we narrow the temperature range to 0– 35 °C, the variation was about 3.7% and it showed much better linearity. This result provides a good instruction on the thermal control of the HERD calorimeter (CALO) to improve its performance.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Altomare et al., Particle identification capability of Plastic scintillator tiles equipped with SiPMs for the High Energy cosmic-Radiation Detection (HERD) facility. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A: Accel Spectrom Detect Assoc Equip 983, 164476 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2020.164476
P.W. Cattaneo, The space station based detector HERD: precise high energy cosmic rays physics and multimessenger astronomy. Nucl Particle Phys Proc 306–308, 85–91 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nuclphysbps.2019.07.013
C. Wanarak et al., Luminescence and scintillation properties of Ce-doped LYSO and YSO crystals. Adv Mater Res 199–200, 1796–1803 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.199-200.1796
T. Yagi et al., A small high sensitivity neutron detector using a wavelength shifting fiber. Appl Radiat Isot 69(1), 176–179 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2010.07.016
L. Cheng et al., Temperature induced spectral lines broadening and fluorescence quenching in Tm:YAG crystals. Acta Opt Sinica (1999). https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0253-2239.1999.02.019
Zhang T et al. (2016) Several main influencing factors of the LYSO:Ce Afterglow. J Synth Cryst https://doi.org/10.16553/j.cnki.issn1000-985x.2016.07.013.
Z. Zong et al., Study of light yield for different configurations of plastic scintillators and wavelength shifting fibers. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res 908, 82–90 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2018.08.029
Kim CL (2005) A study on the temperature characteristics of LYSO PET detector. In: Nuclear science symposium conference record, IEEE vol.4. 2005, 4-.https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=1596728&tag=1
G.V. Ioannis et al., Evaluation of the light emission efficiency of LYSO: Ce scintillator under X-ray excitation for possible applications in medical imaging. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2006.08.018
K. Wei et al., Photoluminescence nonlinearity and picosecond transient absorption in an LYSO: Ce scintillator excited by a 266 nm ultraviolet laser. RSC Adv 11(28), 17020–17024 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA00347J
J.D. Naud, T.A. Tombrello, The role of cerium sites in the scintillation mechanism of LSO. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 43(3), 1324–1328 (1996)
C.M. Pepin et al., Properties of LYSO and recent LSO scintillators for phoswich PET detectors. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 51(3), 789–795 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNS.2004.829781
Suzuki H, Tombrello TA, Melcher CL et al (1992) Light emission mechanism of Lu2(SiO4)O:Ce. Nuclear science symposium and medical imaging conference, 1992. Conference Record of the 1992 IEEE. IEEE. http://authors.library.caltech.edu/50503/1/00256584.pdf
H. Suzuki, T.A. Tombrello, C.L. Melcher et al., UV and gamma-ray excited luminescence of cerium-doped rare-earth oxyorthosilicates. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A: Accel Spectrom Detect Assoc Equip 320(1–2), 263–272 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-9002(92)90784-2
Z. Ji et al., Investigation of optical transmittance and light response uniformity of 600-mm-long BGO crystals. Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res A 753, 143–148 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2014.03.056
Acknowledgements
Thank the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12027803, 11875097, 11975257) and the support from the International Partnership Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. 113111KYSB20190020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Y., Cui, X., Liu, X. et al. Study on temperature response of the HERD calorimeter cell. Radiat Detect Technol Methods 7, 227–233 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-022-00377-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41605-022-00377-7