Abstract
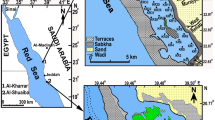
Examination of the surficial sediments of Bardawil lagoon displayed variations in the relative abundance of diatoms deposited in different sites. The disparities were dependent on several environmental factors such as pH, salinity, water depth, and some biological productivity and chemical elements. A total of 88 diatom species belonging to 37 genera were identified and counted from 12 samples that distributed along the lake. The composition of the diatom assemblage showed that the planktonic forms are not dominant as the epiphytic and benthic ones. The recorded assemblage is mainly dominated by littoral cosmopolitan marine species associated with a considerable amount of oligohalobous and mesohalobous diatom taxa. The freshwater forms are normally allochthonous and may be originated from the adjacent areas. Multivariate statistical techniques including canonical correspondence analysis and hierarchical ascending clustering were used to identify the diatom ecological groups and to investigate which environmental variables were important in explaining the variation between these groups. Five ecological groups containing distinctive diatom assemblages were recognized.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd Ellah RG, Hussein M (2009) Physical limnology of Bardawil lagoon, Egypt. American-Eurasian Journal of Agriculture and Environmental Science 5(3):331–336
Alakananda B, Mahesh K, Supriya G, Boominathan MC, Balachandran L, Ramachandra TV (2001) Monitoring tropical urban wetlands through biotic indices. Journal Biodiversity 2(2):91–106
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1989) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater pp 626 17th ed, New York
Ameran A (2004) Studies on the Crustacean fishery in Bardawil Lagoon. Ph.D. Thesis, 228 pp., Fac Environ Agr Sci El-Arish, Suez Canal, Univ. Egypt
Ben-Tuvia A (1975) Comparison of the fish fauna in the Bardawil lagoon and the Bitter Lakes. Rapp Comm Int Mer Médit 233:125–126
Ben-Tuvia A (1979) Studies of the population and fisheries of Sparus aurata in the Bardawil lagoon, eastern Mediterranean. Investig Pesq 431:43–67
Konsowa AH (2007) Phytoplankton evolution in a shallow hypertrophic saline lake- Azhar. J Pharm Sci 132:109–122
De Felice DR, Wise SW (1981) Surface lithofacies, biofaces, and diatom diversity patterns as models for delineation of climatic change in the Southeast Atlantic Ocean. Mar Micropaleontol 6:29–70
Ehrlich A (1975) The diatoms of the surface sediments of the Bardawil lagoon (North Sinai)-Paleoecological significance. Nova Hewigia 53:253–277
El-Bana MI (2006) Floristic composition of a threatened Mediterranean sabkhat of Sinai. - in: khan MA, Böer B, Kust GS, Barth H (eds): Sabkha ecosystems II :109-122, springer publishers, Amsterdam
Farahat HF (2006) Sedimentary processes act on Bardawil lagoon, North Sinai, Egypt. M.Sc. Thesis, 209 pp., Fac. Sci. Banah University, Egypt
Fouda MM, Wanas MK (1987) On the benthic biota of Bardawil lagoon on the Mediterranean coast of Sinai, Egypt. Proceedings of Zoological Society, ARE 14:103–115
Fouda MM, Wanes MK, Saleh MA (1985) Ecology of Bradawil lagoon. A report to the oil pollution res. Unit, Pembroke, U.K. for B.P petroleum ltd. Egypt
Gasse F (1986) East African diatoms. Taxonomy, ecology distribution. Bibl Diatomol 2:1–201
Guzkowska MA, Gasse F (1990) Diatoms as indicators of water quality in some English urban lakes. Freshw Biol 23:233–250
Hammer Ø, Harper DA, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electronica:4
Hustedt F (1930-1966) Die Kieselalgen. - In: Rabenhorst, L. (edit): Kryptogameflora von Deutchland, Oestrreich und der Schweiz 1:1-920, 1-845, 3:1-816. Akademische Verlagesellschaft, Leipzig
Hustedt F (1957) Die Diatomenflora des Fluss-systems der weser im Gebeit der Hansestadt Bremen. Abhandlungen Naturwissenschaften Verein zu Bremen 34:181–440
Khalil MT, Saad AA, Fishar MR, Bedir TZ (2013) Ecological studies on macrobenthic invertebrates of Bardawil wetland, Egypt. World Environment 3(1):1–8
Krammer K, Lange-Bertalot H (1986) Bacillariophyceae. 1Teil: Naviculaceae. - in: Ettl H, Gerloff J, heyning H, Mollenhauer D (eds): Süsswasser von Mitteleuropa 2/1:1-876, Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart and New York
Krammer K, Lange-Bertalot H (1988) Bacillariophyceae. 2 Teil: Bacillariaceae, Epithemiaceae, Surirellaceae. In: Ettl H, Gerloff J, Heyning H, Mollenhauer D (eds) Süsswasser von Mitteleuropa 2/2:1–596. Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart and New York
Krumglaz BS, Hornung H, Oren OH (1980) The study of a natural hypersaline lagoon in a desert area (the Bardawil lagoon in northern Sinai). Estuar Coast Mar Sci 10:403–415
Levente RA (1991) Sediment trap diatom assemblages from the northern Antarctic peninsula region. Deep-Sea Res 8(9):1127–1143
Levy Y (1971) Anomalies of ca+2 and SO4−2 in Bardawil lagoon northern Sinai. Limnol Oceanogr 166:983–987
Lotfy IMH (2003) Mineralogical and geochemical studies on four recent molluscan shells from hypersaline Bardawil lagoon sediments, Egypt. Journal of Egyptian Academic Society of Environment and Development 42:199–218
Prygiel J, Coste M (1993) The assessment of water quality in the Artios-Picardie water basin (France) by the use of diatom indices. Hydrobiology 269(270):343–349
Round FE, Crawford RM, Mann DG (1990) The diatoms. Biology and morphology of the genera. - 747 pp., Cambridge University press, Cambridge
Sabae SZ (2006) Spatial and temporal variations of saprophytic bacteria, fecal indicators and the nutrient cycle bacteria in Lake Bardawil, Sinai, Egypt. Int J Agric Biol 82:178–185
Shaheen SE (1998) Geoenvironmental studies on El-Bardawil lagoon and its surroundings, North Sinai, Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, 165 pp., Mansoura Univ., Mansoura, Egypt
Shehata MB (1989) Essential fatty acids in the Sparus aurata in Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, 210 pp., Fac. Sci. Menoufia Univ. Egypt
Siliem TA (1988) The chemical conditions in Bardawil lagoon. I - Major Cations Bulletin of National Institute of Oceanography and Fisheries ARE 14:123–140
Simonsen R (1962) Untersuchung zur Systematik und Okolegie der Boden-diatomen der westlichen Ostsee. Internationale Revue der gesamten Hydrobiologie und Hydrographie 1:1–144
Ter Braak CJF (1986) Canonical correspondence analysis: a new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology 67:1167–1179
Ter Braak CJF (1988) Partial canonical correspondence analysis. - in: bock HH (ed.), classification and related methods of data analysis, North-Holland, Amsterdam: pp.551-558
Ter Braak CJF (1990) CANOCO–a FORTRAN program for canonical community ordination. Microcomputer power, Ithaca, New York, USA (including update notes)
Vos PC, de Wolf H (1993) Diatoms as a tool for reconstruction sedimentary environments in coastal wetlands; methodological aspects. Hydrobiology 269(270):285–296
Yang JR, Dickman M (1993) Diatoms as indicators of lake trophic status in Central Ontario, Canada. Diatom Research 8(1):179–193
Zalat AA (1997) Distribution of Holocene diatoms and silicoflagellates in bottom sediments of the Lake Timsah, Suez Canal area, Egypt. Egypt J Geol 41(1):103–128
Zalat AA (2002) Distribution and origin of diatoms in the bottom sediments of the Suez canal lakes and adjacent areas, Egypt. Diatom Research 17(1):243–266
Zalat AA (2003) Paleoecological and environmental history of Lake Mariut, Egypt, by means of diatoms. Diatom Research 18(1):161–184
Zalat AA, El-Sheekh M (1999) Diatom assemblages from two brackish Egyptian lakes. Egypt J Bot 39:53–76
Zalat AA, Servant-Vildary S (2005) Distribution of diatom assemblages and their relationship to environmental variables in the surface sediments of three northern Egyptian lakes. J Paleolimnol 34:159–174
Zong Y (1997) Implications of Paralia sulcata abundance in Scottish basins. Diatom Research 12(1):125–150
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zalat, A.A., El-Sheekh, M.M. & Gaballa, M. Distribution Pattern of Diatom Flora in the Surface Sediments of Bardawil Lagoon (North Sinai), Egypt. Thalassas 35, 531–539 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-019-00160-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41208-019-00160-4