Abstract
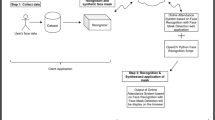
This paper presents a random projection scheme for cancelable iris recognition. Instead of using original iris features, masked versions of the features are generated through the random projection in order to increase the security of the iris recognition system. The proposed framework for iris recognition includes iris localization, sector selection of the iris to avoid eyelids and eyelashes effects, normalization, segmentation of normalized iris region into halves, selection of the upper half for further reduction of eyelids and eyelashes effects, feature extraction with Gabor filter, and finally random projection. This framework guarantees exclusion of eyelids and eyelashes effects, and masking of the original Gabor features to increase the level of security. Matching is performed with a Hamming Distance (HD) metric. The proposed framework achieves promising recognition rates of 99.67% and a leading Equal Error Rate (EER) of 0.58%.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leonard F, Aran S (1987) Iris recognition system. Patent, US4641349 A
Daugman J (1993) High confidence visual recognition of persons by a test of statistical independence. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 15:1148–1161
Rahulkar AD, Holambe RS (2012) Half-iris feature extraction and recognition using a new class of biorthogonal triplet half-band filter bank and flexible k-out-of-n: a postclassifier. IEEE Trans IFS 7:230–240
Tsai CC, Lin HY, Taur J, Tao CW (2012) Iris recognition using possibilistic fuzzy matching on local features. IEEE Trans SMC (Part B) 42:150–162
Wildes RP (1997) Iris recognition: an emerging biometric technology. In: Proceedings of the IEEE, pp 1348–1363
Masek L (2003) Recognition of human iris patterns for biometric identification. M.Sc. thesis, The University of Western Australia
Daugman J (2007) New methods in iris recognition. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern B 37:1167–1175
Shah S, Ross A (2009) Iris segmentation using geodesic active contours. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 4:824–836
Dey S, Samanta D (2007) A novel approach to iris localization for iris biometric processing. Int J Biomed Biol Eng 1(5):293–304
An L, Chen X, Yang S, Bhanu B (2016) Sparse representation matching for person re-identification. Inf Sci 355:74–89
Soliman NF, Mohamed E, Magdi F, Abd El-Samie FE, AbdElnaby M (2017) Efficient Iris localization and recognition. Opt Int J Light Electron Opt 140:469–475
Patel VM, Ratha NK, Chellappa R (2015) Cancelable biometrics: a review. IEEE Signal Process Mag 32(5):54–65
Punithavathi P, Subbiah G (2017) Can cancellable biometrics preserve privacy? Biom Technol Today 2017(7):8–11
Lai Y, Jin J, Teoh ABJ, Goi B, Yap W, Chai T, Rathgeb C (2017) Cancellable iris template generation based on indexing-first-one hashing. Pattern Recognit 64:105–117
Nandakumar K, Jain AK (2015) Biometric template protection: bridging the performance gap between theory and practice. IEEE Signal Process Mag 32(5):88–100
Jain AK, Nandakumar K (2008) Nagar A (2008) Biometric template security. EURASIP J Adv Signal Proc 113:1–17 (Special issue on Biometrics)
Ratha NK, Chikkerur S, Connell JH, Bolle RM (2007) Generating cancelable fingerprint templates. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach 29(4):561–572
Harjoko A, Hartati S, Dwiyasa H (2009) A method for iris recognition based on 1d coiflet wavelet. World Acad Sci Eng Technol 56:126–129
Chong SC, Jin ATB, Ling DNC (2006) High security iris verification system based on random secret integration. Comput Vis Image Underst 102(2):169–177
Pillai JK, Patel VM, Chellappa R, Ratha NK (2010) Sectored random projections for cancelable iris biometrics. In: IEEE international conference on acoustics speech and signal processing, pp 1838–184
Rathgeb C, Breitinger F, Baier H, Busch C (2015) Towards bloom filter-based indexing of iris biometric data. In: 15th IEEE international conference on biometrics, pp 422–429
Rathgeb C, Breitinger F, Busch C, Baier H (2014) On the application of bloom filters to iris biometrics. IET J Biom 3(4):207–218
Zuo J, Ratha NK, Connel JH (2008) Cancelable iris biometric. In: Proceedings of the 19th international. Conference on pattern recognition, pp 1–4
Maiorana E, Campisi P, Fierrez J, Ortega-Garcia J, Neri A (2010) Cancelable templates for sequence-based biometrics with application to on line signature recognition. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 40(3):525–538
Syarif MA, Ong TS, Teoh ABJ, Tee C (2014) Improved biohashing method based on most intensive histogram block location. In: International conference of neural information processing, pp 644–652
Teoh ABJ, Chong LY (2010) Secure speech template protection in speaker verification system. Speech Commun 52(2):150–163
Teoh ABJ, Ngo DCL, Goh A (2004) Biohashing: two factor authentication featuring fingerprint data and tokenised random number. Pattern Recognit 37(11):2245–2255
Ouda O, Tsumura N, Nakaguchi T (2011) On the security of bioencoding based cancelable biometrics. IEICE Trans Inf Syst 94-D(9):1768–1777
Ouda O, Tsumura N, Nakaguchi T (2010) A reliable tokenless cancelable biometrics scheme for protecting iriscodes. IEICE Trans Inf Syst E93-D(7):1878–1888
Lacharme P (2012) Analysis of the iriscodes bioencoding scheme. Int J Comput Sci Softw Eng 6(5):315–321
Hammerle-Uhl J, Pschernig E, Uhl A (2009) Cancelable iris biometrics using block re-mapping and image warping. In: International conference on information security, pp 135–142
Jenisch S, Uhl, A (2011) Security analysis of a cancelable iris recognition system based on block remapping. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on image processing, pp 3274–3277
Dwivedi R, Somnath D (2015) Cancelable iris template generation using look-up table mapping. In: 2nd international conference on signal processing and integrated network, pp 785–790
Tarek M, Ouda O, Hamza T (2016) Robust cancelable biometrics scheme based on neural networks. IET J Biom 5(3):220–228
Tarek M, Ouda O, Hamza T (2017) Pre-image resistant cancelable biometrics scheme using bidirectional memory model. Int J Netw Secur 19(4):498–506
Evans N, Marcel S, Ross A, Teoh ABJ (2015) Biometrics security and privacy protection. IEEE Signal Process Mag 32(5):17–18
Johnson W, Lindenstrauss J (1984) Extensions of Lipschitz maps into a hilbert space. Contemp Math 26:189–206
CASIA-IrisV3 Database. http://www.cbsr.ia.ac.cn/english/IrisDatabase.asp. Accessed June 2017
Kumar A, Passi A (2010) Comparison and combination of iris matchers for reliable personal authentication. Pattern Recognit 43:1016–1026
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soliman, R.F., Amin, M. & Abd El-Samie, F.E. A Modified Cancelable Biometrics Scheme Using Random Projection. Ann. Data. Sci. 6, 223–236 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-018-0172-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40745-018-0172-1