Abstract
Background
Hypertension is a complex disease and is the major cause of cardiovascular complications. In the vast majority of individuals, the aetiology of elevated blood pressure (BP) cannot be determined, thus impairing optimized therapies and prognosis for individual patients. A more precise understanding of the molecular pathogenesis of hypertension remains a pressing priority for both basic and translational research. Here we investigated the effect of salt on naive hypertensive patients in order to better understand the salt intake-blood pressure relationship.
Methods
Patients underwent an acute saline infusion and were defined as salt-sensitive or salt-resistant according to mean blood pressure changes. Urinary proteome changes during the salt load test were analysed by a label-free quantitative proteomics approach.
Results
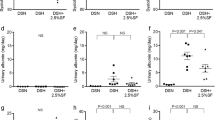
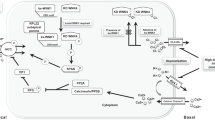
Our data show that salt-sensitive patients display equal sodium reabsorption as salt-resistant patients, as major sodium transporters show the same behaviour during the salt load. However, salt-sensitive patients regulate the renin angiotensin system (RAS) differently from salt-resistant patients, and upregulate proteins, as epidermal growth factor (EGF) and plasminogen activator, urokinase (PLAU), involved in the regulation of epithelial sodium channel ENaC activity.
Conclusions
Salt-sensitive and salt-resistant subjects have similar response to a saline/volume infusion as detected by urinary proteome. However, we identified glutamyl aminopeptidase (ENPEP), PLAU, EGF and Xaa-Pro aminopeptidase 2 precursor XPNPEP2 as key molecules of salt-sensitivity, through modulation of ENaC-dependent sodium reabsorption along the distal tubule.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Proteomic datasets produced in this study are available in the following database: Peptide Atlas repository, https://www.peptideatlas.org/. Accession number PASS00383 for T0 samples; accession number PASS01405 for T120 and T240 samples.
References
Lawes CM, Vander Hoorn S, Rodgers A, International Society of H (2008) Global burden of blood-pressure-related disease, 2001. Lancet 371(9623):1513–1518. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60655-8
Elliott P, Stamler J, Nichols R, Dyer AR, Stamler R, Kesteloot H, Marmot M (1996) Intersalt revisited: further analyses of 24 hour sodium excretion and blood pressure within and across populations. Intersalt Cooperative Research Group BMJ 312(7041):1249–1253. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.312.7041.1249
Stamler J (1997) The INTERSALT study: background, methods, findings, and implications. Am J Clin Nutr 65(2 Suppl):626S–642S. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/65.2.626S
Trepiccione F, Zacchia M, Capasso G (2012) The role of the kidney in salt-sensitive hypertension. Clin Exp Nephrol 16(1):68–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-011-0489-y
Weinberger MH, Fineberg NS (1991) Sodium and volume sensitivity of blood pressure. Age and pressure change over time. Hypertension 18(1):67–71
Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Romero F, Johnson RJ (2007) Pathophysiological mechanisms of salt-dependent hypertension. Am J Kidney Dis 50(4):655–672. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.05.025
Weinberger MH (1996) Salt sensitivity of blood pressure in humans. Hypertension 27(3 Pt 2):481–490
Prisk GK, Olfert IM, Arai TJ, Wagner PD, Hopkins SR (2010) Rapid intravenous infusion of 20 ml/kg saline does not impair resting pulmonary gas exchange in the healthy human lung. J Appl Physiol 108(1):53–59. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00787.2009
Beeks E, Kessels AG, Kroon AA, van der Klauw MM, de Leeuw PW (2004) Genetic predisposition to salt-sensitivity: a systematic review. J Hypertens 22(7):1243–1249
Manunta P, Lavery G, Lanzani C, Braund PS, Simonini M, Bodycote C, Zagato L, Delli Carpini S, Tantardini C, Brioni E, Bianchi G, Samani NJ (2008) Physiological interaction between alpha-adducin and WNK1-NEDD4L pathways on sodium-related blood pressure regulation. Hypertension 52(2):366–372. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.113977
Citterio L, Simonini M, Zagato L, Salvi E, Delli Carpini S, Lanzani C, Messaggio E, Casamassima N, Frau F, D'Avila F, Cusi D, Barlassina C, Manunta P (2011) Genes involved in vasoconstriction and vasodilation system affect salt-sensitive hypertension. PLoS ONE 6(5):e19620. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019620
Weinberger MH, Fineberg NS, Fineberg SE, Weinberger M (2001) Salt sensitivity, pulse pressure, and death in normal and hypertensive humans. Hypertension 37(2 Pt 2):429–432
Petrazzuolo O, Trepiccione F, Zacchia M, Capasso G (2010) Hypertension and renal calcium transport. J Nephrol 23(Suppl 16):S112–117
Matafora V, Zagato L, Ferrandi M, Molinari I, Zerbini G, Casamassima N, Lanzani C, Delli Carpini S, Trepiccione F, Manunta P, Bachi A, Capasso G (2014) Quantitative proteomics reveals novel therapeutic and diagnostic markers in hypertension. BBA Clin 2:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbacli.2014.10.001
Rappsilber J, Ishihama Y, Mann M (2003) Stop and go extraction tips for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization, nanoelectrospray, and LC/MS sample pretreatment in proteomics. Anal Chem 75(3):663–670. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac026117i
Matafora V, D'Amato A, Mori S, Blasi F, Bachi A (2009) Proteomics analysis of nucleolar SUMO-1 target proteins upon proteasome inhibition. Mol Cell Proteom 8(10):2243–2255. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M900079-MCP200
Cox J, Mann M (2008) MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat Biotechnol 26(12):1367–1372. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1511
Cox J, Neuhauser N, Michalski A, Scheltema RA, Olsen JV, Mann M (2011) Andromeda: a peptide search engine integrated into the MaxQuant environment. J Proteome Res 10(4):1794–1805. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr101065j
Takenaka T, Suzuki H, Furukawa T, Ogata Y, Saruta T (1990) Role of intrarenal renin-angiotensin system on pressure-natriuresis in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin Exp Hypertens A 12(8):1377–1394
Kobori H, Nishiyama A, Abe Y, Navar LG (2003) Enhancement of intrarenal angiotensinogen in Dahl salt-sensitive rats on high salt diet. Hypertension 41(3):592–597. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.HYP.0000056768.03657.B4
Drueke TB (2016) Salt and health: time to revisit the recommendations. Kidney Int 89(2):259–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2015.12.009
McDonough AA, Nguyen MT (2015) Maintaining balance under pressure: integrated regulation of renal transporters during hypertension. Hypertension 66(3):450–455. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.04593
Kotlo K, Shukla S, Tawar U, Skidgel RA, Danziger RS (2007) Aminopeptidase N reduces basolateral Na+–K+–ATPase in proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 293(4):F1047–1053. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00074.2007
Capasso G, Cantone A, Evangelista C, Zacchia M, Trepiccione F, Acone D, Rizzo M (2005) Channels, carriers, and pumps in the pathogenesis of sodium-sensitive hypertension. Semin Nephrol 25(6):419–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semnephrol.2005.05.013
Zacchia M, Capasso G (2015) The importance of uromodulin as regulator of salt reabsorption along the thick ascending limb. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30(2):158–160. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfu365
Padmanabhan S, Melander O, Johnson T, Di Blasio AM, Lee WK, Gentilini D, Hastie CE, Menni C, Monti MC, Delles C, Laing S, Corso B, Navis G, Kwakernaak AJ, van der Harst P, Bochud M, Maillard M, Burnier M, Hedner T, Kjeldsen S, Wahlstrand B, Sjogren M, Fava C, Montagnana M, Danese E, Torffvit O, Hedblad B, Snieder H, Connell JM, Brown M, Samani NJ, Farrall M, Cesana G, Mancia G, Signorini S, Grassi G, Eyheramendy S, Wichmann HE, Laan M, Strachan DP, Sever P, Shields DC, Stanton A, Vollenweider P, Teumer A, Volzke H, Rettig R, Newton-Cheh C, Arora P, Zhang F, Soranzo N, Spector TD, Lucas G, Kathiresan S, Siscovick DS, Luan J, Loos RJ, Wareham NJ, Penninx BW, Nolte IM, McBride M, Miller WH, Nicklin SA, Baker AH, Graham D, McDonald RA, Pell JP, Sattar N, Welsh P, Global BC, Munroe P, Caulfield MJ, Zanchetti A, Dominiczak AF (2010) Genome-wide association study of blood pressure extremes identifies variant near UMOD associated with hypertension. PLoS Genet 6(10):e1001177. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1001177
Trudu M, Janas S, Lanzani C, Debaix H, Schaeffer C, Ikehata M, Citterio L, Demaretz S, Trevisani F, Ristagno G, Glaudemans B, Laghmani K, Dell’Antonio G, Team S, Loffing J, Rastaldi MP, Manunta P, Devuyst O, Rampoldi L (2013) Common noncoding UMOD gene variants induce salt-sensitive hypertension and kidney damage by increasing uromodulin expression. Nat Med 19(12):1655–1660. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3384
Capasso G, Rizzo M, Evangelista C, Ferrari P, Geelen G, Lang F, Bianchi G (2005) Altered expression of renal apical plasma membrane Na+ transporters in the early phase of genetic hypertension. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 288(6):F1173–1182. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00228.2004
Capasso G, Rizzo M, Garavaglia ML, Trepiccione F, Zacchia M, Mugione A, Ferrari P, Paulmichl M, Lang F, Loffing J, Carrel M, Damiano S, Wagner CA, Bianchi G, Meyer G (2008) Upregulation of apical sodium-chloride cotransporter and basolateral chloride channels is responsible for the maintenance of salt-sensitive hypertension. m J Physiol Ren Physiol 295(2):F556–567. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00340.2007
Oweis S, Wu L, Kiela PR, Zhao H, Malhotra D, Ghishan FK, Xie Z, Shapiro JI, Liu J (2006) Cardiac glycoside downregulates NHE3 activity and expression in LLC-PK1 cells. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 290(5):F997–1008. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00322.2005
Trepiccione F, Soukaseum C, Iervolino A, Petrillo F, Zacchia M, Schutz G, Eladari D, Capasso G, Hadchouel J (2016) A fate-mapping approach reveals the composite origin of the connecting tubule and alerts on "single-cell"-specific KO model of the distal nephron. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 311(5):F901–F906. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00286.2016
Iervolino A, Trepiccione F, Petrillo F, Spagnuolo M, Scarfo M, Frezzetti D, De Vita G, De Felice M, Capasso G (2015) Selective dicer suppression in the kidney alters GSK3beta/beta-catenin pathways promoting a glomerulocystic disease. PLoS ONE 10(3):e0119142. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0119142
Iervolino A, Prosperi F, De La Motte LR, Petrillo F, Spagnuolo M, D'Acierno M, Siccardi S, Perna AF, Christensen BM, Frische S, Capasso G, Trepiccione F (2020) Potassium depletion induces cellular conversion in the outer medullary collecting duct altering Notch signaling pathway. Sci Rep 10(1):5708. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-61882-7
Chambrey R, Trepiccione F (2015) Relative roles of principal and intercalated cells in the regulation of sodium balance and blood pressure. Curr Hypertens Rep 17(4):538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-015-0538-0
Ji HL, Zhao R, Komissarov AA, Chang Y, Liu Y, Matthay MA (2015) Proteolytic regulation of epithelial sodium channels by urokinase plasminogen activator: cutting edge and cleavage sites. J Biol Chem 290(9):5241–5255. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.623496
Staruschenko A, Palygin O, Ilatovskaya DV, Pavlov TS (2013) Epidermal growth factors in the kidney and relationship to hypertension. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 305(1):F12–20. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00112.2013
Pavlov TS, Levchenko V, O'Connor PM, Ilatovskaya DV, Palygin O, Mori T, Mattson DL, Sorokin A, Lombard JH, Cowley AW Jr, Staruschenko A (2013) Deficiency of renal cortical EGF increases ENaC activity and contributes to salt-sensitive hypertension. J Am Soc Nephrol 24(7):1053–1062. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2012080839
Pidkovka N, Rao R, Mei S, Gong Y, Harris RC, Wang WH, Capdevila JH (2013) Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) regulate epithelial sodium channel activity by extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2)-mediated phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 288(7):5223–5231. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.407981
Ward PE, Chow A, Drapeau G (1991) Metabolism of bradykinin agonists and antagonists by plasma aminopeptidase P. Biochem Pharmacol 42(4):721–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(91)90028-4
Drendel V, Heckelmann B, Chen CY, Weisser J, Espadas G, Schell C, Sabido E, Werner M, Jilg CA, Schilling O (2017) Proteome profiling of clear cell renal cell carcinoma in von Hippel–Lindau patients highlights upregulation of Xaa-Pro aminopeptidase-1, an anti-proliferative and anti-migratory exoprotease. Oncotarget 8(59):100066–100078. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21929
Mamenko M, Zaika O, Pochynyuk O (2014) Direct regulation of ENaC by bradykinin in the distal nephron. Implications for renal sodium handling. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 23(2):122–129. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mnh.0000441053.81339.61
Damiano S, Trepiccione F, Ciarcia R, Scanni R, Spagnuolo M, Manco L, Borrelli A, Capasso C, Mancini R, Schiattarella A, Iervolino A, Zacchia E, Bata-Csere A, Florio S, Anastasio P, Pollastro R, Mancini A, Capasso G (2013) A new recombinant MnSOD prevents the cyclosporine A-induced renal impairment. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28(8):2066–2072. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gft020
Acknowledgements
We thank Mrs Brioni Elena, research nurse in OSR, for performing the saline load tests on patients.
Funding
This work was supported by PRIN 2006 no 2006065339.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CL and PM performed visits of patients and acute salt load test, VM performed the proteomic experiments, VM and AB analysed the data, participated in the discussion on data interpretation and wrote the manuscript, LZ collected biological samples and implemented the clinical database, LZ, CL and PM revised the manuscript. GC proposed the experiments, followed the project in its phases and reviewed the manuscript, FT and MZ participated in the discussion on data interpretation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the San Raffaele Hospital, Milan (Italy).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
The participants signed informed consent regarding publishing their data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matafora, V., Lanzani, C., Zagato, L. et al. Urinary proteomics reveals key markers of salt sensitivity in hypertensive patients during saline infusion. J Nephrol 34, 739–751 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-020-00877-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-020-00877-z