Abstract
Purpose
PATRO adults is an ongoing, multicenter, observational, post-marketing surveillance study aimed at investigating the long-term safety (primary endpoint) and effectiveness (secondary endpoint) of the recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) Omnitrope® during routine clinical practice. This report describes data from Italian participants in PATRO Adults with growth hormone deficiency (GHD), up to August 2017.
Methods
Participants were adults (aged > 18 years) with GHD requiring rhGH therapy and were prescribed Omnitrope®, including those who had previously received another rhGH product. Adverse events (AEs) were evaluated in all study participants. Data were collected on insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I levels and cardiovascular risk factors, including blood pressure, lipids, and anthropometric parameters.
Results
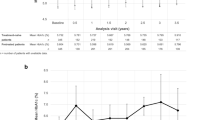
From September 2007 to August 2017, 88 patients (mean age 48.9 years, 58.0% male) were enrolled at 8 sites in Italy. The mean treatment duration with Omnitrope® was 51.5 ± 37 months. AEs occurred in 54 patients; the most common were asthenia (20.5%), headache (14.8%), and arthralgia (13.6%). Serious AEs occurred in 22 patients (25%), including pneumonia (n = 2) and renal failure (n = 2). Neoplasms (2 benign and 1 malignant) developed in three patients, but none were considered to be drug-related. There were no significant changes in fasting glucose or glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) during the study period. Long-term Omnitrope® therapy showed slight positive effects on lipid profile, while no significant changes were observed in body weight and BMI during the study.
Conclusion
This snapshot analysis of Italian participants in PATRO Adults confirmed the long-term safety and effectiveness of Omnitrope® in adults with GHD.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated/analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to the fact that the data generated are issued from an ongoing global non-interventional study. Patient enrollment is still performed as per the objectives and the commitment with the European Medical Agency, but the data are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
de Boer H, Blok GJ, Van der Veen EA (1995) Clinical aspects of growth hormone deficiency in adults. Endocr Rev 16(1):63–86. https://doi.org/10.1210/edrv-16-1-63
Jorgensen JO, Christiansen JS (2005) Clinical aspects of growth hormone deficiency in adults: an overview. Front Horm Res 33:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1159/000088338
Boguszewski CL (2017) Update on GH therapy in adults. F1000Res 6:2017. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.12057.1
Tanriverdi F, Kelestimur F (2017) Classical and non-classical causes of GH deficiency in adults: best practice and research. Clin Endocrinol Metab 31(1):3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2017.02.001
Woodhouse LJ, Mukherjee A, Shalet SM, Ezzat S (2006) The influence of growth hormone status on physical impairments, functional limitations, and health-related quality of life in adults. Endocr Rev 27(3):287–317. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2004-0022
Growth Hormone Research Society (1998) Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of adults with growth hormone deficiency: summary statement of the growth hormone research society workshop on adult growth hormone deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83(2):379–381. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.83.2.4611
Mathioudakis N, Salvatori R (2008) Adult-onset growth hormone deficiency: causes, complications and treatment options. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 15(4):352–358. https://doi.org/10.1097/MED.0b013e3282ffd97d
Gasco V, Caputo M, Lanfranco F, Ghigo E, Grottoli S (2017) Management of GH treatment in adult GH deficiency. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 31(1):13–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2017.03.001
Bengtsson BA, Eden S, Lonn L, Kvist H, Stokland A, Lindstedt G, Bosaeus I, Tolli J, Sjostrom L, Isaksson OG (1993) Treatment of adults with growth hormone (GH) deficiency with recombinant human GH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 76(2):309–317. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.76.2.8432773
Burman P, Broman JE, Hetta J, Wiklund I, Erfurth EM, Hagg E, Karlsson FA (1995) Quality of life in adults with growth hormone (GH) deficiency: response to treatment with recombinant human GH in a placebo-controlled 21-month trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80(12):3585–3590. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.80.12.8530603
Ikeda H, Kudo M (2016) Long-term follow-up results of growth hormone therapy for patients with adult growth hormone deficiency. Hormones (Athens) 15(1):45–53. https://doi.org/10.14310/horm.2002.1637
Ferone D, Profka E, Gasco V, Ambrosio MR, Colao A, Di Somma C, Puxeddu E, Arnaldi G, Pagano C, Zecchi E, Pietropoli A, Beck-Peccoz P (2017) Long-term safety and efficacy of Omnitrope((R)) in adults with growth hormone deficiency: Italian interim analysis of the PATRO Adults study. J Endocrinol Invest 40(6):669–678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-016-0604-8
Borson-Chazot F, Serusclat A, Kalfallah Y, Ducottet X, Sassolas G, Bernard S, Labrousse F, Pastene J, Sassolas A, Roux Y, Berthezene F (1999) Decrease in carotid intima-media thickness after one year growth hormone (GH) treatment in adults with GH deficiency. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 84(4):1329–1333. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.84.4.5595
Sesmilo G, Biller BM, Llevadot J, Hayden D, Hanson G, Rifai N, Klibanski A (2000) Effects of growth hormone administration on inflammatory and other cardiovascular risk markers in men with growth hormone deficiency. A randomized, controlled clinical trial. Ann Intern Med 133(2):111–122
Beauregard C, Utz AL, Schaub AE, Nachtigall L, Biller BM, Miller KK, Klibanski A (2008) Growth hormone decreases visceral fat and improves cardiovascular risk markers in women with hypopituitarism: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 93(6):2063–2071. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2007-2371
Colao A, Di Somma C, Spiezia S, Savastano S, Rota F, Savanelli MC, Lombardi G (2008) Growth hormone treatment on atherosclerosis: results of a 5-year open, prospective, controlled study in male patients with severe growth hormone deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(9):3416–3424. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2007-2810
Ramos-Levi AM, Marazuela M (2018) Treatment of adult growth hormone deficiency with human recombinant growth hormone: an update on current evidence and critical review of advantages and pitfalls. Endocrine 60(2):203–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-017-1492-1
European Medical Agency (2018) Omnitrope® Summary of product characteristics. https://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/000607/WC500043695.pdf. Accessed 30 Oct 2001
Beck-Peccoz P, Minuto F, Leal-Cerro A, Zabransky M, Stalla G (2012) Rationale and design of PATRO Adults, a multicentre, noninterventional study of the long-term efficacy and safety of Omnitrope((R)) for the treatment of adult patients with growth hormone deficiency. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab 3(3):85–91. https://doi.org/10.1177/2042018812444152
Elmlinger MW, Kuhnel W, Weber MM, Ranke MB (2004) Reference ranges for two automated chemiluminescent assays for serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and IGF-binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3). Clin Chem Lab Med 42(6):654–664. https://doi.org/10.1515/CCLM.2004.112
Molitch ME, Clemmons DR, Malozowski S, Merriam GR, Vance ML (2011) Evaluation and treatment of adult growth hormone deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(6):1587–1609
Beshyah SA, Henderson A, Niththyananthan R, Skinner E, Anyaoku V, Richmond W, Sharp P, Johnston DG (1995) The effects of short and long-term growth hormone replacement therapy in hypopituitary adults on lipid metabolism and carbohydrate tolerance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80(2):356–363. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.80.2.7852490
Borras Perez MV, Kristrom B, Romer T, Walczak M, Hobel N, Zabransky M (2017) Ten years of clinical experience with biosimilar human growth hormone: a review of safety data. Drug Des Devel Ther 11:1497–1503. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S130909
Attanasio AF, Jung H, Mo D, Chanson P, Bouillon R, Ho KK, Lamberts SW, Clemmons DR (2011) Prevalence and incidence of diabetes mellitus in adult patients on growth hormone replacement for growth hormone deficiency: a surveillance database analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(7):2255–2261. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2011-0448
Hew FL, Koschmann M, Christopher M, Rantzau C, Vaag A, Ward G, Beck-Nielsen H, Alford F (1996) Insulin resistance in growth hormone-deficient adults: defects in glucose utilization and glycogen synthase activity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81(2):555–564. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.81.2.8636267
Sadeghi-Nejad A (2007) Development of diabetes mellitus in two boys after the initiation of growth hormone therapy. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 20(4):541–544
Luger A, Mattsson AF, Koltowska-Haggstrom M, Thunander M, Goth M, Verhelst J, Abs R (2012) Incidence of diabetes mellitus and evolution of glucose parameters in growth hormone-deficient subjects during growth hormone replacement therapy: a long-term observational study. Diabetes Care 35(1):57–62. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc11-0449
Giavoli C, Porretti S, Ronchi CL, Cappiello V, Ferrante E, Orsi E, Arosio M, Beck-Peccoz P (2004) Long-term monitoring of insulin sensitivity in growth hormone-deficient adults on substitutive recombinant human growth hormone therapy. Metab Clin Exp 53(6):740–743
Stochholm K, Kiess W (2018) Long-term safety of growth hormone: a combined registry analysis. Clin Endocrinol 88(4):515–528. https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.13502
Cook J, Haynes K, Werther G (1988) Mitogenic effects of growth hormone in cultured human fibroblasts: evidence for action via local insulin-like growth factor I production. J Clin Investig 81(1):206
Laron Z (1999) Somatomedin-1 (recombinant insulin-like growth factor-1): clinical pharmacology and potential treatment of endocrine and metabolic disorders. BioDrugs 11(1):55–70
Krzyzanowska-Mittermayer K, Mattsson AF, Maiter D, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Camacho-Hubner C, Luger A, Abs R (2018) New neoplasm during GH replacement in adults with pituitary deficiency following malignancy: a KIMS analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 103(2):523–531. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2017-01899
Pekic S, Popovic V (2013) GH therapy and cancer risk in hypopituitarism: what we know from human studies. Eur J Endocrinol 169(5):R89–97. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-13-0389
Cuneo RC, Judd S, Wallace JD, Perry-Keene D, Burger H, Lim-Tio S, Strauss B, Stockigt J, Topliss D, Alford F (1998) The Australian multicenter trial of growth hormone (GH) treatment in GH-deficient adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83(1):107–116
Cuneo RC, Salomon F, Watts GF, Hesp R, Sonksen PH (1993) Growth hormone treatment improves serum lipids and lipoproteins in adults with growth hormone deficiency. Metabolism 42(12):1519–1523
Rosen T (1994) Beneficial effects of 12 months replacement therapy with recombinant human growth hormone to growth hormone deficient adults. Endocrinol Metab 1:55–66
Attanasio AF, Lamberts SW, Matranga AM, Birkett MA, Bates PC, Valk NK, Hilsted J, Bengtsson BA, Strasburger CJ (1997) Adult growth hormone (GH)-deficient patients demonstrate heterogeneity between childhood onset and adult onset before and during human GH treatment: Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency Study Group. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82(1):82–88. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.82.1.3643
Schneider HJ, Buchfelder M, Wallaschofski H, Luger A, Johannsson G, Kann PH, Mattsson A (2015) Proposal of a clinical response score and predictors of clinical response to 2 years of GH replacement therapy in adult GH deficiency. Eur J Endocrinol 173(6):843–851. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-15-0305
Thankamony A, Capalbo D, Jonsson PJ, Simpson HL, Dunger DB (2016) Predictors of insulin-like growth factor-I responses to growth hormone replacement in young adults with growth hormone deficiency. Horm Res Paediatr 85(6):379–388. https://doi.org/10.1159/000445832
Salomon F, Cuneo RC, Hesp R, Sonksen PH (1989) The effects of treatment with recombinant human growth hormone on body composition and metabolism in adults with growth hormone deficiency. N Engl J Med 321(26):1797–1803. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm198912283212605
Verhelst J, Mattsson AF, Camacho-Hubner C, Luger A, Abs R (2018) The prevalence of the metabolic syndrome and associated cardiovascular complications in adult-onset GHD during GH replacement: a KIMS analysis. Endocr Connect 7(5):653–662. https://doi.org/10.1530/EC-18-0096
Fuhr U, Tuculanu D, Berghout A, Balser S, Schwebig A, Saenger P (2010) Bioequivalence between novel ready-to-use liquid formulations of the recombinant human GH Omnitrope and the original lyophilized formulations for reconstitution of Omnitrope and Genotropin. Eur J Endocrinol 162(6):1051–1058. https://doi.org/10.1530/eje-09-1101
Gunnarsson R, Wilton P (1987) Clinical experience with genotropin worldwide: an update March 1987. Acta Paediatr 76(s337):147–152
Ullah A, Peacock H, Arutchelvam V, Nag S, Ashwell S (2012) The cost, efficacy and safety of Omnitrope compared with Genotropin in adults with growth hormone deficiency
Stalla G, Leal-Cerro A, Simsek S, Minuto F, Zabransky M, Beck-Peccoz P (2013) First results from the PATRO adults study of omnitrope for the treatment of adult patients with GH deficiency Paper presented at the 15th European Congress of Endocrinology (ECE) 2013, Copenhagen, Denmark, April 29-May 1
Beck-Peccoz P, Höybye C, Murray RD, Simsek S, Leal-Cerro A, Minuto F, Zabransky M, Stalla G (2014) The PATRO Adults study of Omnitrope® for the treatment of adult patients with growth hormone deficiency: latest results Paper presented at the 16th International Congress of Endocrinology and the Endocrine Society’s 96th Annual Meeting & Expo (ICE/ENDO) Chicago, IL, USA, 21–24 June
Beck-Peccoz P, Höybye C, Murray RD, Simsek S, Leal-Cerro A, Zabransky M, Stalla G (2015) The PATRO adult study of Omnitrope® for the treatment of adult patients with GH deficiency: latest results. In: Paper presented at the 17th European Congress of Endocrinology (ESE), Dublin, Ireland, 16–20 May
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all investigators and patients involved in this study, plus Nishad Parkar, PhD, of Springer Healthcare Communications, who wrote the outline of the manuscript and Luca Giacomelli, PhD, who wrote the first draft of the manuscript on behalf of Springer Healthcare Communications. This medical writing assistance was funded by Sandoz, Italy.
Funding
The PATRO global study was funded by Sandoz GmbH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CG and MA contributed to the preparation of the manuscript; CG enrolled patients and conducted follow-up; GA, VG, and MRA enrolled patients, conducted follow-up, collected data, and critically revised various manuscript drafts; DF provided critical revision of the manuscript drafts and study coordination; RV enrolled patients, conducted follow-up, collected data, and read the manuscript drafts; PG, HZ, and PF contributed to the drafting of the manuscript, and critically revised the various drafts of the manuscript; EP critically revised the various drafts of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
MA, VG, CG, EP, RV, and DF declare that they have no conflicts of interest. GA has received lecture fees from Novartis and Otsuka, and consulting honoraria from HRA Pharma. MRA has received registration fees for scientific meetings from Ipsen, Novartis, Pfizer, and ItaPharma. PG and PF are employees of Sandoz S.p.A, Origgio (MI), Italy. HZ is an employee of Sandoz Biopharmaceutical c/o HEXAL AG, Holzkirchen, Germany.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by each study site’s Independent Ethics Committee or Institutional Review Board before initiation and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consent
All patients included in the study provided written informed consent at enrolment.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arosio, M., Arnaldi, G., Gasco, V. et al. Safety and effectiveness of Omnitrope® in patients with growth hormone deficiency: snapshot analysis of PATRO Adults study in the Italian population. J Endocrinol Invest 44, 327–337 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-020-01308-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-020-01308-3