Abstract
Purpose
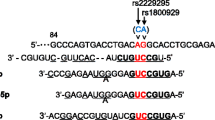
The study was aimed at investigating the association between hsa-mir-27a polymorphism rs895819 (T/C) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) susceptibility in a large Iranian cohort.
Methods
In this case–control study, the investigated population consisted of T2DM patients (n = 204) and sex- and age-matched controls (n = 209). We used the polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR–RFLP) for genotyping.
Results
We observed significant differences between T2DM patients and controls for weight (p = 0.002), BMI (p < 0.001), systolic blood pressure (p < 0.001), diastolic blood pressure (p < 0.001), fasting plasma glucose (p < 0.001), triglyceride (p = 0.004) and LDL cholesterol (p = 0.051). Moreover, we found that genotype distributions were significantly different between groups (p < 0.05) and that the rs895819-C allele is more frequent in controls (p = 0.030, OR = 0.72, 95 % CI 0.53–0.97).
Conclusion
Our study shows that rs895819 in hsa-mir-27a is associated with T2DM susceptibility and that the C allele conveyed a protective role against T2DM. Larger multicentric and specific functional studies will be necessary to obtain a deeper comprehension of the role of rs895819 and hsa-mir-27a and how they are involved in the development of diabetes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanghera DK, Blackett PR (2012) Type 2 diabetes genetics: beyond GWAS. J Diabetes Metab 3(198):6948
Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ (2010) Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 87(1):4–14
Amutha A, Mohan V (2016) Diabetes complications in childhood and adolescent onset type 2 diabetes—a review. J Diabetes Complicat. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.02.009
Ciccacci C, Di Fusco D, Cacciotti L, Morganti R, D’Amato C, Greco C, Rufini S, Novelli G, Sangiuolo F, Spallone V, Borgiani P (2013) MicroRNA genetic variations: association with type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 50(6):867–872
Zhao X, Ye Q, Xu K, Cheng J, Gao Y, Li Q, Du J, Shi H, Zhou L (2013) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms inside microRNA target sites influence the susceptibility to type 2 diabetes. J Hum Genet 58(3):135–141
Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431(7006):350–355
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297
Rottiers V, Naar AM (2012) MicroRNAs in metabolism and metabolic disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(4):239–250
Heneghan HM, Miller N, Kerin MJ (2010) Role of microRNAs in obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Obes Rev 11(5):354–361
Chen H, Lan HY, Roukos DH, Cho WC (2014) Application of microRNAs in diabetes mellitus. J Endocrinol 222(1):R1–R10
Kim SY, Kim AY, Lee HW, Son YH, Lee GY, Lee JW, Lee YS, Kim JB (2010) miR-27a is a negative regulator of adipocyte differentiation via suppressing PPARgamma expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 392(3):323–328
Qin L, Chen Y, Niu Y, Chen W, Wang Q, Xiao S, Li A, Xie Y, Li J, Zhao X, He Z, Mo D (2010) A deep investigation into the adipogenesis mechanism: profile of microRNAs regulating adipogenesis by modulating the canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. BMC Genom 11(320):1471–2164
Tan CK, Chong HC, Tan EH, Tan NS (2012) Getting ‘Smad’ about obesity and diabetes. Nutr Diabetes 5(2):1
Offer SM, Butterfield GL, Jerde CR, Fossum CC, Wegner NJ, Diasio RB (2014) microRNAs miR-27a and miR-27b directly regulate liver dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase expression through two conserved binding sites. Mol Cancer Ther 13(3):742–751
Wang T-T, Chen Y-J, Sun L-L, Zhang S-J, Zhou Z-Y, Qiao H (2015) Affection of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in miR-27a, miR-124a, and miR-146a on susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese Han people. Chin Med J 128(4):533
Association AD (2014) Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 37(Supplement 1):S81–S90
Sievers F, Higgins DG (2014) Clustal omega, accurate alignment of very large numbers of sequences. Multiple sequence alignment methods. Springer, Berlin, pp 105–116
Sabarinathan R, Tafer H, Seemann SE, Hofacker IL, Stadler PF, Gorodkin J (2013) RNAsnp: efficient detection of local RNA secondary structure changes induced by SNPs. Hum Mutat 34(4):546–556
Gruber AR, Lorenz R, Bernhart SH, Neuböck R, Hofacker IL (2008) The vienna RNA websuite. Nucleic Acids Res 36(suppl 2):W70–W74
Siva N (2008) 1000 Genomes project. Nat Biotechnol 26(3):256
Menashe I, Rosenberg PS, Chen BE (2008) PGA: power calculator for case-control genetic association analyses. BMC Genet 9(1):36
González JR, Armengol L, Solé X, Guinó E, Mercader JM, Estivill X, Moreno V (2007) SNPassoc: an R package to perform whole genome association studies. Bioinformatics 23(5):654–655
McCauley JL, Kenealy SJ, Margulies EH, Schnetz-Boutaud N, Gregory SG, Hauser SL, Oksenberg JR, Pericak-Vance MA, Haines JL, Mortlock DP (2007) SNPs in multi-species conserved sequences (MCS) as useful markers in association studies: a practical approach. BMC Genom 8(1):266
Zeng Y, Yi R, Cullen BR (2005) Recognition and cleavage of primary microRNA precursors by the nuclear processing enzyme Drosha. EMBO J 24(1):138–148
Zakharov S, Wong TY, Aung T, Vithana EN, Khor CC, Salim A, Thalamuthu A (2013) Combined genotype and haplotype tests for region-based association studies. BMC Genom 14(1):569
Ridolfi E, Fenoglio C, Cantoni C, Calvi A, De Riz M, Pietroboni A, Villa C, Serpente M, Bonsi R, Vercellino M (2013) Expression and genetic analysis of microRNAs involved in multiple sclerosis. Int J Mol Sci 14(3):4375–4384
Acknowledgments
We thank the Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Grant Number 1393-1-91-13285) and the Italian Ministry of Health (RC-2015 and RC-2016) for financial support.
Funding
This study was granted by Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Grant Number: 1393-1-91-13285) and the Italian Ministry of Health (RC-2015 and RC-2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghaedi, H., Tabasinezhad, M., Alipoor, B. et al. The pre-mir-27a variant rs895819 may contribute to type 2 diabetes mellitus susceptibility in an Iranian cohort. J Endocrinol Invest 39, 1187–1193 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-016-0499-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-016-0499-4