Abstract
Purpose
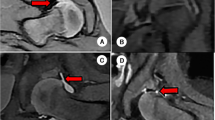
The position of the femoral head in spica cast after the reduction of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) should be examined and followed up closely and regularly. The study aimed to use the transgluteal ultrasonography approach for this purpose and compare its accuracy with the results of CT scan, which is the most commonly used modality.
Methods
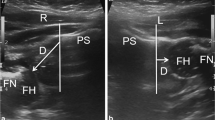
Twenty-three patients with an average age of 20–21 months were examined for 1 year after the reduction of DDH, both closed and open. Ultrasonography and CT scan were performed on the patients on the same day, and the results were interpreted by different radiologists. Transgluteal ultrasonography in spica cast was performed while the legs were abducted, internally rotated, and flexed. A blanket was placed under the patient to elevate the cast.
Results
Thirty cases of proper reduction (81%) and 7 cases of dislocated hip (19%) were reported in transgluteal ultrasonography, and 29 cases of proper reduction (78%) and 8 cases of dislocated hip (22%) were reported in the CT scan. The rate of agreement between the results of ultrasonography and CT scan was 91%.
Conclusion
Transgluteal ultrasonography can be used as an excellent modality to examine the position of the femoral head in relation to the posterior rim of the acetabulum in spica cast. The position of the femoral head can be viewed properly needless of perineal opening in the cast. Thus, transgluteal ultrasonography can replace the CT scan to assess the position of the femoral head. Sonography does not expose patients to radiation and does not require sedation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garvey M, Donoghue VB, Gorman WA et al (1992) Radiographic screening at four months of infants at risk for congenital hip dislocation. J Bone Jt Surg Br 74:704–707
De Pellegrin M, Moharamzadeh D (2010) Developmental dysplasia of the hip in twins: the importance of mechanical factors in the etiology of DDH. J Pediatr Orthop 30:774–778
Stevenson DA, Mineau G, Kerber RA et al (2009) Familial predisposition to developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 29:463–466
Simic S, Vukasinovic Z, Samardzic J et al (2009) Does the gestation age of newborn babies influence the ultrasonic assessment of hip condition? Srp Arh Celok Lek 137:402–408
Barlow TG (1962) Early diagnosis and treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Jt Surg Br Vol 44-B:292–301
Churgay CA, Caruthers BS (1992) Diagnosis and treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. Am Fam Phys 45:1217–1228
Frankenburg WK (1981) To screen or not to screen: congenital dislocation of the hip. Am J Public Health 71:1311–1313
Fredensborg N, Nilsson BE (1976) Overdiagnosis of congenital dislocation of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 119:89–92
Jones D (1977) An assessment of the value of examination of the hip in the newborn. J Bone Jt Surg Br 59:318–322
Committee on Quality Improvement, Subcommittee on Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip, American Academy of Pediatrics (2000) Clinical practice guideline: early detection of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Pediatrics 105:896–905
Arti H, Mehdinasab SA, Arti S (2013) Comparing results of clinical versus ultrasonographic examination in developmental dysplasia of hip. J Res Med Sci. 18:1051–1055
Lehmann HP, Hinton R, Morello P et al (2000) Developmental dysplasia of the hip practice guideline: technical report. Pediatrics. 105:E57 (committee on quality improvement, and subcommittee on developmental dysplasia of the hip)
Weinstein SL, Ponseti IV (1979) Congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Jt Surg Am 61:119–124
Furnes O, Lie SA, Espehaug B et al (2001) Hip disease and the prognosis of total hip replacements. A review of 53,698 primary total hip replacements reported to the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register 1987-99. J Bone Jt Surg Br. 83:579–586
Herring JA (2008) Tachdjian’s pediatric orthopedics, 4th edn. Saunders Elsevier, Ottawa
Beek FJ, Nievelstein RJ, Pruijs HE et al (2010) Transinguinal sonographic determination of the position of the femoral head after reposition and follow-up in a spica cast. Pediatr Radiol 40:1794–1799
Berrington de Gonzalez A, Mahesh M, Kim KP et al (2009) Projected cancer risks from computed tomographic scans performed in the United States in 2007. Arch Intern Med. 169:2071–2077
Vade A, Sukhani R, Dolenga M et al (1995) Chloral hydrate sedation of children undergoing CT and MR imaging: safety as judged by American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines. AJR Am J Roentgenol 165:905–909
Eberhardt O, Zieger M, Langendoerfer M et al (2009) Determination of hip reduction in spica cast treatment for DDH: a comparison of radiography and ultrasound. J Child Orthop 3:313–318
Portinaro NM, Pelillo F, Cerutti P (2007) The role of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 27:247–250
Hansson G, Jacobsen S (1997) Ultrasonography screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip joint. Acta Paediatr 86:913–915
van Douveren FQ, Pruijs HE, Sakkers RJ et al (2003) Ultrasound in the management of the position of the femoral head during treatment in a spica cast after reduction of hip dislocation in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Jt Surg Br 85:117–120
Graf R (1984) Fundamentals of sonographic diagnosis of infant hip dysplasia. J Pediatr Orthop. 4:735–740
Graf R (1984) Classification of hip joint dysplasia by means of sonography. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 102:248–255
Dorn U, Neumann D (2005) Ultrasound for screening developmental dysplasia of the hip: a European perspective. Curr Opin Pediatr 17:30–33
Laor T, Roy DR, Mehlman CT (2000) Limited magnetic resonance imaging examination after surgical reduction of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 20:572–574
Suzuki S, Kasahara Y, Futami T (1992) Ultrasonography In congenital dislocation of the hip. J Pediatric Orthop 12:416
Smith BG, Kasser JR, Hey LA et al (1997) Postreduction computed tomography in developmental dislocation of the hip: part I: analysis of measurement reliability. J Pediatr Orthop 17:626–630
Teng J-B, Yu C-W, Wang Y-Z et al (2012) Sonographic detection of unilateral hip dislocation in a spica cast after closed reduction for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Ultrasound Med 31:827–831
Tennant S, Kinmont C, Lamb G et al (1999) The use of dynamic interventional MRI in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Jt Surg Br 81-B:392–397
Westhoff B, Wild A, Seller K et al (2003) Magnetic resonance imaging after reduction for congenital dislocation of the hip. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 123:289–292
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr Mehrzad Mehdizade, Ms Mehrshad Dehnavi, Dr Aylin Tahmasebi, Dr Seyed Amir Mahlisha Kazemi Shishvan, Dr Nasir Babakhan Kondori, Dr Razieh Shahnazari declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human rights statements
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study. Additional informed consent was obtained from all patients whose identifying information is included in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehdizadeh, M., Dehnavi, M., Tahmasebi, A. et al. Transgluteal ultrasonography in spica cast in postreduction assessment of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Ultrasound 23, 509–514 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-019-00408-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-019-00408-y