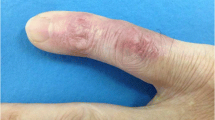
Abstract
Purpose of Review
Atypical Mycobacterium infections are occasionally encountered in clinical practice. As a result of immune function modulation in some particular populations (i.e., transplant, immunotherapies for chronic rheumatological diseases, chronic steroid therapy), there has been an increase in the number of diagnosed cases with atypical Mycobacterium, in particular M. marinum, associated with a history of exposure to natural or artificial water systems. The aim of this study is to review recent clinical presentations, risk factors, and management of M. marinum infections in immunocompromised individuals.
Recent Findings
M. marinum exposure may potentially cause skin and soft tissue infections leading to important morbidity with sometimes life-threatening complications among immunocompromised hosts. The diagnosis of this infection is frequently delayed by months due to the often-atypical clinical presentations. A common immunosuppression associated with infection is TNF inhibition secondary to novel TNF inhibitors. These patients often present with infection within the nose. This atypical clinical presentation, in contrast to the classic “fish tank granuloma” hand lesion, may be related to immunosuppressive factors.
Summary
Increasing awareness of this particular nontuberculous mycobacterial infection among physicians caring for patients with potential exposure to aquatic environments may reduce the time of diagnosis to treatment and avoid further complications.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Vinnard C, Longworth S, Mezochow A, Patrawalla A, Kreiswirth BN, Hamilton K. Deaths related to nontuberculous mycobacterial infections in the United States, 1999–2014. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016;13:1951–5.
Gonzalez-Santiago TM, Drage LA. Nontuberculous mycobacteria: skin and soft tissue infections. Dermatol Clin. 2015;33(3):563–77.
Smidt KP, Stern PJ, Kiefhaber TR. Atypical mycobacterial infections of the upper extremity. Orthopedics. 2018:1–6.
Steinbrink J, Alexis M, Angulo-Thompson D, Ramesh M, Alangaden G, Miceli MH. Mycobacterium marinum remains an unrecognized cause of indolent skin infections. Cutis. 2017;100:331–6.
Linell F, Norden A. Mycobacterium balnei, a new acid-fast bacillus occurring in swimming pools and capable of producing skin lesions in humans. Acta Tuberc Scand Suppl. 1954;33:1–84.
• Hashish E, Merwad A, Elgaml S, Amer A, Kamal H, Elsadek A, et al. Mycobacterium marinum infection in fish and man: epidemiology, pathophysiology and management; a review. Vet Q. 2018;38:35–46. Nice review of the pathogenesis of M. marinum infection and virulent factors.
•• Holden IK, Kehrer M, Andersen AB, Wejse C, Svensson E, Johansen IS. Mycobacterium marinum infections in Denmark from 2004 to 2017: a retrospective study of incidence, patient characteristics, treatment regimens and outcome. Sci Rep. 2018;8:6738. Good epidemiological study in Denmark of this rare infection; one of the largest series of cases of M. marinum .
Schliemann S, Rässler F, Tittelbach J, Kranzer K, Zollmann C, Elsner P. Disseminated Mycobacterium marinum skin infection due to chronic lymphedema in an immunocompetent patient. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2018;16:614–6.
Yacisin K, Hsieh JL, Weiss D, Ackelsberg J, Lee E, Jones L, et al. Outbreak of non-tuberculous mycobacteria skin or soft tissue infections associated with handling fish—New York City, 2013-2014. Epidemiol Infect. 2017;145:2269–79.
Avneri L, Eidlitz-Markus T, Mor M, Zeharia A, Amir J, Haimi-Cohen Y. Mycobacterium marinum: a rare cause of chronic lymphocutaneous syndrome. Eur J Pediatr. 2018; https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-018-3102-5.
Yao A, Sia TY, Fong D. Mycobacterium marinum and carpal tunnel syndrome: three case reports. J Hand Surg. 2017;42(12):1037–e1.
Nguyen HH, Fadul N, Ashraf MS, Siraj DS. Osteomyelitis infection of Mycobacterium marinum: a case report and literature review. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2015:905–20.
Oh TH, Kim UJ, Kang SJ, Jang HC, Park KH, Jung SI, et al. Disseminated invasive Mycobacterium marinum infection involving the lung of a patient with diabetes mellitus. Infect Chemother. 2018;50:59–64.
Velu PP, Fernandes SE, Laurenson IF, Noble DD. Pulmonary Mycobacterium marinum infection: ‘fish tank granuloma’ of the lung. Scott Med J. 2016;61:203–6.
•• Johnson MG, Stout JE. Twenty-eight cases of Mycobacterium marinum infection: retrospective case series and literature review. Infection. 2015;43:655–62. Nice review on a large series of cases of M. marinum infection comparing skin versus invasive disease and treatment outcomes.
Timoney I, Lynch M, Timoney L, Feeney E, Kirby B. Mycobacterium marinum infection contracted from seaweed wrap in a psoriasis patient undergoing treatment with adalimumab. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23(8)
Lopez M, Croley J, Murphy KD. Atypical mycobacterial infections of the upper extremity: becoming more atypical? Hand (NY). 2017;12:188–92.
Sia TY, Taimur S, Blau DM, Lambe J, Ackelsberg J, Yacisin K, et al. Clinical and pathological evaluation of Mycobacterium marinum group skin infections associated with fish markets in New York City. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62:590–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/civ937.
Veronese F, Zavattaro E, Farinelli P, Colombo E, Savoia P. An unusual cutaneous infection caused by Mycobacterium marinum. JMM case reports. 2017:4(4).
Riera J, Conesa X, Pisa J, Moreno J, Siles E, Novell J. Septic arthritis caused by Mycobacterium marinum. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136:131–4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-015-2358-8.
Steinbrink J, Alexis M, Angulo-Thompson D, Ramesh M, Alangaden G, Miceli MH. Mycobacterium marinum remains an unrecognized cause of indolent skin infections. Cutis. 2017;100:331–6.
Sette CS, Wachholz PA, Masuda PY, da Costa Figueira RB, de Oliveira Mattar FR, Ura DG. Mycobacterium marinum infection: a case report. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2015;21:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40409-015-0008-9.
Griffith DE, Aksamit T, Brown-Elliot BA, Catanzaro A, Daley C, Gordin F, et al. An official ATS/IDSA statement: diagnosis, treatment and prevention of nontuberculous mycobacterial diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;175:367–416.
Chiba M, Yanaba K, Kohara A, Nakayama M, Nakagawa H, Fukuda T, et al. Septic arthritis caused by Mycobacterium marinum infection. J Dermatol. 2017;44:1179–80.
Asakura, T., Ishii, M., Kikuchi, T., Kameyama, K., Namkoong, H., Nakata, N., et al. Disseminated Mycobacterium marinum infection with a destructive nasal lesion mimicking extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma: a case report. Medicine, 2016;95(11).
Djurinec P, Radoš J, Katalinić-Janković V, Lakoš Jukić I, Kostović K. Mycobacterium marinum infection of the hand in an immunocompromised aquarium hobbyist. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2017;25:50–0.
Belz D, Tantcheva-Poor I, Rasokat H, Fabri M, Schlaak M. Mycobacterium marinum infection initially diagnosed as metastatic Crohn's disease. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:514–5.
Di Meo, N., Stinco, G., Trevisini, S., De Marchi, S., Albano, A., & Trevisan, G. Sporotrichoid Mycobacterium marinum infection in an elderly woman. Dermatology online journal, 2015;21(5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Annabelle Jones and Luis A. Marcos declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Cutaneous Mycobacterial Diseases of the Skin and Soft Tissues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, A., Marcos, L.A. Manifestations of Mycobacterium marinum in the Immunocompromised Host. Curr Trop Med Rep 5, 233–237 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40475-018-0163-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40475-018-0163-5