Abstract
Background
Apalutamide is a next-generation androgen receptor inhibitor approved for treatment of subjects with high-risk, non-metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer (NM-CRPC).
Objective
The objective of this study was to characterize the population pharmacokinetics of apalutamide and its metabolite N-desmethyl-apalutamide in healthy male and castration-resistant prostate cancer subjects.
Methods
Plasma concentration data for apalutamide and N-desmethyl-apalutamide from 1092 subjects (seven clinical studies) receiving oral apalutamide (30–480 mg) once daily were pooled for a population pharmacokinetic analysis using a non-linear mixed-effect modelling approach. The impact of clinically relevant covariates was also assessed.
Results
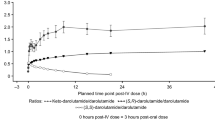
Apalutamide absorption was rapid, and the apparent steady-state volume of distribution was large (276 L), reflecting a wide body distribution. Apalutamide was eliminated slowly, with its apparent clearance increasing from 1.31 L/h after the first dose to 2.04 L/h at steady state. No evidence of time-dependent disposition was observed for N-desmethyl-apalutamide, which was also widely distributed and slowly cleared (1.5 L/h). After 4 weeks of treatment, more than 95% of steady-state exposure of apalutamide and N-desmethyl-apalutamide was reached. At a dose of apalutamide 240 mg/day, apalutamide and N-desmethyl-apalutamide exposure exhibited 5.3- and 85.2-fold accumulation in plasma, respectively. Inter-individual variability in apalutamide apparent clearance is low (< 20%). Among the covariates evaluated, apalutamide and N-desmethyl-apalutamide exposure were statistically associated only with health status, body weight, and albumin concentration, and the effect was low (< 25%).
Conclusions
A population pharmacokinetic modelling approach was successfully applied to describe the pharmacokinetics of apalutamide and N-desmethyl-apalutamide. No clinically relevant covariates were identified as predictors of apalutamide and N-desmethyl-apalutamide pharmacokinetics.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
Gartrell BA, Saad F. Managing bone metastases and reducing skeletal related events in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2014;11(6):335–45.
Hotte SJ, Saad F. Current management of castrate-resistant prostate cancer. Curr Oncol. 2010;17(S2):S72–9.
Clegg NJ, Wongvipat J, Joseph JD, Tran C, Ouk S, Dilhas A, et al. ARN-509: a novel antiandrogen for prostate cancer treatment. Cancer Res. 2012;72(6):1494–503.
Rathkopf DE, Morris MJ, Fox JJ, Danila DC, Slovin SF, Hager JH, et al. Phase I study of ARN-509, a novel antiandrogen, in the treatment of castration resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(28):3525–30.
Janssen Research & Development. A study of apalutamide (ARN-509) in men with non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (SPARTAN) [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT01946204]. US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov. 2013. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01946204. Accessed 11 Jan 2019
Rathkopf DE, Attard G, Efstathiou E, Yu MK, Griffin TW, Todd MB, et al. A phase 3 randomized, placebo-controlled double-blind study of ARN-509 plus abiraterone acetate (AA) in chemotherapy-naive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) [abstract no. TPS507]. J Clin Oncol Conf. 2015;33(15):TPS507.
Chi KN, Chowdhury S, Radziszewski P, et al. TITAN: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial of apalutamide (ARN-509) plus androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer (mHSPC) [abstract no. 771TiP]. Ann Oncol. 2016;27(6):243–65.
McKenzie M, Dearnaley D, Tombal B, et al. ATLAS: a randomized, double-blind, phase 3 study of ARN-509 in patients with high-risk localized or locally advanced prostate cancer receiving primary radiation therapy [abstract no. MP-07.10]. Can Urol Assoc J. 2016;10(1):S73–4.
ERLEADA™ (apalutamide) prescribing information. 2018. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/210951s000lbl.pdf. Accessed 11 Jan 2019.
Janssen Research & Development. Bioavailability study of 3 tablet formulations vs. capsule formulation of JNJ-56021927 in fasting healthy male participants [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02160756]. US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov. 2016. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02160756. Accessed 11 Jan 2019
Janssen Research & Development. Safety, pharmacokinetic and proof-of-concept study of ARN-509 (apalutamide) in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT01171898]. US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov. 2019. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01171898. Accessed 11 Jan 2019
Janssen Research & Development. A study of androgen receptor (AR) antagonist apalutamide in Chinese participants with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT03523442]. US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov. 2019. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03523442. Accessed 11 Jan 2019
Janssen Research & Development. A study to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of JNJ-56021927 in participants with mild or moderate hepatic impairment compared with participants with normal hepatic function [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02524717]. US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov. 2019. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02524717. Accessed 11 Jan 2019
Janssen Research & Development. A JNJ-56021927 (ARN-509; apalutamide) QT/QTc study [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02578797]. US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov. 2019. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02578797. Accessed 11 Jan 2019
Janssen Research & Development. Pharmacokinetic study of JNJ-56021927 when taken orally as tablet formulation in healthy male Japanese participants [ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02835508]. US National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov. 2017. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT02835508. Accessed 11 Jan 2019
Beal SL, Sheiner LB, Boeckmann AJ, Bauer RJ, editors. NONMEM 7.1.0 users guides. Ellicott City: Icon Development Solutions; 1989–2009.
R Development Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2012. http://www.R-project.org/Guidance for Industry. Accessed 11 Jan 2019
Girard P. Data transformation and parameter transformations in NONMEM. http://www.page-meeting.org/page/page2002/PascalGirardPage2002.pdf. Accessed 11 Jan 2019.
Nguyen TH, Mouksassi MS, Holford N, Al-Huniti N, Freedman I, Hooker AC, et al. Model evaluation of continuous data pharmacometric models: metrics and graphics. CPT Pharmacometr Syst Pharmacol. 2017;6(2):87–109.
Savic RM, Karlsson MO. Importance of shrinkage in empirical bayes estimates for diagnostics: problems and solutions. AAPS J. 2009;11(3):58–69.
Mandema JW, Verotta D, Sheiner LB. Building population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic models. I: models for covariate effects. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1992;20(5):511–28.
Bergstrand M, Hooker AC, Wallin JE, Karlsson MO. Prediction-corrected visual predictive checks for diagnosing nonlinear mixed-effects models. AAPS J. 2011;13(2):143–51.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the patients, investigators, and the medical, nursing, and laboratory staff who participated in the clinical studies included in the present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Caly Chien, Margaret Yu, Daniele Ouellet, and Juan-José Pérez-Ruixo were employees and shareholders of Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies at the time this analysis was conducted. Carlos Pérez-Ruixo, Jonás Samuel Pérez-Blanco, and Oliver Ackaert were employees of Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies at the time this analysis was conducted.
Funding
The clinical studies were supported by research funding from Janssen Research & Development, and the analyses presented here were supported by Janssen Research & Development.
Ethical approval and informed consent
All studies were conducted in accordance with principles for human experimentation as defined in the Declaration of Helsinki and were approved by the Human Investigational Review Board of each study center and by the Competent Authority of each country. Informed consent was obtained from each subject before enrollment in the studies after being advised of the potential risks and benefits of the study, as well as the investigational nature of the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez-Ruixo, C., Pérez-Blanco, J.S., Chien, C. et al. Population Pharmacokinetics of Apalutamide and its Active Metabolite N-Desmethyl-Apalutamide in Healthy and Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Subjects. Clin Pharmacokinet 59, 229–244 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-019-00808-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-019-00808-7