Abstract
Background and objective
Taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy (TIPN) is a main toxicity of taxanes with no effective treatment. This study aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of pregabalin (150 mg daily) and duloxetine (60 mg daily) for managing TIPN in breast cancer patients.
Methods
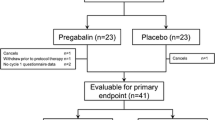
This randomized, double-blind, Phase II clinical trial was carried out at a chemotherapy center affiliated to Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences. Patients with breast cancer who received paclitaxel or docetaxel and had a grade 1 or more neuropathy (based on the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version (NCI-CTCAE v4.03), and who had score 4 or higher neuropathic pain severity [based on the visual analog scale (VAS)] were enrolled. Response to treatment was assessed based on improvements in the VAS, NCI-CTCAE, and Patient Neurotoxicity Questionnaire (PNQ) scores during a 6-week trial.
Results
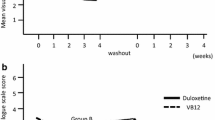
Both interventions were effective in decreasing TIPN compared to baseline. At Week 6, the VAS scores were improved in 37/40 (92.5%) and 16/42 (38.1%) of the patients in the pregabalin and duloxetine groups, respectively (p < 0.001). Improvement in NCI-CTCAE sensory neuropathy was also more significant with pregabalin (37/40; 92.5%) in comparison to duloxetine (13/42; 31%) (p < 0.001). Pregabalin was also more beneficial than duloxetine in improving the PNQ scores by 36/40 (90%) and 13/42 (31%), respectively (p < 0.001). Both interventions were tolerated well with mild adverse events.
Conclusions
Both pregabalin and duloxetine were well tolerated and efficacious in relieving neuropathic pain, however a 60 mg dose of duloxetine is inferior to a 150 mg dose of pregabalin.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolf S, Barton D, Kottschade L, Grothey A, Loprinzi C. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: prevention and treatment strategies. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44(11):1507–15.
Areti A, Yerra VG, Naidu V, Kumar A. Oxidative stress and nerve damage: role in chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy. Redox Biol. 2014;18(2):289–95.
Majithia N, Temkin SM, Ruddy KJ, Beutler AS, Hershman DL, Loprinzi CL. National Cancer Institute-supported chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy trials: outcomes and lessons. Support Care Cancer. 2016;24(3):1439–47.
Shimozuma K, Ohashi Y, Takeuchi A, Aranishi T, Morita S, Kuroi K, et al. Taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy and health-related quality of life in postoperative breast cancer patients undergoing adjuvant chemotherapy: N-SAS BC 02, a randomized clinical trial. Support Care Cancer. 2012;20(12):3355–64.
Speck RM, Sammel MD, Farrar JT, Hennessy S, Mao JJ, Stineman MG, DeMichele A. Impact of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy on treatment delivery in nonmetastatic breast cancer. J Oncol Pract. 2013;9(5):e234–40.
Rostock M, Jaroslawski K, Guethlin C, Ludtke R, Schröder S, Bartsch HH. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in cancer patients: a four-arm randomized trial on the effectiveness of electroacupuncture. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:1–9.
Chu SH, Lee YJ, Lee ES, Geng Y, Wang XS, Cleeland CS. Current use of drugs affecting the central nervous system for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in cancer patients: a systematic review. Support Care Cancer. 2015;23(2):513–24.
Rao RD, Michalak JC, Sloan JA, Loprinzi CL, Soori GS, Nikcevich DA, et al. Efficacy of gabapentin in the management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Cancer. 2007;110(9):2110–8.
Backonja M, Beydoun A, Edwards KR, et al. Gabapentin for the symptomatic treatment of painful neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1998;280(21):1831–6.
Rowbotham M, Harden N, Stacey B, Bernstein P, Magnus-Miller L, for the Gabapentin Postherpetic Neuralgia Study G. Gabapentin for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1998;280(21):1837–42.
Smith EML, Pang H, Cirrincione C, Fleishman S, Paskett ED, Ahles T, et al. Effect of duloxetine on pain, function, and quality of life among patients with chemotherapy-induced painful peripheral neuropathy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2013;309(13):1359–67.
Takenaka M, Iida H, Matsumoto S, Yamaguchi S, Yoshimura N, Miyamoto M. Successful treatment by adding duloxetine to pregabalin for peripheral neuropathy induced by paclitaxel. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2013;30(7):734–6.
Kus T, Aktas G, Alpak G, Kalender ME, Sevinc A, Kul S, et al. Efficacy of venlafaxine for the relief of taxane and oxaliplatin-induced acute neurotoxicity: a single-center retrospective case–control study. Support Care Cancer. 2016;24(5):2085–91.
Cohen K, Shinkazh N, Frank J, Israel I, Fellner C. Pharmacological treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Pharm Ther. 2015;40(6):372–88.
Isufi I, James E, Keley K, Peccerillo J, Saif MW. Pregabalin (PGB) in treatment of oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(15_suppl):e15045-e.
Saif MW, Syrigos K, Kaley K, Isufi I. Role of pregabalin in treatment of oxaliplatin-induced sensory neuropathy. Anticancer Res. 2010;30(7):2927–33.
Shimozuma K, Ohashi Y, Takeuchi A, Aranishi T, Morita S, Kuroi K, et al. Feasibility and validity of the Patient Neurotoxicity Questionnaire during taxane chemotherapy in a phase III randomized trial in patients with breast cancer: N-SAS BC 02. Support Care Cancer. 2009;17(12):1483–91.
Vondracek P, Oslejskova H, Kepak T, Mazanek P, Sterba J, Rysava M, et al. Efficacy of pregabalin in neuropathic pain inpaediatric oncological patients. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2009;13:332–6.
Ling B, Coudoré F, Decalonne L, Eschalier A, Authier N. Comparative antiallodynic activity of morphine, pregabalin and lidocaine in a rat model of neuropathic pain produced by one oxaliplatin injection. Neuropharmacology. 2008;55(5):724–8.
Peng P, Xi Q, Xia S, Zhuang L, Gui Q, Chen Y, et al. Pregabalin attenuates docetaxel-induced neuropathy in rats. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Med Sci. 2012;32(4):586–90.
Baidya DK, Agarwal A, Khanna P, Arora MK. Pregabalin in acute and chronic pain. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2011;27(3):307–14.
Verma V, Singh N, Singh Jaggi A. Pregabalin in neuropathic pain: evidences and possible mechanisms. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2014;12(1):44–56.
Quilici S, Chancellor J, Löthgren M, Simon D, Said G, Le TK, et al. Meta-analysis of duloxetine vs. pregabalin and gabapentin in the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. BMC Neurol. 2009;9(1):6.
Fradkin M, Batash R, Elamleh S, Debi R, Schafer P, Schafer M, et al. Management of peripheral neuropathy induced by chemotherapy. Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(25):4698–708.
Tanenberg RJ, Irving GA, Risser RC, Ahl J, Robinson MJ, Skljarevski V, et al. Duloxetine, pregabalin, and duloxetine plus gabapentin for diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain management in patients with inadequate pain response to gabapentin: an open-label, randomized, noninferiority comparison. Mayo Clin Proc. 2011;86(7):615–26.
Boyle J, Eriksson ME, Gribble L, Gouni R, Johnsen S, Coppini DV, Kerr D. Randomized, placebocontrolled comparison of amitriptyline, duloxetine, and pregabalin in patients with chronic diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Diabetes Care. 2012;35(12):2451–8.
Hirayama Y, Ishitani K, Sato Y, Iyama S, Takada K, Murase K, et al. Effect of duloxetine in Japanese patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a pilot randomized trial. Int J Clin Oncol. 2015;20(5):866–71.
Otake A, Yoshino K, Ueda Y, Sawada K, Mabuchi S, Kimura T, et al. Usefulness of duloxetine for paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy treatment in gynecological cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 2015;35(1):359–63.
Yang Y-H, Lin J-K, Chen W-S, Lin T-C, Yang S-H, Jiang J-K, et al. Duloxetine improves oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy in patients with colorectal cancer: an open-label pilot study. Support Care Cancer. 2012;20(7):1491–7.
Sisignano M, Baron R, Scholich K, Geisslinger G. Mechanism-based treatment for chemotherapyinduced peripheral neuropathic pain. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014;10(12):694–707.
Velasco R, Bruna J. Taxane-induced peripheral neurotoxicity. Toxics. 2015;3(2):152–69.
Jang CE, Jung MS, Sohn EH, Kim M, Yoo HS, Bae K, et al. The evaluation of changes in peripheral neuropathy and quality-of-life using low-frequency electrostimulation in patients treated with chemotherapy for breast cancer: a study protocol. Trials. 2018;19(1):526.
Shimozuma K, Ohashi Y, Takeuchi A, Morita S, Ohsumi S, Sunada Y, et al. Validation of the Patient Neurotoxicity Questionnaire (PNQ) during taxane chemotherapy in a phase III randomized trial in patients withbreast cancer: N-SAS BC 02. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2004;88:S232–3.
Freeman R, Durso-DeCruz E, Emir B. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of pregabalin treatment for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy findings from seven randomized, controlled trials across a range of doses. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(7):1448–54.
Freynhagen R, Strojek K, Griesing T, Whalen E, Balkenohl M. Efficacy of pregabalin in neuropathic pain evaluated in a 12-week, randomised, double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial of flexible-and fixed dose regimens. Pain. 2005;115(3):254–63.
van Seventer R, Feister HA, Young JP Jr, Stoker M, Versavel M, Rigaudy L. Efficacy and tolerability of twice-daily pregabalin for treating pain and related sleep interference in postherpetic neuralgia: a 13- week, randomized trial. Curr Med Res Opin. 2006;22(2):375–84.
Hudson JI, Wohlreich MM, Kajdasz DK, Mallinckrodt CH, Watkin JG, Martynov OV. Safety and tolerability of duloxetine in the treatment of major depressive disorder: analysis of pooled data from eight placebocontrolled clinical trials. Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp. 2005;20(5):327–41.
Devi P, Madhu K, Ganapathy B, Sarma G, John L, Kulkarni C. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of gabapentin, duloxetine, and pregabalin in patients with painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Indian J Pharmacol. 2012;44(1):51–6.
Hirayama Y, Sasaki J, Dosaka-Akita H, Ishitani K. Survey of the management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in Japan: Japanese Society of Medical Oncology. ESMO Open. 2016;1(3):e000053.
Spina E, Trifirò G, Caraci F. Clinically significant drug interactions with newer antidepressants. CNS Drugs. 2012;26(1):39–67.
Higgins MJ, Stearns V. CYP2D6 polymorphisms and tamoxifen metabolism: clinical relevance. Curr Oncol Rep. 2010;12(1):7–15.
Aubert RE, Stanek EJ, Yao J, Teagarden JR, Subar M, Epstein RS, et al. Risk of breast cancer recurrence in women initiating tamoxifen with CYP2D6 inhibitors. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(18S):CRA508-CRA.
Kelly CM, Juurlink DN, Gomes T, Duong-Hua M, Pritchard KI, Austin PC, Paszat LF. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and breast cancer mortality in women receiving tamoxifen: a population based cohort study. BMJ. 2010;340:c693.
Farrar JT, Portenoy RK, Berlin JA, Kinman JL, Strom BL. Defining the clinically important difference in pain outcome measures. Pain. 2000;88(3):287–94.
Rivera E, Cianfrocca M. Overview of neuropathy associated with taxanes for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2015;75(4):659–70.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the kind assistance and financial support provided by Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences (Proposal ID: 1897–20/05/94).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study design. ES was responsible for the study conception, definition of intellectual content, literature search, and manuscript preparation. GJ was responsible for the study conception, and clinical studies. NH conducted to definition of intellectual content. AA contributed to the data analysis and statistical analysis. NT contributed to data acquisition, and clinical studies. RA contributed to study conception, literature search, data acquisition, manuscript preparation and is guarantor for the study. All authors reviewed and edited the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
The authors acknowledge the kind assistance and financial support provided by Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences (Proposal ID: 1897–20/05/94).
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by ethics committee of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences (IR.MAZUMS.REC.94-1897). The study was submitted, evaluated and approved by the Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials (IRCT201602112027N5). All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from each patient prior to study enrolment.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salehifar, E., Janbabaei, G., Hendouei, N. et al. Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Pregabalin and Duloxetine in Taxane-Induced Sensory Neuropathy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin Drug Investig 40, 249–257 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-019-00882-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-019-00882-6