Abstract
Background and Objectives
Eltrombopag seems to be effective in treating patients with aplastic anemia in several clinical trials. This paper aims to perform the first meta-analysis analyzing the efficacy and safety of eltrombopag for aplastic anemia.
Methods
Literatures were retrieved from PubMed, EMBASE, OVID, Web of Science, Cochrane, Wanfang, http://clinicaltrials.gov and World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform search portal from establishment to July 2018. Using Stata statistical software version 12.0, subgroup analyses and sensitivity analyses were conducted.
Results
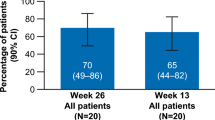
The overall hematologic response rate is 88% (95% CI 83–94%) for patients treated with eltrombopag plus immunosuppressive therapy, and 47% (95% CI 38–56%) for patients with refractory aplastic anemia using eltrombopag alone. Karyotype abnormality rates include an overall rate of 10% (95% CI 7–14%), a subtotal rate of 8% (95% CI 3–13%) for patients who are treated with eltrombopag plus immunosuppressive therapy without using antithymocyte globulin before, and a subtotal rate of 17% (95% CI 10–24%) for patients with refractory aplastic anemia treated with eltrombopag alone.
Conclusions
With different treatments and in different conditions eltrombopag showed a distinctive effect for aplastic anemia. However, clone evolution and adverse events were associated with treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Killick SB, Bown N, Cavenagh J, Dokal I, Foukaneli T, Hill A, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of adult aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 2016;172(2):187–207. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.13853.
Kaushansky K, Lichtman M, Prchal J, Levi MM, Press O, Burns L, et al. Williams hematology. 9th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2015.
Damodar S, Bafna V, Khanna-Gupta A, Prabhu S, Nataraj KS, Sarvepalli D, et al. Predicting response to immunosuppressive therapy in patients with acquired aplastic anemia using EGFR and TWIST1 expression levels. Blood. 2016;128(22):5076.
Goubran H, Seghatchian J, Prokopchuk-Gauk O, Radosevic J, Sabry W, Iqbal N, et al. Reflections on multiple strategies to reduce transfusion in cancer patients: a joint narrative. Transfus Apheres Sci. 2017;56(3):322–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transci.2017.05.018.
Peinemann F, Grouven U, Kroger N, Pittler M, Zschorlich B, Lange S. Unrelated donor stem cell transplantation in acquired severe aplastic anemia: a systematic review. Haematologica. 2009;94(12):1732–42. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2009.007583.
Rosenfeld S, Follmann D, Nunez O, Young NS. Antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine for severe aplastic anemia: association between hematologic response and long-term outcome. JAMA. 2003;289(9):1130–5. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.9.1130.
Young NS, Calado RT, Scheinberg P. Current concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of aplastic anemia. Blood. 2006;108(8):2509–19. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-03-010777.
Peinemann F, Bartel C, Grouven U. First-line allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation of HLA-matched sibling donors compared with first-line ciclosporin and/or antithymocyte or antilymphocyte globulin for acquired severe aplastic anemia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;7:CD006407. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd006407.pub2.
Argote VEF, Peñafiel COR, Sánchez MH, García JJG, Sinco HC, González GL, et al. Androgen treatment for acquired aplastic anemia in mexican adults. Blood. 2008;112(11):1046.
Scheinberg P, Young NS. How I treat acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 2012;120(6):1185–96. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-12-274019.
Cheruku PS, Cash A, Dunbar CE, Young NS, Larochelle A. The thrombopoietin receptor agonist eltrombopag has dna repair activity in human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Blood. 2015;126(23):2407.
Giammarco S, Van Lint MT, Lamparelli T, Gualandi F, Di Grazia C, Dominietto A et al. Androgens MAY BOOST hematologic response to ANTIThymocyte globulin in acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 2016;128(22):3900.
Salamonowicz M, Pawelec K, Panasiuk A, Matysiak M. Are colony stimulating factors (G-CSF) still needed in treatment of severe aplastic anemia in children? Blood. 2012;120(21):4400.
Cheng H, Cheruku PS, Alvarado L, Cash A, Dunbar CE, Young NS, et al. Interferon-γ perturbs key signaling pathways induced by thrombopoietin, but not eltrombopag, in human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Blood. 2016;128(22):3870.
Alvarado LJ, Andreoni A, Huntsman HD, Cheng H, Knutson JR, Larochelle A. Heterodimerization of TPO and IFNγ impairs human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell signaling and survival in chronic inflammation. Blood. 2017;130(Suppl 1):4.
Debili N, Wendling F, Cosman D, Titeux M, Florindo C, Dusanter-Fourt I, et al. The Mpl receptor is expressed in the megakaryocytic lineage from late progenitors to platelets. Blood. 1995;85(2):391–401.
Solar GP, Kerr WG, Zeigler FC, Hess D, Donahue C, de Sauvage FJ, et al. Role of c-mpl in Early Hematopoiesis. Blood. 1998;92(1):4–10.
Di Buduo CA, Currao M, Pecci A, Kaplan DL, Balduini CL, Balduini A. Revealing eltrombopag’s promotion of human megakaryopoiesis through AKT/ERK-dependent pathway activation. Haematologica. 2016;101(12):1479–88. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2016.146746.
Kaushansky K, Lok S, Holly RD, Broudy VC, Lin N, Bailey MC, et al. Promotion of megakaryocyte progenitor expansion and differentiation by the c-Mpl ligand thrombopoietin. Nature. 1994;369:568. https://doi.org/10.1038/369568a0.
Zeigler FC, de Sauvage F, Widmer HR, Keller GA, Donahue C, Schreiber RD, et al. In vitro megakaryocytopoietic and thrombopoietic activity of c-mpl ligand (TPO) on purified murine hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 1994;84(12):4045–52.
Qian H, Buza-Vidas N, Hyland CD, Jensen CT, Antonchuk J, Mansson R, et al. Critical role of thrombopoietin in maintaining adult quiescent hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1(6):671–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2007.10.008.
Decker M, Leslie J, Liu Q, Ding L. Hepatic thrombopoietin is required for bone marrow hematopoietic stem cell maintenance. Science. 2018;360(6384):106–10. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aap8861.
Lin F-c, Karwan M, Saleh B, Hodge DL, Chan T, Boelte KC, et al. IFN-γ causes aplastic anemia by altering hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell composition and disrupting lineage differentiation. Blood. 2014;124(25):3699–708. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-01-549527.
Kim MJ, Park SH, Opella SJ, Marsilje TH, Michellys PY, Seidel HM, et al. NMR structural studies of interactions of a small, nonpeptidyl Tpo mimic with the thrombopoietin receptor extracellular juxtamembrane and transmembrane domains. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(19):14253–61. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M611616200.
Erickson-Miller CL, Delorme E, Tian S-S, Hopson CB, Landis AJ, Valoret EI, et al. Preclinical activity of eltrombopag (SB-497115), an oral, nonpeptide thrombopoietin receptor agonist. Stem Cells (Dayton, Ohio). 2009;27(2):424–30. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2008-0366.
Guenther KL, Cheruku PS, Smith RH, Larochelle A. Eltrombopag promotes DNA repair in human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells: implications for the treatment of fanconi anemia. Blood. 2017;130(Suppl 1):776.
Socié G, Rosenfeld S, Frickhofen N, Gluckman E, Tichelli A. Late clonal diseases of treated aplastic anemia. Semin Hematol. 2000;37(1):91–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0037-1963(00)90033-7.
Desmond R, Townsley DM, Dumitriu B, Olnes MJ, Scheinberg P, Bevans M, et al. Eltrombopag restores trilineage hematopoiesis in refractory severe aplastic anemia that can be sustained on discontinuation of drug. Blood. 2014;123(12):1818–25. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-10-534743.
Steensma DP. Clinical Implications of Clonal Hematopoiesis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018;93(8):1122–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.04.002.
Prica A, Sholzberg M, Buckstein R. Thrombopoietin (TPO)-receptor agonists in myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood. 2013;122(21):2806.
Rivera D, Bastida JM, Corral LL, Sanchez-Guijo F, Vazquez L, Cabrero M et al. Usefulness of thrombopoietin receptor agonists for thrombocytopenia after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. An eight-year single center experience. Blood. 2017;130(Suppl 1):3222.
Soff GA, Miao Y, Devlin SM, Mantha S, Mones JV, Li VJ et al. Romiplostim for chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia (CIT). Results of a Phase 2 Trial. Blood. 2017;130(Suppl 1):289.
Itzykson R, Lambert J, Barbieri D, Gruson B, Thepot S, Braun T et al. A phase II trial of eltrombopag in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) with thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2017;130(Suppl 1):4266.
Gonzalez-Lopez TJ, Alvarez-Roman MT, Pascual C, Sanchez-Gonzalez B, Fernandez-Fuentes F, Perez-Rus G, et al. Use of eltrombopag for secondary immune thrombocytopenia in clinical practice. Br J Haematol. 2017;178(6):959–70. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.14788.
Mittelman M, Platzbecker U, Afanasyev B, Grosicki S, Wong RSM, Anagnostopoulos A, et al. Eltrombopag for advanced myelodysplastic syndromes or acute myeloid leukaemia and severe thrombocytopenia (ASPIRE): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2018;5(1):34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2352-3026(17)30228-4.
Afdhal NH, Dusheiko GM, Giannini EG, Chen PJ, Han KH, Mohsin A, et al. Eltrombopag increases platelet numbers in thrombocytopenic patients with HCV infection and cirrhosis, allowing for effective antiviral therapy. Gastroenterology. 2014;146(2):442-52e1. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2013.10.012.
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000100. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100.
Olnes MJ, Scheinberg P, Calvo KR, Desmond R, Tang Y, Dumitriu B, et al. Eltrombopag and improved hematopoiesis in refractory aplastic anemia. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(1):11–9. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1200931.
Patel B, Przychodzen BP, Clemente MJ, Hirsch CM, Saygin C, Versalle M et al. Clonal dynamics of refractory aplastic anemia in patients treated with eltrombopag. Blood. 2016;128(22):3892.
Kadia T, Ravandi F, Daver N, Borthakur G, Cortes JE, Jabbour E, et al. Single-center experience of immunosuppressive therapy with or without eltrombopag in patients with aplastic anemia. Blood. 2015;126(23):4779.
Nance D, Rodgers G, Nuttall M. Efficacy and safety of eltrombopag in patients with moderate, severe and very severe aplastic anemia. Haematologica. 2015;100:299.
Townsley DM, Scheinberg P, Winkler T, Desmond R, Dumitriu B, Rios O, et al. Eltrombopag added to standard immunosuppression for aplastic anemia. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(16):1540–50. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1613878.
Winkler T, Cooper JN, Townsley DM, Scheinberg P, Grasmeder S, Wu C, et al. Eltrombopag for refractory severe aplastic anemia: dosing regimens, long-term follow-up, clonal evolution and somatic mutation profiling. Blood. 2017;130(Suppl 1):777.
Fattizzo B, Benson-Quarm N, Hill A, Arnold L, Riley K, Munir T, et al. Eltrombopag in a real world cohort of aplastic anemia patients: large retrospective analysis of two UK centers. Br J Haematol. 2018;181:9.
Avgerinou G, Katsibardi K, Filippidou M, Tourkantoni N, Atmatzidou E, Roka K et al. The changing landscape of treatment in pediatric aplastic anemia; a single institution’s experience. Blood. 2016;128(22):5082.
Gill H, Leung GM, Lopes D, Kwong YL. The thrombopoietin mimetics eltrombopag and romiplostim in the treatment of refractory aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 2017;176(6):991–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.14024.
Lengline E, Drenou B, Peterlin P, Tournilhac O, Abraham J, Berceanu A, et al. Nationwide survey on the use of eltrombopag in patients with severe aplastic anemia: a report on behalf of the French Reference Center for Aplastic Anemia. Haematologica. 2018;103(2):212–20. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2017.176339.
Saleh MN, Bussel JB, Wong RS, Meddeb B, Salama A, Ocak O, et al. Thromboembolic event management and outcomes in patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia (CITP) during treatment with eltrombopag (EPAG): results from the extend study. Haematologica. 2017;102:292.
Ogawa S. Clonal hematopoiesis in acquired aplastic anemia. Blood. 2016;128(3):337–47. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-01-636381.
Yoshizato T, Dumitriu B, Hosokawa K, Makishima H, Yoshida K, Townsley D, et al. Somatic mutations and clonal hematopoiesis in aplastic anemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(1):35–47. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1414799.
Brodsky RA, Mukhina GL, Nelson KL, Lawrence TS, Jones RJ, Buckley JT. Resistance of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells to the glycosylphosphatidylinositol-binding toxin aerolysin. Blood. 1999;93(5):1749–56.
Brodsky RA, Mukhina GL, Li S, Nelson KL, Chiurazzi PL, Buckley JT, et al. Improved detection and characterization of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria using fluorescent aerolysin. Am J Clin Pathol. 2000;114(3):459–66.
Mukhina GL, Buckley JT, Barber JP, Jones RJ, Brodsky RA. Multilineage glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor-deficient haematopoiesis in untreated aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 2001;115(2):476–82.
Yoshida N, Yagasaki H, Kosaka Y, Kobayashi R, Yabe H, Kaneko T, et al. Predicting response to immunosuppressive therapy in childhood aplastic anemia. Blood. 2008;112(11):1049.
Chang H, Zhang J-Y, Mu X-Y, Meng W-T, Liu T. Association of interferon-gamma +874(T/A) single nucleotide polymorphism with response to immunosuppressive therapy in patients with severe aplastic anemia. Blood. 2010;116(21):1157.
Shin SH, Yahng SA, Lee SE, Cho BS, Eom KS, Kim YJ et al. The efficacy of rabbit antithymocyte globulin (Thymoglobulin®) with cyclosporin as first-line treatment in aplastic anemia. Blood. 2011;118(21):3430.
Lisukov I, Ivanova M, Golubovskaya I, Kruchkova I, Bondarenko S, Vavilov V, et al. Preceding chronic course and watch and wait practice for moderate aplastic anemia (MAA) are associated with low response rate and poor long-term outcome after immunosuppressive therapy (IST). Blood. 2013;122(21):1232.
Narita A, Sekiya Y, Sakaguchi H, Nishio N, Muramatsu H, Okuno Y, et al. Predicting response to immunosuppressive therapy by the combination of minor paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clones and lymphocyte telomere length in children with aplastic anemia. Blood. 2014;124(21):4386.
Pawelec K, Janiak M, Matysiak M, Salamonowicz M, Wlodarski PK. Association of telomere length of peripheral blood leukocyte with hematological response of immunosuppressive therapy in children with severe aplastic anemia. Blood. 2012;120(21):4403.
Stanley N, Olson TS, Babushok DV. Recent advances in understanding clonal haematopoiesis in aplastic anaemia. Br J Haematol. 2017;177(4):509–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.14510.
Kulagin A, Golubovskaya I, Ivanova M, Babenko E, Pronkina N, Kruchkova I, et al. Incidence and risk factors for hemolytic paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinurea (PNH) in aplastic anemia (AA) patients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49:S42–3. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2014.43.
Dumitriu B, Feng X, Townsley DM, Ueda Y, Yoshizato T, Calado RT, et al. Telomere attrition and candidate gene mutations preceding monosomy 7 in aplastic anemia. Blood. 2015;125(4):706–9. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-10-607572.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by Youth Project of National Natural Science Foundation (Grant no. 81200400), top-notch innovative talents project and Fujian project (Grants 2016Y9025 & 2016J06018 & 2017I0004); Fujian Medical University teaching reform project (Y17005) and Fujian Provincial Health and Family planning Commission Youth Research Project (2017-1-6).
Conflict of interest
Yaqun Hong, Xiaofan Li, Bo Wan, Nainong Li, and Yuanzhong Chen declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, Y., Li, X., Wan, B. et al. Efficacy and Safety of Eltrombopag for Aplastic Anemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin Drug Investig 39, 141–156 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-018-0725-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-018-0725-2