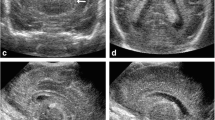
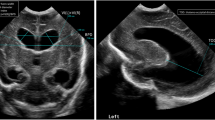
Abstract
Neonatal brain injury results from a complex interplay of maternal and perinatal factors, and can be challenging to diagnose from both clinical and radiologic perspectives. Depending on infant age and severity of insult, various types of brain injury can result. We will discuss the benefits and disadvantages of different imaging modalities: US, CT, MRI, PET, and SPECT. Focusing on MRI, we will discuss special considerations for neonates, including clinical stabilization, technical challenges, and advanced imaging approaches such as ASL, MRS, and SWI. In the remainder of the article, we will review the pathophysiology and MR imaging patterns of brain injury in preterm and term infants.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AA:
-
Amino acids
- ADC:
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient
- ASL:
-
Arterial spin labeling
- CBF:
-
Cerebral blood flow
- CbH:
-
Cerebellar hemorrhage
- Cho:
-
Choline
- Cr:
-
Creatine
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- DWI:
-
Diffusion-weighted imaging
- DTI:
-
Diffusion tensor imaging
- EGL:
-
External granular layer
- FA:
-
Fractional anisotropy
- FDG:
-
Fluorodeoxyglucose
- Glx:
-
Glutamate-glutamine
- HIE:
-
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy
- IGL:
-
Internal granular layer
- IVH:
-
Intraventricular hemorrhage
- Lac:
-
Lactate
- Lip:
-
Lipids
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MRS:
-
MR spectroscopy
- mI:
-
Myo-inositol
- ms:
-
Milliseconds
- MT:
-
Magnetization transfer
- NAA:
-
N-acetylaspartate
- NIRS:
-
Near-infrared spectroscopy
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- PLIC:
-
Posterior limb of internal capsule
- ppm:
-
Parts per million
- PVL:
-
Periventricular leukomalacia
- SNR:
-
Signal-to-noise ratio
- SPECT:
-
Single positron emission tomography
- SWI:
-
Susceptibility-weighted imaging
- TE:
-
Time to echo
- US:
-
Ultrasound
- VM:
-
Ventriculomegaly
- WMI:
-
White matter injury
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Ferriero DM. Neonatal brain injury. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1985–95.
Thornton C, Rousset CI, Kichev A, Miyakuni Y, Vontell R, Baburamani AA, Fleiss B, Gressens P, Hagberg H. Molecular mechanisms of neonatal brain injury. Neurol Res Int. 2012;. doi:10.1155/2012/506320.
Tagin MA, Woolcott CG, Vincer MJ, Whyte RK, Stinson DA. Hypothermia for neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2012;166(6):558–66.
Ment LR, Bada HS, Barnes P, Grant PE, Hirtz D, Papile LA, Pinto-Martin J, Rivkin M, Slovis TL. Practice parameter: neuroimaging of the neonate: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Neurology. 2002;58(12):1726–38.
Miller S, Ferriero D, Barkovich AJ, Silverstein F. Practice parameter: neuroimaging of the neonate: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Neurology. 2002;59(10):1663 author reply 1663-4.
Miller SP, Cozzio CC, Goldstein RB, Ferriero DM, Partridge JC, Vigneron DB, Barkovich AJ. Comparing the diagnosis of white matter injury in premature newborns with serial MR imaging and transfontanel ultrasonography findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24(8):1661–9.
• de Vries LS, Benders MJ, Groenendaal F. Imaging the premature brain: ultrasound or MRI? Neuroradiology. 2013;55 Suppl 2:13–22. This article discusses the complementary roles of US in MRI in neonatal neuroimaging, advantages/disadvantages of each modality, and recommendations for best utilization.
• Dinan D, Daneman A, Guimaraes CV. Easily overlooked sonographic findings in the evaluation of neonatal encephalopathy: lessons learned from magnetic resonance imaging. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2014;35(6):627–51. This article compares the findings of HIE on US and MR, and points out subtle findings that can often be missed at US.
• Epelman M, Daneman A, Chauvin N, et al. Head ultrasound and MR imaging in the evaluation of neonatal encephalopathy: competitive or complementary imaging studies? Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2012;20(1):93–115. This article discusses the benefits and disadvantages of US in detection and follow-up of HIE, with focus on subtle abnormalities that often progress to MR.
• Arthurs OJ, Edwards A, Austin T, et al. The challenges of neonatal magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr Radiol. 2012;42(10):1183–94. This article discusses the practical challenges of neonatal MRI, including both clinical and technical considerations.
Ditchfield M. 3T MRI in paediatrics: challenges and clinical applications. Eur J Radiol. 2008;68(2):309–19.
•• Plaisier A, Govaert P, Lequin MH, et al. Optimal timing of cerebral MRI in preterm infants to predict long-term neurodevelopmental outcome: a systematic review. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014;35(5):841–7. This article discusses the relevance of MRI findings in preterm infants on early scans versus term-equivalent age.
Bonifacio SL, Glass HC, Vanderpluym J, Agrawal AT, Xu D, Barkovich AJ, Ferriero DM. Perinatal events and early magnetic resonance imaging in therapeutic hypothermia. J Pediatr. 2011;158(3):360–5.
Barkovich AJ, Latal-Hajnal B, Partridge JC, Sola A, Ferriero DM. MR contrast enhancement of the normal neonatal brain. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997;18(9):1713–7.
• Stanescu L, Ishak GE, Khanna PC, et al. FDG PET of the brain in pediatric patients: imaging spectrum with MR imaging correlation. Radiographics. 2013;33(5):1279–303. This article discusses the applications of PET in pediatric neuroimaging with MR correlation.
Barkovich AJ. MR imaging of the neonatal brain. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2006;16(1):117–35.
El-Dib M, Massaro AN, Bulas D, et al. Neuroimaging and neurodevelopmental outcome of premature infants. Am J Perinatol. 2010;27(10):803–18.
•• Kwon SH, Vasung L, Ment LR, et al. The role of neuroimaging in predicting neurodevelopmental outcomes of preterm neonates. Clin Perinatol. 2014;41(1):257–83. This article discusses the predictive value of conventional and advanced MRI techniques for prediction of neurodevelopmental outcome following preterm brain injury.
Mathur AM, Neil JJ, Inder TE. Understanding brain injury and neurodevelopmental disabilities in the preterm infant: the evolving role of advanced magnetic resonance imaging. Semin Perinatol. 2010;34(1):57–66.
Panigrahy A, Borzage M, Blüml S. Basic principles and concepts underlying recent advances in magnetic resonance imaging of the developing brain. Semin Perinatol. 2010;34(1):3–19.
Burstein J, Papile LA, Burstein R. Intraventricular hemorrhage and hydrocephalus in premature newborns: a prospective study with CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979;132(4):631–5.
• Benders MJ, Kersbergen KJ, de Vries LS. Neuroimaging of white matter injury, intraventricular and cerebellar hemorrhage. Clin Perinatol. 2014;41(1):69–82. This article discusses the characteristic imaging findings of preterm birth injury including white matter injury, intraventricular hemorrhage, and cerebellar hemorrhage.
•• Buckner RL. The cerebellum and cognitive function: 25 years of insight from anatomy and neuroimaging. Neuron. 2013;80(3):807–15. This article reviews the body of research supporting the role of the cerebellum in cognition, from neuroimaging to animal studies and molecular neurobiology.
Tam EW, Rosenbluth G, Rogers EE, Ferriero DM, Glidden D, Goldstein RB, Glass HC, Piecuch RE, Barkovich AJ. Cerebellar hemorrhage on magnetic resonance imaging in preterm newborns associated with abnormal neurologic outcome. J Pediatr. 2011;158(2):245–50.
• Kim H, Gano D, Ho MH, Guo XM, Unzueta A, Hess C, Ferriero DM, Xu D, Barkovich AJ. Hindbrain regional growth in preterm newborns and its impairment in relation to brain injury. Human Brain Mapp. 2015;37:678–88. This article discusses the incidence of cerebellar hemorrhage on 3T MRI in preterm infants, and proposes a clinical scoring system that is correlated with morphometric growth patterns.
• Melbourne A, Kendall GS, Cardoso MJ. Preterm birth affects the developmental synergy between cortical folding and cortical connectivity observed on multimodal MRI. Neuroimage. 2014;89:23–34. This article discusses the effects of preterm birth on cortical sulcation and white matter connectivity.
• Tusor N, Arichi T, Counsell SJ, et al. Brain development in preterm infants assessed using advanced MRI techniques. Clin Perinatol. 2014;41(1):25–45. This article discusses structural DTI and functional fMRI applications in preterm brain injury.
Arzoumanian Y, Mirmiran M, Barnes PD, et al. Diffusion tensor brain imaging findings at term-equivalent age may predict neurologic abnormalities in low birth weight preterm infants. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24(8):1646–53.
Gaglioti P, Danelon D, Bontempo S, Mombrò M, Cardaropoli S, Todros T. Fetal cerebral ventriculomegaly: outcome in 176 cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2005;25(4):372–7.
Heinz ER, Provenzale JM. Imaging findings in neonatal hypoxia: a practical review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;192(1):41–7.
Barkovich AJ, Hajnal BL, Vigneron D, Sola A, Partridge JC, Allen F, Ferriero DM. Prediction of neuromotor outcome in perinatal asphyxia: evaluation of MR scoring systems. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998;19(1):143–9.
Shroff MM, Soares-Fernandes JP, Whyte H, et al. MR imaging for diagnostic evaluation of encephalopathy in the newborn. Radiographics. 2010;30(3):763–80.
Chao CP, Zaleski CG, Patton AC. Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: multimodality imaging findings. Radiographics. 2006;26(Suppl 1):S159–72.
de Vries LS, Groenendaal F. Patterns of neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic brain injury. Neuroradiology. 2010;52(6):555–66.
Huang BY, Castillo M. Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury: imaging findings from birth to adulthood. Radiographics. 2008;28(2):417–39.
Barkovich AJ, Westmark KD, Bedi HS, et al. Proton spectroscopy and diffusion imaging on the first day of life after perinatal asphyxia: preliminary report. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22(9):1786–94.
Barkovich AJ, Westmark K, Partridge C, Sola A, Ferriero DM. Perinatal asphyxia: MR findings in the first 10 days. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1995;16(3):427–38.
Barkovich AJ, Miller SP, Bartha A, Newton N, Hamrick SE, Mukherjee P, Glenn OA, Xu D, Partridge JC, Ferriero DM, Vigneron DB. MR imaging, MR spectroscopy, and diffusion tensor imaging of sequential studies in neonates with encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27(3):533–47.
• Cauley KA, Filippi CG. Apparent diffusion coefficient histogram analysis of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Radiol. 2014;44(6):738–46. This article correlates 2D histograms of ADC maps with gestational age at birth and severity of HIE.
Rodrigues K, Grant PE. Diffusion-weighted imaging in neonates. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2011;21(1):127–51.
Chan KC, Khong PL, Lau HF, et al. Late measures of microstructural alterations in severe neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy by MR diffusion tensor imaging. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2009;27(6):607–15.
Dağ Y, Firat AK, Karakaş HM, et al. Clinical outcomes of neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy evaluated with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2006;12(3):109–14.
Brissaud O, Amirault M, Villega F, et al. Efficiency of fractional anisotropy and apparent diffusion coefficient on diffusion tensor imaging in prognosis of neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a methodologic prospective pilot study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(2):282–7.
Wintermark P, Hansen A, Gregas MC, et al. Brain perfusion in asphyxiated newborns treated with therapeutic hypothermia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32(11):2023–9.
Wintermark P, Moessinger AC, Gudinchet F, Meuli R. Temporal evolution of MR perfusion in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008;27(6):1229–34. doi:10.1002/jmri.21379.
•• De Vis JB, Hendrikse J, Petersen ET, et al. Arterial spin-labelling perfusion MRI and outcome in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Eur Radiol. 2015;25(1):113–21. This article discusses the added value of ASL and MRS over conventional MRI and DWI in prediction of neurodevelopmental outcome following HIE.
• Bonifacio SL, Saporta A, Glass HC, Lee P, Glidden DV, Ferriero DM, Barkovich AJ, Xu D. Therapeutic hypothermia for neonatal encephalopathy results in improved microstructure and metabolism in the deep gray nuclei. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33(11):2050–5. This paper discusses ADC and MRS as biomarkers for HIE, with significant quantitative differences compared to controls following hypothermia.
•• Ancora G, Testa C, Grandi S, et al. Prognostic value of brain proton MR spectroscopy and diffusion tensor imaging in newborns with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy treated by brain cooling. Neuroradiology. 2013;55(8):1017–25. This article discusses the superiority of 1H-MRS and DTI in prognostication of HIE patient outcomes, even in the presence of hypothermia.
Ancora G, Soffritti S, Lodi R, et al. A combined a-EEG and MR spectroscopy study in term newborns with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Brain Dev. 2010;32(10):835–42.
Arrigoni F, Parazzini C, Righini A, et al. Deep medullary vein involvement in neonates with brain damage: an MR imaging study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32(11):2030–6.
Panigrahy A, Blüml S, et al. Advances in magnetic resonance neuroimaging techniques in the evaluation of neonatal encephalopathy. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;18(1):3–29.
Ramenghi LA, Rutherford M, Fumagalli M, et al. Neonatal neuroimaging: going beyond the pictures. Early Hum Dev. 2009;85(10 Suppl):S75–7.
Ho et al. Preterm brain injury at 3T: association of imaging scores with cerebellar growth and neurological outcome. Chicago, IL: Radiological Society of North America; 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Mai-Lan Ho, Alice C. Patton, David R. DeLone, Hosung Kim, Julie R. Gilbertson, Joel Felmlee, and Robert E. Watson each declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Neuroimaging.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ho, ML., Patton, A.C., DeLone, D.R. et al. Brain Injury in the Preterm and Term Neonate. Curr Radiol Rep 4, 39 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40134-016-0161-0
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40134-016-0161-0