Abstract
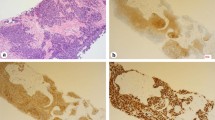
A 67-year-old man with metastatic prostate cancer was treated with leuprorelin and enzalutamide, but presented radiographic progression after 1 year. Although docetaxel chemotherapy was initiated, liver metastasis appeared with elevation of nerve-specific enolase in serum. Pathological findings of needle biopsy of lymph node metastasis in the right inguinal region showed neuroendocrine carcinoma. FoundationOne CDx® using a biopsy sample of the prostate at initial diagnosis detected the BRCA1 mutation (deletion of intron 3–7), but BRACAnalysis® test revealed no BRCA mutation in germline. Then, olaparib treatment was initiated, resulting in remarkable remission of tumors, but comorbidity with interstitial pneumonia. This case suggested that olaparib could be effective for neuroendocrine prostate cancer with BRCA1 gene mutation, but may cause interstitial pneumonia.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data in this report are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Nadal R, Schweizer M, Kryvenko ON et al (2014) Small cell carcinoma of the prostate. Nat Rev Urol 11(4):213–219. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2014.21
Wang HT, Yao YH, Li BG et al (2014) Neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC) progressing from conventional prostatic adenocarcinoma: factors associated with time to development of NEPC and survival from NEPC diagnosis—a systematic review and pooled analysis. J Clin Oncol 32(30):3383–3390. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2013.54.3553
Okasho K, Ogawa O, Akamatsu S (2021) Narrative review of challenges in the management of advanced neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Transl Androl Urol 10(10):3953–3962. https://doi.org/10.21037/tau-20-1131
de Bono J, Mateo J, Fizazi K et al (2020) Olaparib for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 382(22):2091–2102. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1911440
National cancer center Japan: Projected Cancer Statistics. https://ganjoho.jp/reg_stat/statistics/stat/short_pred_en.html [Accessed on 21 Sep. 2022]
Heinlein CA, Chang C (2004) Androgen receptor in prostate cancer. Endocr Rev 25(2):276–308. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2002-0032
Ryan CJ, Tindall DJ (2011) Androgen receptor rediscovered: the new biology and targeting the androgen receptor therapeutically. J Clin Oncol 29(27):3651–3658. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.35.2005
Galletti G, Leach BI, Lam L et al (2017) Mechanisms of resistance to systemic therapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 57:16–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.04.008
Vlachostergious PJ, Puca L, Beltran H (2017) Emerging variants of castration-resistant prostate cancer. Curr Oncol Rep 19(5):32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-017-0593-6
Aggarwal R, Huang J, Alumkal JJ et al (2018) Clinical and genomic characterization of treatment-emergent small-cell neuroendocrine prostate cancer: a multi-institutional prospective study. J Clin Oncol 36(24):2492–2503. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.77.6880
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network (2015) The molecular taxonomy of primary prostate cancer. Cell 163(4):1011–1025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.025
Tetu B, Ro JY, Ayala AG et al (1987) Small cell carcinoma of the prostate Part I A clinicopathologic study of 20 cases. Cancer 59(10):1803–1809. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19870515)59:10%3c1803::aid-cncr2820591019%3e3.0.co;2-x
Yamada Y, Beltran H (2021) Clinical and biological features of neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Curr Oncol Rep 23(2):15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11912-020-01003-9
Cooper CS, Eeles R, Wedge DC et al (2015) Analysis of the genetic phylogeny of multifocal prostate cancer identifies multiple independent clonal expansions in neoplastic and morphologically normal prostate tissue. Nat Genet 47(4):367–372. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3221
Boutros PC, Fraser M, Harding NJ et al (2015) Spatial genomic heterogeneity within localized, multifocal prostate cancer. Nat Genet 47(7):736–745. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3315
Fraser M, Sabelnykova VY, Yamaguchi TN et al (2017) Genomic hallmarks of localized, non-indolent prostate cancer. Nature 541(7637):359–364. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature20788
Ku SY, Gleave ME, Beltran H (2019) Towards precision oncology in advanced prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol 16(11):645–654. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41585-019-0237-8
Robinson D, Van Allen EM, Wu YM et al (2015) Integrative clinical genomics of advanced prostate cancer. Cell 161(5):1215–1228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.06.053
Beltran H, Oromendia C, Danila DC et al (2019) A phase II trial of the Aurora Kinase A inhibitor alisertib for patients with castration-resistant and neuroendocrine prostate cancer: efficacy and biomarkers. Clin Cancer Res 25(1):43–51. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1912
Symonds L, Konnick E, Vakar-Lopez F et al (2022) BRCA2 alternations in neuroendocrine/small-cell carcinoma prostate cancer: a case series. JCO Precis Oncol 6:e2200091. https://doi.org/10.1200/PO.22.00091
Lozano R, Castro E, Aragón IM et al (2021) Genetic aberrations in DNA repair pathways: a cornerstone of precision oncology in prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 124(3):552–563. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-020-01114-x
Momozawa Y, Iwasaki Y, Parsons MT et al (2018) Germline pathogenic variants of 11 breast cancer genes in 7051 Japanese patients and 11,241 controls. Nat Commun 9(1):4083. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06581-8
Enomoto T, Aoki D, Hattori K et al (2019) The first Japanese nationwide multicenter study of BRCA mutation testing in ovarian cancer: CHARacterizing the cross-sectionaL approach to Ovarian cancer geneTic TEsting of BRCA (CHARLOTTE). Int J Gynecol Cancer 29(6):1043–1049. https://doi.org/10.1136/ijgc-2019-000384
Momozawa Y, Iwasaki Y, Hirata M et al (2020) Germline pathogenic variants in 7636 Japanese patients with prostate cancer and 12 366 controls. J Natl Cancer Inst 112(4):369–376. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djz124
Hussain M, Mateo J, Fizazi K et al (2020) Survival with olaparib in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 383(24):2345–2357. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2022485
Pandya D, Shah M, Kaplan F et al (2021) Treatment-emergent neuroendocrine prostate cancer with a germline BRCA2 mutation: identification of a candidate reversion mutation associated with platinum/PARP-inhibitor resistance. Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud 7(1):a005801. https://doi.org/10.1101/mcs.a005801
Turina CB, Coleman DJ, Thomas GV et al (2019) Molecular testing identifies determinants of exceptional response and guides precision therapy in a patient with lethal, treatment-emergent neuroendocrine prostate cancer. Cureus 11(7):e5197. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.5197
Wu Y, Gao Y, Dou X et al (2020) Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with neuroendocrine transformation and BRCA 1 germ-line mutation: a case report and literature review. Onco Targets Ther 13:8049–8054. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S264347
Suzuki H, Oshino T, Hagio K et al (2020) Interstitial pneumonia caused by olaparib during treatment of breast cancer-a case report. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 47(9):1351–1353
Shu Y, He X, Liu Y et al (2022) A real-world disproportionality analysis of olaparib: data mining of the public version of FDA adverse event reporting system. Epidemiology 14:789–802. https://doi.org/10.2147/CLEP.S365513
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Masaki Shiota received honoraria from Janssen Pharmaceutical, AstraZeneca, Astellas Pharma, and Sanofi. Masatoshi Eto received honoraria from Takeda Pharmaceutical, and Janssen Pharmaceutical, and research funding support from Sanofi, Bayer Yakuhin, Astellas Pharma, and Takeda Pharmaceutical.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee (Approval No. 2021–123).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Kaitsumaru, M., Shiota, M., Takamatsu, D. et al. Interstitial pneumonia after regression by olaparib for neuroendocrine prostate cancer with BRCA1 mutation: a case report. Int Canc Conf J 12, 131–136 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13691-022-00592-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13691-022-00592-5