Abstract
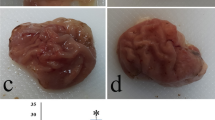
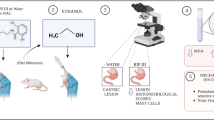
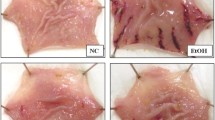
The aim of this study was to evaluate whether betaine ameliorates ethanol-induced gastric injury in rats. The morphological, histological and biochemical characteristics of gastric hemorrhagic lesions in ethanol-injured rats (n = 5/group) pretreated with betaine were analyzed and compared to non-treated controls. We compared the hemorrhagic dimensions using the Image J software, lipid peroxidation by malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) immunoreactivity in the gastric mucosa among treatment groups. Oral administration of 250 mg/kg betaine significantly reduced gastric hemorrhage dimensions compared with the vehicle-treated control (p <0.05). Immunohistochemical analysis showed that the expression of iNOS and its byproduct nitrotyrosine were significantly reduced in betaine-pretreated rats compared to vehicle-treated rats with ethanol injury (p < 0.05). Lipid peroxidation was also significantly reduced in the ethanol-injured rats pretreated with betaine compared with the vehicle-treated ethanol-injured group (p <0.05). Collectively, these results suggest that pretreatment of betaine ameliorates ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury, possibly through the inhibition of oxidative stress.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn M, Koh RK, Kim GO, Shin T (2013) Aqueous extract of purple Bordeaux radish, Raphanus sativus L. Ameliorates ethanol-induced gastric injury in rats. Orient Pharm Exp Med 13:247–252
Alirezaei M, Jelodar G, Niknam P, Ghayemi Z, Nazifi S (2011) Betaine prevents ethanol-induced oxidative stress and reduces total homocysteine in the rat cerebellum. J Physiol Biochem 67:605–612
Alirezaei M, Dezfoulian O, Neamati S, Rashidipour M, Tanideh N, Kheradmand A (2012a) Oleuropein prevents ethanol-induced gastric ulcers via elevation of antioxidant enzyme activities in rats. J Physiol Biochem 68:583–592
Alirezaei M, Reza Gheisari H, Reza Ranjbar V, Hajibemani A (2012b) Betaine: a promising antioxidant agent for enhancement of broiler meat quality. Br Poult Sci 53:699–707
Craig SA (2004) Betaine in human nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr 80:539–549
Franke A, Teyssen S, Singer MV (2005) Alcohol-related diseases of the esophagus and stomach. Dig Dis 23:204–213
Ganesan B, Anandan R, Lakshmanan PT (2011) Studies on the protective effects of betaine against oxidative damage during experimentally induced restraint stress in Wistar albino rats. Cell Stress Chaperones 16:641–652
Gazzieri D, Trevisani M, Springer J, Harrison S, Cottrell GS, Andre E et al (2007) Substance P released by TRPV1-expressing neurons produces reactive oxygen species that mediate ethanol-induced gastric injury. Free Radic Biol Med 43:581–589
Hayes KC, Pronczuk A, Cook MW, Robbins MC (2003) Betaine in sub-acute and sub-chronic rat studies. Food Chem Toxicol 41:1685–1700
Jeon WY, Lee MY, Shin IS, Lim HS, Shin HK (2012) Protective effects of the traditional herbal formula oryeongsan water extract on ethanol-induced acute gastric mucosal injury in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012:438191
Lee MY, Shin IS, Jeon WY, Seo CS, Ha H, Huh JI et al (2012) Protective effect of Bojungikki-tang, a traditional herbal formula, against alcohol-induced gastric injury in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 142:346–353
Li NS, Luo XJ, Zhang YS, He L, Liu YZ, Peng J (2011) Phloroglucinol protects gastric mucosa against ethanol-induced injury through regulating myeloperoxidase and catalase activities. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 25:462–468
Mayer MP (2013) Hsp70 chaperone dynamics and molecular mechanism. Trends Biochem Sci 38:507–514
Nanji AA, Jokelainen K, Fotouhinia M, Rahemtulla A, Thomas P, Tipoe GL et al (2001) Increased severity of alcoholic liver injury in female rats: role of oxidative stress, endotoxin, and chemokines. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281:G1348–1356
Siegmund SV, Haas S, Singer MV (2005) Animal models and their results in gastrointestinal alcohol research. Dig Dis 23:181–194
Sowndhararajan K, Kang SC (2013) Protective effect of ethyl acetate fraction of Acacia ferruginea DC. against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 148:175–181
Suemasu S, Tanaka K, Namba T, Ishihara T, Katsu T, Fujimoto M et al (2009) A role for HSP70 in protecting against indomethacin-induced gastric lesions. J Biol Chem 284:19705–19715
Yeo M, Kim DK, Cho SW, Hong HD (2008) Ginseng, the root of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer, protects ethanol-induced gastric damages in rat through the induction of cytoprotective heat-shock protein 27. Dig Dis Sci 53:606–613
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by the 2014 scientific promotion program funded by Jeju National University.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Meejung Ahn and Yoonhyoung Kang equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, M., Kang, Y., Moon, J. et al. Oral administration of betaine ameliorates ethanol-induced gastric injury in rats through its antioxidant effects. Orient Pharm Exp Med 14, 237–243 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-014-0158-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-014-0158-2