Abstract
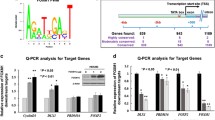
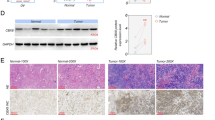
The oncogenic function of TEA domain transcription factor 4 (TEAD4) has been confirmed in multiple human malignancies, while its potential role and regulatory mechanism in serous ovarian cancer progression are left unknown. By the gene expression analyses from Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) database, TEAD4 expression is shown to be up-regulated in serous ovarian cancer samples. Here, we confirmed the high expression of TEAD4 in clinical serous ovarian cancer specimens. In the following functional experiments, we found that TEAD4 overexpression promoted serous ovarian cancer malignant phenotypes, including proliferation, migration and invasion in serous ovarian cancer SK-OV-3 and OVCAR-3 cells, while TEAD4 knockout exerted the opposite function. The tumor growth inhibition of TEAD4 depletion was also affirmed by a Xenograft model in mice. In addition, this phenotypic deterioration induced by TEAD4 overexpression was diminished by PLAG1 like zinc finger 2 (PLAGL2) silencing. More importantly, combined with the results of the dual-luciferase assay, the transcriptional regulation of TEAD4 on PLAGL2 promoter was evidenced. Our results showed that the cancer-promoting gene TEAD4 was involved in serous ovarian cancer progression via targeting PLAGL2 at the transcriptional level.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Kuroki L, Guntupalli SR. Treatment of epithelial ovarian cancer. BMJ. 2020;9(371): m3773.
Prat J. Ovarian carcinomas: five distinct diseases with different origins, genetic alterations, and clinicopathological features. Virchows Arch. 2012;460(3):237–49.
Kaldawy A, Segev Y, Lavie O, Auslender R, Sopik V, Narod SA. Low-grade serous ovarian cancer: a review. Gynecol Oncol. 2016;143(2):433–8.
Hoppenot C, Eckert MA, Tienda SM, Lengyel E. Who are the long-term survivors of high grade serous ovarian cancer? Gynecol Oncol. 2018;148(1):204–12.
Rojas V, Hirshfield KM, Ganesan S, Rodriguez-Rodriguez L. Molecular characterization of epithelial ovarian cancer: implications for diagnosis and treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):2113.
Shi Y, Zhou C, Lu H, Cui X, Li J, Jiang S, Zhang H, Zhang R. Ceramide synthase 6 predicts poor prognosis and activates the AKT/mTOR/4EBP1 pathway in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(9):5924–39.
Moore K, Colombo N, Scambia G, Kim BG, Oaknin A, Friedlander M, Lisyanskaya A, Floquet A, Leary A, Sonke GS, Gourley C, Banerjee S, Oza A, González-Martín A, Aghajanian C, Bradley W, Mathews C, Liu J, Lowe ES, Bloomfield R, DiSilvestro P. Maintenance olaparib in patients with newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(26):2495–505.
Chen CL, Hsu SC, Chung TY, Chu CY, Wang HJ, Hsiao PW, Yeh SD, Ann DK, Yen Y, Kung HJ. Arginine is an epigenetic regulator targeting TEAD4 to modulate OXPHOS in prostate cancer cells. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2398.
Nishioka N, Inoue K, Adachi K, Kiyonari H, Ota M, Ralston A, Yabuta N, Hirahara S, Stephenson RO, Ogonuki N, Makita R, Kurihara H, Morin-Kensicki EM, Nojima H, Rossant J, Nakao K, Niwa H, Sasaki H. The Hippo signaling pathway components Lats and Yap pattern Tead4 activity to distinguish mouse trophectoderm from inner cell mass. Dev Cell. 2009;16(3):398–410.
Holden JK, Cunningham CN. Targeting the Hippo pathway and cancer through the TEAD family of transcription factors. Cancers (Basel). 2018;10(3):81.
Gibault F, Sturbaut M, Bailly F, Melnyk P, Cotelle P. Targeting transcriptional enhanced associate domains (TEADs). J Med Chem. 2018;61(12):5057–72.
Huh HD, Kim DH, Jeong HS, Park HW. Regulation of TEAD transcription factors in cancer biology. Cells. 2019;8(6):600.
Zhou Y, Huang T, Cheng AS, Yu J, Kang W, To KF. The TEAD family and its oncogenic role in promoting tumorigenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(1):138.
Pobbati AV, Hong W. Emerging roles of TEAD transcription factors and its coactivators in cancers. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013;14(5):390–8.
He L, Yuan L, Sun Y, Wang P, Zhang H, Feng X, Wang Z, Zhang W, Yang C, Zeng YA, Zhao Y, Chen C, Zhang L. Glucocorticoid receptor signaling activates TEAD4 to promote breast cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2019;79(17):4399–411.
Tang JY, Yu CY, Bao YJ, Chen L, Chen J, Yang SL, Chen HY, Hong J, Fang JY. TEAD4 promotes colorectal tumorigenesis via transcriptionally targeting YAP1. Cell Cycle. 2018;17(1):102–9.
Lim B, Park JL, Kim HJ, Park YK, Kim JH, Sohn HA, Noh SM, Song KS, Kim WH, Kim YS, Kim SY. Integrative genomics analysis reveals the multilevel dysregulation and oncogenic characteristics of TEAD4 in gastric cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35(5):1020–7.
Xia Y, Chang T, Wang Y, Liu Y, Li W, Li M, Fan HY. YAP promotes ovarian cancer cell tumorigenesis and is indicative of a poor prognosis for ovarian cancer patients. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(3): e91770. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0091770. (Erratum in: PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0152712).
Wu L, Zhao N, Zhou Z, Chen J, Han S, Zhang X, Bao H, Yuan W, Shu X. PLAGL2 promotes the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells via USP37-mediated deubiquitination of Snail1. Theranostics. 2021;11(2):700–14.
Wu L, Zhou Z, Han S, Chen J, Liu Z, Zhang X, Yuan W, Ji J, Shu X. PLAGL2 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and mediates colorectal cancer metastasis via β-catenin-dependent regulation of ZEB1. Br J Cancer. 2020;122(4):578–89.
Hu W, Zheng S, Guo H, Dai B, Ni J, Shi Y, Bian H, Li L, Shen Y, Wu M, Tian Z, Liu G, Hossain MA, Yang H, Wang D, Zhang Q, Yu J, Birnbaumer L, Feng J, Yu D, Yang Y. PLAGL2-EGFR-HIF-1/2α signaling loop promotes HCC progression and erlotinib insensitivity. Hepatology. 2021;73(2):674–91.
Majem B, Parrilla A, Jiménez C, Suárez-Cabrera L, Barber M, Marín A, Castellví J, Tamayo G, Moreno-Bueno G, Ponce J, Matias-Guiu X, Alameda F, Romero I, Sánchez JL, Pérez-Benavente A, Moran S, Esteller M, Reventós J, Rigau M, Gil-Moreno A, Segura MF, Santamaría A. MicroRNA-654-5p suppresses ovarian cancer development impacting on MYC, WNT and AKT pathways. Oncogene. 2019;38(32):6035–50.
Sekiya R, Maeda M, Yuan H, Asano E, Hyodo T, Hasegawa H, Ito S, Shibata K, Hamaguchi M, Kikkawa F, Kajiyama H, Senga T. PLAGL2 regulates actin cytoskeletal architecture and cell migration. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35(9):1993–2001.
Quinn HM, Vogel R, Popp O, Mertins P, Lan L, Messerschmidt C, Landshammer A, Lisek K, Château-Joubert S, Marangoni E, Koren E, Fuchs Y, Birchmeier W. YAP and β-catenin cooperate to drive oncogenesis in basal breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2021;81(8):2116–27.
Stein C, Bardet AF, Roma G, Bergling S, Clay I, Ruchti A, Agarinis C, Schmelzle T, Bouwmeester T, Schübeler D, Bauer A. YAP1 exerts its transcriptional control via TEAD-mediated activation of enhancers. PLoS Genet. 2015;11(8): e1005465.
Yu T, Song J, Zhou H, Wu T, Liang Z, Du P, Liu CY, Wang G, Cui L, Liu Y. Nuclear TEAD4 with SIX1 overexpression is an independent prognostic marker in the stage I-III colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2021;17(13):1581–9.
Hu Y, Mu H, Deng Z. The transcription factor TEAD4 enhances lung adenocarcinoma progression through enhancing PKM2 mediated glycolysis. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(10):2063–73.
Wu Y, Li M, Lin J, Hu C. Hippo/TEAD4 signaling pathway as a potential target for the treatment of breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 2021;21(4):313.
Huang Z, Yan Y, Tang P, Cai J, Cao X, Wang Z, Zhang F, Shen B. TEAD4 as a prognostic marker promotes cell migration and invasion of urinary bladder cancer via EMT. Onco Targets Ther. 2021;10(14):937–49.
He S, Gao K, Mao L, Bhushan S, Xiao Z. Gene silencing of transcription factor TEAD4 inhibits esophageal cancer cells by regulating TCF7. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2023;38(2):132–9. https://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2020.3870.
Bradner JE, Hnisz D, Young RA. Transcriptional addiction in cancer. Cell. 2017;168(4):629–43.
Yang WH, Huang Z, Wu J, Ding CC, Murphy SK, Chi JT. A TAZ-ANGPTL4-NOX2 axis regulates ferroptotic cell death and chemoresistance in epithelial ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2020;18(1):79–90.
Declercq J, Hensen K, Van De Ven WJ, Chavez M. PLAG proteins: how they influence apoptosis and cell proliferation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;1010:264–5.
Zheng H, Ying H, Wiedemeyer R, Yan H, Quayle SN, Ivanova EV, Paik JH, Zhang H, Xiao Y, Perry SR, Hu J, Vinjamoori A, Gan B, Sahin E, Chheda MG, Brennan C, Wang YA, Hahn WC, Chin L, DePinho RA. PLAGL2 regulates Wnt signaling to impede differentiation in neural stem cells and gliomas. Cancer Cell. 2010;17(5):497–509.
Liu B, Lu C, Song YX, Gao P, Sun JX, Chen XW, Wang MX, Dong YL, Xu HM, Wang ZN. The role of pleomorphic adenoma gene-like 2 in gastrointestinal cancer development, progression, and prognosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(6):3089–100.
Li N, Li D, Du Y, Su C, Yang C, Lin C, Li X, Hu G. Overexpressed PLAGL2 transcriptionally activates Wnt6 and promotes cancer development in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2019;41(2):875–84.
Li C, Dong B, Xu X, Li Y, Wang Y, Li X. LncRNA ARAP1-AS1 aggravates the malignant phenotypes of ovarian cancer cells through sponging miR-4735–3p to enhance PLAGL2 expression. Cytotechnology. 2021;73(3):363–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10616-021-00463-6. (Erratum in: Cytotechnology. 2022 Feb;74(1):201).
Lu LL, Chen XH, Zhang G, Liu ZC, Wu N, Wang H, Qi YF, Wang HS, Cai SH, Du J. CCL21 facilitates chemoresistance and cancer stem cell-like properties of colorectal cancer cells through AKT/GSK-3β/Snail signals. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:5874127.
Liu HY, Zhang YY, Zhu BL, Feng FZ, Zhang HT, Yan H, Zhou B. MiR-203a-3p regulates the biological behaviors of ovarian cancer cells through mediating the Akt/GSK-3β/Snail signaling pathway by targeting ATM. J Ovarian Res. 2019;12(1):60.
Funding
This work was supported by Shenyang Young and Middle-aged Innovation Support Project (no. RC190500) and the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (no. 2020-MS-063).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, X., Liu, YS., Tong, R. et al. TEAD4 predicts poor prognosis and transcriptionally targets PLAGL2 in serous ovarian cancer. Human Cell 36, 1535–1547 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-023-00908-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-023-00908-4