Abstract
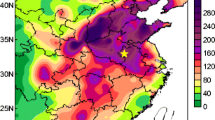
With rapid urbanization in recent years, severe air pollution has emerged as a major issue for many regions of China, especially in some metropolises. A persistent pollution case during 6 December 2016–8 January 2017 was selected to investigate the relations between turbulent intermittency and frequent PM2.5 (particulate matters with diameter less than 2.5 μm) pollution events over the metropolitan region of Beijing, China. The accumulation of PM2.5 near the surface frequently occurred as a combined result of strong inversion layers, stagnant winds, high ambient humidity levels, and stable stratification during this case. Arbitrary-order Hilbert spectral analysis indicated that steep decreases in the PM2.5 concentration were simultaneous with the occurrence of intermittent turbulence and strong vertical mixing. A wind profiler observation revealed existence of low-level jets (LLJs) at the end of the polluted periods, suggesting that the upper-level turbulent mixing accompanied by the wind shear of LLJ was transported downward and enhanced the vertical mixing near the surface, which might have caused an abrupt reduction in PM2.5 and improvement in air conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acevedo, O. C, and D. R. Fitzjarrald, 2003: In the core of the night-effects of intermittent mixing on a horizontally heterogeneous surface. Bound-Layer Meteor., 106, 1–33, doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1020824109575.
Banta, R. M., Y. L. Pichugina, and W. A. Brewer, 2006: Turbulent velocity-variance profiles in the stable boundary layer generated by a nocturnal low-level jet. J. Atmos. Sci., 63, 2700–2719, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/jas3776.1.
Banta, R. M., L. Mahrt, D. Vickers, et al., 2007: The very stable boundary layer on nights with weak low-level jets. J. Atmos. Sci., 64, 3068–3090, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/jas4002.1.
Baumbach, G., and U. Vogt, 1999: Experimental determination of the effect of mountain-valley breeze circulation on air pollution in the vicinity of Freiburg. Atmos. Environ., 33, 4019–4027, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1352-2310(99)00143-0.
Bressi, M., J. Sciare, V. Ghersi, et al., 2013: A one-year comprehensive chemical characterisation of fine aerosol (PM2 5) at urban, suburban and rural background sites in the region of Paris (France). Atmos. Chem. Phys., 13, 7825–7844, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-7825-2013.
Cai, W. J., K. Li, H. Liao, et al., 2017: Weather conditions conducive to Beijing severe haze more frequent under climate change. Nat. Climate Change, 7, 257–262, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncli-mate3249.
Charlson, R. J., S. E. Schwartz, J. M. Hales, et al., 1992: Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science, 255, 423–430, doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.255.5043.423.
Chen, H. P., and H. J. Wang, 2015: Haze days in North China and the associated atmospheric circulations based on daily visibility data from 1960 to 2012. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 120, 5895–5909, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/2015jd023225.
Cheng, N. L., D. W. Zhang, Y. T. Li, et al, 2017: Spatio-temporal variations of PM2 5 concentrations and the evaluation of emission reduction measures during two red air pollution alerts in Beijing. Sci. Rep., 7, 8220, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08895-x.
Cohen, L., 1995: Time-Frequency Analysis. Prentice Hall, Engle-wood Cliffs, NJ, 153–161.
Dawson, J. P., P. J. Adams, and S. N. Pandis, 2007: Sensitivity of PM25 to climate in the eastern US: A modeling case study. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 7, 4295–4309, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-7-4295-2007.
Deb Burman, P. K., T. V. Prabha, R. Morrison, et al, 2018: A case study of turbulence in the nocturnal boundary layer during the Indian summer monsoon. Bound.-Layer Meteor, 169, 115–138, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-018-0364-4.
Ding, A. J., C. B. Fu, X. Q. Yang, et al., 2013: Ozone and fine particle in the western Yangtze River Delta: An overview of 1 yr data at the SORPES station. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 13, 5813–5830, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-5813-2013.
Dominici, F., M. Greenstone, and C. R. Sunstein, 2014: Particulate matter matters. Science, 344, 257–259, doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1247348.
Frisch, U., 1995: Turbulence: The legacy of AN Kolmogorov, Cambridge University Press, UK, 72–97.
Gao, S. H., Y. J. Wang, Y. X. Huang, et al, 2016: Spatial statistics of atmospheric particulate matter in China. Atmos. Environ., 134, 162–167, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.03.052.
Grange, S. K., J. A. Salmond, W. J. Trompetter, et al., 2013: Effect of atmospheric stability on the impact of domestic wood combustion to air quality of a small urban township in winter. Atmos. Environ., 70, 28–38, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.12.047.
Helgason, W., and J. W. Pomeroy, 2012: Characteristics of the near-surface boundary layer within a mountain valley during winter. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol, 51, 583–597, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/jamc-d-11-058.1.
Hu, J. L., Y. G. Wang, Q. Ying, et al, 2014: Spatial and temporal variability of PM25 and PM10 over the North China Plain and the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ., 95, 598–609, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.07.019.
Hu, X. M., Y. Zhang, M. Z. Jacobson, et al, 2008: Coupling and evaluating gas/particle mass transfer treatments for aerosol simulation and forecast. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 113, D11208, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2007jd009588.
Hu, X. M., P. M. Klein, M. Xue, et al, 2013: Impact of the vertical mixing induced by low-level jets on boundary layer ozone concentration. Atmos. Environ., 70, 123–130, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.12.046.
Huang, N. E., Z. Shen, S. R. Long, et al, 1998: The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. Roy. Soc. A. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci., 454, 903–995, doi: https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1998.0193.
Huang, N. E., Z. Shen, and S. R. Long, 1999: A new view of nonlinear water waves: The Hilbert spectrum. Annu. Rev. Fluid Meek, 31, 417–457, doi: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.fluid.31.1.417.
Huang, Y. X., F. G. Schmitt, Z. M. Lu, et al., 2008: An amplitude-frequency study of turbulent scaling intermittency using Empirical Mode Decomposition and Hilbert Spectral Analysis. EPL (Europhys. Lett), 84, 40010, doi: https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/84/40010.
Huang, Y. X., F. G. Schmitt, J. P. Hermand, et al, 2011: Arbitrary-order Hilbert spectral analysis for time series possessing scaling statistics: Comparison study with detrended fluctuation analysis and wavelet leaders. Phys. Rev. E, 84, 016208, doi: https://doi.org/10.1103/physreve.84.016208.
Jia, B., Y. Wang, Y. Yao, et al., 2015: A new indicator on the impact of large-scale circulation on wintertime particulate matter pollution over China. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 15, 11919–11929, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-11919-2015.
Kalthoff, N., V. Horlacher, U. Corsmeier, et al., 2000: Influence of valley winds on transport and dispersion of airborne pollutants in the Freiburg-Schauinsland area. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 105, 1585–1597, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/1999jd900999.
Karipot, A., M. Y. Leclerc, G. S. Zhang, et al., 2008: Influence of nocturnal low-level jet on turbulence structure and C02 flux measurements over a forest canopy. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 113, D10102, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2007jd009149.
Klipp, C. L., and L. Mahrt, 2004: Flux-gradient relationship, self-correlation and intermittency in the stable boundary layer. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc, 130, 2087–2103, doi: https://doi.org/10.1256/qj.03.161.
Kolmogorov, A. N., 1941: The local structure of turbulence in incompressible viscous fluid for very large Reynolds numbers. Dokl. Akad. NaukSRSS, 30, 301–305.
Mahrt, L., 1998: Nocturnal boundary-layer regimes. Bound.-Layer Meteor, 88, 255–278, doi: https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1001171313493.
Mahrt, L., 2014: Stably stratified atmospheric boundary layers. Annu. Rev. Fluid Meek, 46, 23–45, doi: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-fluid-010313-141354.
Miao, Y. C, J. P. Guo, S. H. Liu, et al., 2017: Relay transport of aerosols to Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region by multi-scale atmospheric circulations. Atmos. Environ., 165, 35–445, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.06.032.
Miao, Y. C, J. P. Guo, S. H. Liu, et al, 2018: The climatology of low-level jet in Beijing and Guangzhou, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 123, 2816–2830, doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/2017jd027321.
Nel, A., 2005: Air pollution-related illness: Effects of particles. Science, 308, 804–806, doi: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1108752.
Noone, D., C. Risi, A. Bailey, et al., 2013: Determining water sources in the boundary layer from tall tower profiles of water vapor and surface water isotope ratios after a snowstorm in Colorado. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 13, 1607–1623, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-13-1607-2013.
Petaja, T., L. Jarvi, V. M. Kerminen, et al., 2016: Enhanced air pollution via aerosol-boundary layer feedback in China. Sci. Rep., 6, 18998, doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/srepl8998.
Poulos, G. S., W. Blumen, D. C. Fritts, et al., 2002: CASES-99: A comprehensive investigation of the stable nocturnal boundary layer. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc, 83, 555–581, doi: https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(2002)083<0555:CACIOT>2.3.CO;2.
Quan, J. N., X. X. Tie, Q. Zhang, et al, 2014: Characteristics of heavy aerosol pollution during the 2012–2013 winter in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ., 88, 83–89, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.01.058.
Quan, J. N., Q. Liu, X. Li, et al., 2015: Effect of heterogeneous aqueous reactions on the secondary formation of inorganic aerosols during haze events. Atmos. Environ., 122, 306–312, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.09.068.
Reitebuch, O., A. Strassburger, S. Emeis, et al., 2000: Nocturnal secondary ozone concentration maxima analysed by sodar observations and surface measurements. Atmos. Environ., 34, 4315–4329, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1352-2310(00)00185-0.
Ren, Y., S. W. Zheng, W. Wei, et al., 2018: Characteristics of turbulent transfer during episodes of heavy haze pollution in Beijing in winter 2016/17. J. Meteor. Res., 32, 69–80, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-018-7072-3.
Rodriguez, A., A. Sanchez-Arcilla, J. M. Redondo, et al., 1995: Pollutant dispersion in the nearshore region: Modelling and measurements. Water Sci. Technol, 32, 169–178, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-1223(96)00088-1.
Salmond, J. A., 2005: Wavelet analysis of intermittent turbulence in a very stable nocturnal boundary layer: Implications for the vertical mixing of ozone. Bound-Layer Meteor, 114, 463–488, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-004-2422-3.
Salmond, J. A., and I. G. McKendry, 2005: A review of turbulence in the very stable nocturnal boundary layer and its implications for air quality. Prog. Phys. Geogr: Earth Environ., 29, 171–188, doi: https://doi.org/10.1191/0309133305pp442ra.
Schafer, K., S. Emeis, H. Hoffmann, et al., 2006: Influence of mixing layer height upon air pollution in urban and sub-urban areas. Meteor. Z, 15, 647–658, doi: https://doi.org/10.1127/0941-2948/2006/0164.
Seibert, P., H. Feldmann, B. Neininger, et al., 2000: South foehn and ozone in the eastern Alps-Case study and climatological aspects. Atmos. Environ., 34, 1379–1394, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1352-2310(99)00439-2.
Shao, P. Y., H. Z. Tian, Y. J. Sun, et al, 2018: Characterizing remarkable changes of severe haze events and chemical compositions in multi-size airborne particles (PMb PM25 and PM10) from January 2013 to 2016–2017 winter in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ., 189, 133–144, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.06.038.
Shen, Z., G. X. Cui, and Z. S. Zhang, 2017: Turbulent dispersion of pollutants in urban-type canopies under stable stratification conditions. Atmos. Environ., 156, 1–14, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.02.017.
Sorbjan, Z., and A. Czerwinska, 2013: Statistics of turbulence in the stable boundary layer affected by gravity waves. Bound-Layer Meteor, 148, 73–91, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-013-9809-y.
Strassburger, A., and W. Kuttler, 1998: Diurnal courses of ozone in an inner urban park. Meteor. Z., 7, 15–18, doi: https://doi.org/10.1127/metz/7/1998/15.
Tang, G., X. Li, Y. Wang, et al., 2009: Surface ozone trend details and interpretations in Beijing, 2001–2006. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 8813–8823, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-9-8813-2009.
Tang, G. Q., J. Q. Zhang, X. W. Zhu, et al., 2016: Mixing layer height and its implications for air pollution over Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 16, 2459–2475, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-16-2459-2016.
Tao, S., Y. Wang, S. M. Wu, et al., 2007: Vertical distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in atmospheric boundary layer of Beijing in winter. Atmos. Environ., 41, 9594–9602, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.08.026.
Terradellas, E., M. R. Soler, E. Ferreres, et al., 2005: Analysis of oscillations in the stable atmospheric boundary layer using wavelet methods. Bound.-Layer Meteor, 114, 489–518, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-004-1293-y.
Thompson, T. M., R. K. Saari, and N. E. Selin, 2014: Air quality resolution for health impact assessment: Influence of regional characteristics. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 14, 969–978, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-14-969-2014.
Vindel, J. M., and C. Yagiie, 2011: Intermittency of turbulence in the atmospheric boundary layer: Scaling exponents and stratification influence. Bound.-Layer Meteor, 140, 73–85, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-011-9597-1.
Walters, J. T., R. T. McNider, X. Z. Shi, et al., 2007: Positive surface temperature feedback in the stable nocturnal boundary layer. Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, L12709, doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2007gl029505.
Wang, G., S. Y. Cheng, J. B. Li, et al., 2015: Source apportionment and seasonal variation of PM2 5 carbonaceous aerosol in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of China. Environ. Monit. Assess., 187, 143, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4288-x.
Wang, P L, J. X. Xu, M. Zhang, et al, 2014: A study of the meteorological causes of a prolonged and severe haze episode in January 2013 over central-eastern China. Atmos. Environ., 98, 146–157, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.08.053.
Wang, L. L., N. Zhang, Z. R. Liu, et al, 2014: The influence of climate factors, meteorological conditions, and boundary-layer structure on severe haze pollution in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region during January 2013. Adv. Meteor, 685971, doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/685971.
Wang, T., W. Nie, J. Gao, et al., 2010: Air quality during the 2008 Beijing Olympics: Secondary pollutants and regional impact. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 10, 7603–7615, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-10-7603-2010.
Wang, X. F., W. X. Wang, L. X. Yang, et al, 2012: The secondary formation of inorganic aerosols in the droplet mode through heterogeneous aqueous reactions under haze conditions. Atmos. Environ., 63, 68–76, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.09.029.
Wang, Y., M. B. McElroy, J. W. Munger, et al, 2008: Variations of O3 and CO in summertime at a rural site near Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, 6355–6363, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-8-6355-2008.
Wang, Z. F., J. Li, Z. Wang, et al., 2014: Modeling study of regional severe hazes over mid-eastern China in January 2013 and its implications on pollution prevention and control. Sci. China Earth Sci., 57, 3–13, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-013-4793-0.
Wei, W., F. G. Schmitt, Y. X. Huang, et al., 2016: The analyses of turbulence characteristics in the atmospheric surface layer using arbitrary-order Hilbert spectra. Bound.-Layer Meteor, 159, 391–406, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-015-0122-9.
Wei, W., H. S. Zhang, F. G. Schmitt, et al, 2017: Investigation of turbulence behaviour in the stable boundary layer using arbitrary-order Hilbert spectra. Bound.-Layer Meteor, 163, 311–326, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10546-016-0227-9.
Wei, W., M. Z. Wang, H. S. Zhang, et al., 2019: Diurnal characteristics of turbulent intermittency in the Takhmakan Desert. Meteor. Atmos. Phys., 131, 287–297, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-017-0572-3.
Xia, H. X., 2006: The preliminary study of introducing the superhigh chimney to the plain area of Beijing. Municipal Administration & Technology, 8, 70–72, doi: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1008-2271.2006.02.009. (in Chinese)
Yagiie, C, S. Viana, G. Maqueda, et al., 2006: Influence of stability on the flux-profile relationships for wind speed, <Pm, and temperature, <Ph, for the stable atmospheric boundary layer. Nonlinear Process. Geophys., 13, 185–203, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/npg-13-185-2006.
Ye, X. X., Y. Song, X. H. Cai, et al, 2016: Study on the synoptic flow patterns and boundary layer process of the severe haze events over the North China Plain in January 2013. Atmos. Environ., 124, 129–145, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.06.011.
Yin, Z. C, and H. J. Wang, 2017: Role of atmospheric circulations in haze pollution in December 2016. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 17, 11673–11681, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-17-11673-2017.
Yu, L. D., G. F. Wang, R. J. Zhang, et al., 2013: Characterization and source apportionment of PM2 5 in an urban environment in Beijing. Aerosol Air Qual. Res., 13, 574–583, doi: https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2012.07.0192.
Zhang, H. F., S. X. Wang, J. M. Hao, et al., 2016: Air pollution and control action in Beijing. J. Clean. Prod., 112, 1519–1527, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.04.092.
Zhang, J. P., T. Zhu, Q. H. Zhang, et al., 2012: The impact of circulation patterns on regional transport pathways and air quality over Beijing and its surroundings. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 12, 5031–5053, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-12-5031-2012.
Zheng, G. J., F. K. Duan, H. Su, et al., 2015: Exploring the severe winter haze in Beijing: The impact of synoptic weather, regional transport and heterogeneous reactions. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 15, 2969–2983, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-2969-2015.
Zheng, S., A. Pozzer, C. X. Cao, et al., 2015: Long-term (2001–2012) concentrations of fine particulate matter (PM25) and the impact on human health in Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 15, 5715–5725, doi: https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-15-5715-2015.
Zhong, J. T., X. Y. Zhang, Y. Q. Wang, et al., 2017: Relative contributions of boundary-layer meteorological factors to the explosive growth of PM25 during the red-alert heavy pollution episodes in Beijing in December 2016. J. Meteor. Res., 31, 809–819, doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-017-7088-0.
Acknowledgments
Photos in Fig. 1 are authorized by Mr. Zou Yi, who promoted BeijingAirNow at http://weibo.com/p/1005051000481815.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0203300) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (91544216 and 41705003).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, W., Zhang, H., Cai, X. et al. Influence of Intermittent Turbulence on Air Pollution and Its Dispersion in Winter 2016/2017 over Beijing, China. J Meteorol Res 34, 176–188 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-020-9128-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13351-020-9128-4