Abstract
Purpose
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disorder characterized by insulin deficiency or insulin resistance. Pregabalin (PGB) is an antiepileptic drug with proven efficacy in the treatment of epilepsy, generalized anxiety disorder, and neuropathic pain. In this study, we aimed to investigate the protective effects of PGB in brain tissue of rats with streptozotocin (STZ)-induced experimental diabetes.
Materials and methods
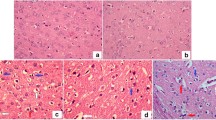
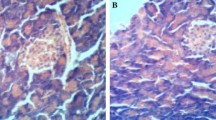
Twenty-eight Wistar albino male rats were randomly divided into four groups with seven rats each: (I) Control group, (II) PGB (50 mg/kg PBG), (III) DM, and (IV) DM + PGB (50 mg/kg/day PGB per orally for 8 weeks). Diabetes was induced with an intraperitoneal (i.p.) STZ injection (Sigma Chemical Co Louis Missour, USA) at a dose of 180 mg/kg. STZ was dissolved in 0.1 M phosphate-citrate tampon (pH 4.5). Paraffin sections were examined using histological and immunohistochemical analyses. To detect oxidative damage biochemically, malondialdehyde (MDA), the end product of lipid peroxidation; superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione (GSH) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) which are antioxidant enzymes, levels were studied. In addition, bax, caspase-3 enzyme activities and TUNEL assay were studied to evaluate the apoptosis status.
Results
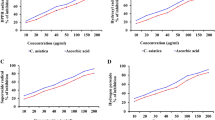
In the DM group, MDA concentrations were significantly higher and GPx and SOD activities were significantly lower compared to the control group. MDA concentrations were significantly lower and SOD activity was significantly higher in the DM + PGB group than in the DM group. The GPx activity in the DM group decreased significantly compared to the control group. In immunohistochemical examinations (Bax, Caspase-3 and TUNEL), the apoptosis rate was significantly lower in the in DM + PGB group than in the DM group.
Conclusion
Pregabalin may prevent harmful effects of oxidative damage by decreasing the MDA levels and increasing the SOD levels. In addition, it was thought that PGB may have antiapoptotic properties due to decreased bax and caspase-3 immunoreactivity and TUNEL positivity in PGB groups. Based on these findings, we think that PGB may be effective in reducing the risk of brain damage associated with DM.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hasselbaink DM, Glatz JFC, Luiken JJFP, Roemen THM, Vusse GJV. Ketone bodies disturb fatty acid handling in isolated cardiomyocytes derived from control and diabetic rats. Biochem J. 2003;371:753–60.
Abou-Seif MA, Youssef AA. Evaluation of some biochemical chenges in diabetic patients. Clin Chim Acta. 2004;346:161–70.
Stratton MI, Adler IA, Neil WA, Mattheus ND, Manley ES, Cull AC, Hadden D, Turner CR, Holman RR. Association of glycemia macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS35): prospective observational study. BMJ. 2000;321:405–12.
Klin R. Hyperglicemia and microvascular and macrovascular disease in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1995;18:258–68.
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M. Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact. 2006;160:1–40.
Charnogursky G. Neurological complications of diabetes. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2014;14:457.
Ünal E, Akan O, Üçler S. Diyabetin komplikasyonları. Okmeydanı Tıp Dergisi. 2015;31:45–51.
Ninomiya T. Diabetes mellitus and dementia. Curr Diabetes Rep. 2014;14:487.
Zhao WQ, Alkon DL. Role of insulinandinsulinreceptor in learning and memory. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2001;177:125–34.
Sałat K, Gdula-Argasińska J, Malikowska N, Podkowa A, Lipkowska A, Librowski T. Effect of pregabalin on contextual memory deficits and inflammatory state-related protein expression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. 2016;389:613–23.
Li WA, Moore-Langston S, Chakraborty T, Rafols JA, Conti AC, Ding Y. Hyperglycemia in stroke and possible treatments. Neurol Res. 2013;35:479–91.
Nader MA, Ateyya H, El-Shafey M, El-Sherbeeny NA. Sitagliptin enhances the neuroprotective effect of pregabalin against pentylenetetrazole-induced acute epileptogenesis in mice: implication of oxidative, inflammatory, apoptotic and autophagy pathways. Neurochem Int. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2017.10.006.
Aşcı S, Demirci S, Aşcı H, Doğuç DK, Onaran İ. Neuroprotective effects of pregabalin on cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Trakya Univ Fac Med Balkan Med J. 2016;33:221–7.
Okutan H, Savas C, Delibas N. The antioxidant effect of melatonin in lung injury after aortic occlusion-reperfusion. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2004;3:519–22.
Placer ZA, Cushmann LL, Johnson BC. Estimation of products of lipid peroxidation in biochemical systems. Anal Biochem. 1966;16:359–64.
Matkovics B, Szabo I, Varga IS. Determination of enzyme activities in lipid peroxidation and glutathione pathways (in Hungarian). Lab Diagn. 1988;15:248–9.
Meister A, Anderson ME. Glutathione. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:711–60.
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y. A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem. 1988;34:497–500.
Lawrence RA, Burk RF. Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976;71:952–8.
Aebi H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:121–6.
Sedlak J, Lindsay RHC. Estimation of total protein bound and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellmann’s reagent. Anal Biochem. 1968;25:192–205.
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr ALL, Randall RJ. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:265–75.
Turgut B, Demir T, Çeliker Ü. Oftalmolojide apoptosis. Fırat Tıp Dergisi. 2006;11:6–11.
Birrell AM, Heffernan SJ, Ansselin AD, McLennan S, Church DK, Gillin AG, Yue DK. Functional and structural abnormalities in the nerves of type 1 diabetic baboons: aminoguanidine treatment does not improve nerve function. Diabetologia. 2000;43:110–6.
Sima AA, Sugimoto K. Experimental diabetic neuropathy: an update. Diabetologia. 1999;42:773–88.
Tamaddonfard E, Farshid AA, Asri-Rezaee S, Javadi S, Khosravi V, Rahman B, Mirfakhraee Z. Crocin improved learning and memory impairments in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2013;16:91–100.
Pamidi N, Satheesha Nayak BN. Effect of streptozotocin induced diabetes on rat hippocampus. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2012;113:583–8.
Meymandi MS, Soltani Z, Sepehri G, Amiresmaili G, Farahani F, Aghtaei MM. Effects of pregabalin on brain edema, neurologic and histologic outcomes in experimental traumatic brain injury. Brain Res Bull. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.05.001.
Bissels GJ, Heide LP, Kamal A. Ageing and diabetes: implications for brain function. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;441:1–14.
Ha KY, Kim YH, Rhyu KW, Kwon SE. Pregabalin as a neuroprotector after spinal cord injury in rats. Eur Spine J. 2008;17:864–72.
Andre V, Dube C, Francois J, Leroy C, Rigoulot MA, Roch C, Namer IJ, Nehlig A. Pathogenesis and pharmacology of epilepsy in the lithium-pilocarpine model. Epilepsia. 2007;48:41–7.
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39:44–84.
Romero FJ, Bosch-Morell F, Romero MJ, Jareño EJ, Romero B, Marín N, Romá J. Lipid peroxidation products and antioxidants in human disease. Environ Health Perspect. 1998;106:1229–34.
Cosar M, Songur A, Sahin O, Uz E, Yilmaz R, Yagmurca M, Ozen OA. The neuroprotective effect of fish n-3 fatty acids in the hippocampus of diabetic rats. Nutr Neurosci. 2008;11:161–6.
Halliwell B. Oxidants and central nervous system: some fundamental questions. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1989;126:23–33.
Southorn PA, Powis G. Free radicals in medicine. Mayo Clin Proc. 1988;63:381–9.
Seghrouchni I, Drai J, Bannier E, Riviere J, Calmard P, Garcia I, Orgiazzi J, Revol A. Oxidative stress parameters in Type I, Type II and insulin-treated Type II Diabetes Mellitus; insulin treatment efficiency. Clin Chim Acta. 2002;321:89–96.
Martínez-Tellez R, Gómez-Villalobos Mde J, Flores G. Alteration in dendritic morphology of cortical neurons in rats with diabetes mellitus induced by streptozotocin. Brain Res. 2005;1048:108–15.
Li ZG, Zhang W, Sima AA. C-peptide prevents hippocampal apoptosis in type 1 diabetes. Int J Exp Diabetes Res. 2002;3:241–5.
Xue H, Jin L, Jin L, Zhang P, Li D, Xia Y, Lu Y, Xu Y. Neuroprotection of aucubin in primary diabetic encephalopathy. Sci China C Life Sci. 2008;51:495–502.
Takahashi A, Masuda A, Sun M, Centonze VE, Herman B. Oxidative stress-induced apoptosis is associated with alterations in mitochondrial caspase activity and Bcl-2-dependent alterations in mitochondrial pH (pHm). Brain Res Bull. 2004;62:497–504.
Pugazhenthi S, Nesterova A, Jambal P, Audesirk G, Kern M, Cabell L, Eves E, Rosner MR, Boxer LM, Reusch JE. Oxidative stress-mediated downregulation of bcl-2 promoter in hippocampal neurons. J Neurochem. 2003;84:982–96.
Çalıkoglu G, Aytekin H, Akgül O, Akgül MH, Gezen AF, Akyüz F, Çakır M. Effect of pregabalin in preventing secondary damage in traumatic brain injury: an experimental study. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:813–20.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Firat University Experimental Research Center for their contributions. This study was supported by a grant from Firat University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All autors confirm that this work is original and has not been published elsewhere nor is it currently under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Demir, C.F., Balduz, M., Taşcı, İ. et al. Protective effect of pregabalin on the brain tissue of diabetic rats. Diabetol Int 12, 207–216 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-020-00476-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-020-00476-0