Abstract
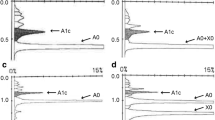
The level of glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is widely used to monitor long-term glycemic control in patients with diabetes mellitus. There are more than 30 methods for measuring HbA1c levels. In recent times, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) has become the most commonly used method in Japan. However, HPLC-based HbA1c level measurements do not accurately reflect glycemic control in the presence of Hb variants. We report the case of a patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus, who was incidentally found to having an extremely rare Hb variant. A 69-year-old Japanese female visited our clinic and was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. Her HbA1c level, which was measured using HPLC at our clinic, could not be determined. DNA sequencing revealed a heterozygous mutation in the α1 globin gene (HBA1: c.301C > T, p.Leu101Phe). Hb Weesp was detected. Many Hb variants have been reported; however, to the best of our knowledge, this is only the second report about Hb Weesp in the world and the first from Japan. Clinicians should consider the possibility of Hb variants in cases in which abnormal elution patterns are detected during the measurement of HbA1c using HPLC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inoue K, Nakashima M, Masunaga S, Tanigaki N, Hatoyama Y, Nagashio H, Baba T, Nohara M. A case of HbE-Saskatoon and false-low HbA1c value determined by ion-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Igakukensa. 2018;67(4):575–9.
Iizuka K, Mizuno M, Niwa H, Takeda J. A rare case of variant hemoglobin (Hb Yahata) suspected based on inconsistent plasma glucose and HbA1c levels. Intern Med. 2015;54(14):1771–5.
International Expert Committee. International Expert Committee report on the role of A1C assay in the diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(7):1327–34.
Bry L, Chen PC, Sack DB. Effect of hemoglobin variants and chemically modified derivatives on assays for glycohemoglobin. Clin Chem. 2001;47:153–63.
Van Zweiten R, Veldthuis M, Delzenne B, Berfhuis J, Groen J, Ait Ichou F, Clifford E, Harteveld CL, Stroobants AK. Hemoglobin analyses in the Netherlands reveal more than 80 different variants including six novel ones. Hemoglobin. 2014;38(1):1–7.
Bots M, Stroobants AK, Delzenne B, Soeters MR, de Vries JE, Weykamp CW, Norg RJ, Veldthuis M, van Zwieten R. Two novel haemoglobin variants that affect haemoglobin A1c measurement by ion-exchange chromatography. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2015;53(9):1465–71.
John WG. Glycated haemoglobin analysis. Ann Clin Biochem. 1997;34(Pt1):17–31.
Server GG: Hb Var: a database of human hemoglobin variants and thalassemias. http://globin.bx.psu.edu/hbvar/menu.html. Accessed 30 Oct 2018
Yamashiro Y, Hattori Y. Hemoglobinopathies in Japan: characteristics and comparison with those of other ethnic groups. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2015;56(7):752–9.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Takashi Miyazawa for making valuable suggestions and Arkray Co. for their help with the data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no conflicts of interest.
Human rights statement
All the procedures were performed in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained for the publication of this case report.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Hatayama, T., Umeda, F., Yamauchi, T. et al. A diabetic patient in whom Hb Weesp was incidentally detected when her HbA1c level was measured. Diabetol Int 10, 300–302 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-019-00402-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13340-019-00402-z