Abstract
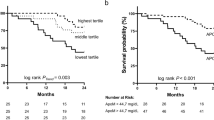
ApoE has been reported to be associated with tumorigenesis and tumor progression. In this study, we explored the potential diagnostic and prognostic role of serum ApoE in breast cancer patients. Subject cohorts consisted of 152 normal healthy controls female and 257 breast cancer cases. Serum levels of ApoE were determined with turbidimetric immunoassay. The serum levels of ApoE were significantly elevated in breast cancer patients compared with normal healthy controls (45.82 ± 13.96 mg/L vs. 33.61 ± 6.44 mg/L, respectively, P < 0.0001) and also significantly associated with TNM stage and lymph nodes status (all P < 0.05). Area under receiver operating characteristic curve for serum ApoE discriminate breast cancer patients from controls was 0.786 with specificity of 0.974 and sensitivity of 0.541, the cut-off value of ApoE was 43.15 mg/L. Kaplan-Meier log rank analysis showed that the high serum ApoE group (serum ApoE ≥ 43.15 mg/L) had a poorer progression-free survival and overall survival compared with low serum ApoE group (serum ApoE < 43.15 mg/L) (all P < 0.05). In addition, univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis displayed serum ApoE as an independent risk factor of breast cancer patients prognosis (all P < 0.05). Serum ApoE played a role as serological biomarkers that indicated diagnostic and prognostic evaluation in breast cancer patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32.
Chi Y, Yao L, Hu X, Huang S, Huang N, Li S, Shao Z, Wu J: The bmp inhibitor dand5 in serum predicts poor survival in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016
Rivenbark AG, O’Connor SM, Coleman WB. Molecular and cellular heterogeneity in breast cancer: challenges for personalized medicine. Am J Pathol. 2013;183:1113–24.
Etzioni R, Urban N, Ramsey S, McIntosh M, Schwartz S, Reid B, Radich J, Anderson G, Hartwell L. The case for early detection. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:243–52.
Blue ML, Williams DL, Zucker S, Khan SA, Blum CB. Apolipoprotein e synthesis in human kidney, adrenal gland, and liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983;80:283–7.
Chen YC, Pohl G, Wang TL, Morin PJ, Risberg B, Kristensen GB, Yu A, Davidson B, Shih Ie M. Apolipoprotein E is required for cell proliferation and survival in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:331–7.
Herz J, Beffert U. Apolipoprotein e receptors: linking brain development and alzheimer’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2000;1:51–8.
Liu Z, Gao Y, Hao F, Lou X, Zhang X, Li Y, Wu D, Xiao T, Yang L, Li Q, Qiu X, Wang E. Secretomes are a potential source of molecular targets for cancer therapies and indicate that APOE is a candidate biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma metastasis. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41:7507–23.
Pencheva N, Tran H, Buss C, Huh D, Drobnjak M, Busam K, Tavazoie SF. Convergent multi-miRNA targeting of ApoE drives LRp1/LRp8-dependent melanoma metastasis and angiogenesis. Cell. 2012;151:1068–82.
Rice SJ, Liu X, Miller B, Joshi M, Zhu J, Caruso C, Gilbert C, Toth J, Reed M, Rassaei N, Das A, Barochia A, El-Bayoumy K, Belani CP. Proteomic profiling of human plasma identifies apolipoprotein E as being associated with smoking and a marker for squamous metaplasia of the lung. Proteomics. 2015;15:3267–77.
Luo J, Song J, Feng P, Wang Y, Long W, Liu M, Li L: Elevated serum apolipoprotein e is associated with metastasis and poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol 2016
Singletary SE, Allred C, Ashley P, Bassett LW, Berry D, Bland KI, Borgen PI, Clark GM, Edge SB, Hayes DF, Hughes LL, Hutter RV, Morrow M, Page DL, Recht A, Theriault RL, Thor A, Weaver DL, Wieand HS, Greene FL. Staging system for breast cancer: revisions for the 6th edition of the ajcc cancer staging manual. Surg Clin North Am. 2003;83:803–19.
Cibeira GH, Giacomazzi J, Aguiar E, Schneider S, Ettrich B, De Souza CI, Camey S, Caleffi M, Weber B, Ashton-Prolla P, Moriguchi EH. Apolipoprotein e genetic polymorphism, serum lipoprotein levels and breast cancer risk: a case-control study. Molecular and clinical oncology. 2014;2:1009–15.
Saadat M. Apolipoprotein e (APOE) polymorphisms and susceptibility to breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Cancer research and treatment : official journal of Korean Cancer Association. 2012;44:121–6.
Mahley RW, Rall Jr SC. Apolipoprotein E: far more than a lipid transport protein. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2000;1:507–37.
Uen YH, Liao CC, Lin JC, Pan YH, Liu YC, Chen YC, Chen WJ, Tai CC, Lee KW, Liu YR, Lin HT, Lin CY. Analysis of differentially expressed novel post-translational modifications of plasma apolipoprotein E in Taiwanese females with breast cancer. J Proteome. 2015;126:252–62.
Goodison S, Chang M, Dai Y, Urquidi V, Rosser CJ. A multi-analyte assay for the non-invasive detection of bladder cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7:e47469.
Mrkonjic M, Chappell E, Pethe VV, Manno M, Daftary D, Greenwood CM, Gallinger S, Zanke BW, Knight JA, Bapat B. Association of apolipoprotein E polymorphisms and dietary factors in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2009;100:1966–74.
Oue N, Hamai Y, Mitani Y, Matsumura S, Oshimo Y, Aung PP, Kuraoka K, Nakayama H, Yasui W. Gene expression profile of gastric carcinoma: identification of genes and tags potentially involved in invasion, metastasis, and carcinogenesis by serial analysis of gene expression. Cancer Res. 2004;64:2397–405.
Su WP, Chen YT, Lai WW, Lin CC, Yan JJ, Su WC. Apolipoprotein E expression promotes lung adenocarcinoma proliferation and migration and as a potential survival marker in lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2011;71:28–33.
Boylan KL, Andersen JD, Anderson LB, Higgins L, Skubitz AP. Quantitative proteomic analysis by iTRAQ(R) for the identification of candidate biomarkers in ovarian cancer serum. Proteome Sci. 2010;8:31.
Tang X. Tumor-associated macrophages as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013;332:3–10.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Specialized Research Fund for the Science and Technology Department of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2014A020212477 to LSL, 2014A020212720 to JML), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (Grant No. 2015A030313035 to LSL), the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (Grant No. 20130171120069 to LSL), and the Science and Technology Department of Guangzhou City, China (Grant No. 201400000004-2 to ML). The funder had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Authors’ contributions
LSL and JML designed the experiment, interpreted the data, and prepared the manuscript. XDX, JXW, LJY, JHB, PNF, WQL, HH, PJL, YSC, ML, JML, and LSL conducted the experiment, collected the data, and helped to prepare the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Additional information
Xiangdong Xu and Jianxin Wan contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Wan, J., Yuan, L. et al. Serum levels of apolipoprotein E correlates with disease progression and poor prognosis in breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 15959–15966 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5453-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5453-8