Abstract
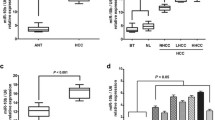
Human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most prevalent malignancies in the world. Research on HCC has recently focused on microRNAs (miRNAs) that play crucial roles in cancer development and progression of HCC. In this study, we aimed to analyze the expression and function of a metastasis-associated microRNA-608 (miR-608) in HCC. Samples of human HCC and matched adjacent normal tissues were surgically removed, and miR-608 expression and the pathological characteristics of HCC were investigated. In this study, we found that miR-608 expression was significantly reduced in HCC and its expression levels were highly associated with tumor size, differentiation, clinical stage, and overall and disease-free survival of HCC. Overexpression of miR-608 in HCC cell lines HepG2 and SK-Hep-1 inhibited cell proliferation by G1 arrest. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), a potential target gene of miR-608, was inversely correlated with miR-608 expression in HCC tissues and cell lines. Furthermore, we demonstrated that MIF was directly regulated by miR-608 and the restoration of MIF expression reversed the inhibitory effects of miR-608 on HCC cell proliferation. Taken together, these findings collectively demonstrate that miR-608 exerts its anti-cancer function by directly targeting MIF in HCC, indicating a potential novel prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for HCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huntzicker EG, Hotzel K, Choy L, Che L, Ross J, Pau G, et al. Differential effects of targeting notch receptors in a mouse model of liver cancer. Hepatology. 2015;61:942–52.
Chen Z, Huang Z, Ye Q, Ming Y, Zhang S, Zhao Y, et al. Prognostic significance and anti-proliferation effect of microRNA-365 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:1705–11.
Ho C, Wang C, Mattu S, Destefanis G, Ladu S, Delogu S, et al. Akt (v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1) and n-ras (neuroblastoma ras viral oncogene homolog) coactivation in the mouse liver promotes rapid carcinogenesis by way of mtor (mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1), foxm1 (forkhead box m1)/skp2, and c-myc pathways. Hepatology. 2012;55:833–45.
El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2557–76.
Wu Y, Cain-Hom C, Choy L, Hagenbeek TJ, de Leon GP, Chen Y, et al. Therapeutic antibody targeting of individual notch receptors. Nature. 2010;464:1052–7.
Huang X, Qin J, Lu S. Up-regulation of mir-877 induced by paclitaxel inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation though targeting foxm1. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:1515–24.
Wang X, Zhang J, Zhou L, Lu P, Zheng ZG, Sun W, et al. Significance of serum microRNA-21 in diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): clinical analyses of patients and an HCC rat model. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:1466–78.
Dou C, Wang Y, Li C, Liu Z, Jia Y, Li Q, Yang W, Yao Y, Liu Q, Tu K. Microrna-212 suppresses tumor growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting FOXA1. Oncotarget. 2015.
Yates LA, Norbury CJ, Gilbert RJ. The long and short of microRNA. Cell. 2013;153:516–9.
Garzon R, Marcucci G. Potential of microRNAs for cancer diagnostics, prognostication and therapy. Curr Opin Oncol. 2012;24:655–9.
Wang G, Sun Y, He Y, Ji C, Hu B, Sun Y. MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by target forkhead box p4 (foxp4). Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8:337–44.
Xiao ZD, Jiao CY, Huang HT, He LJ, Zhao JJ, Lu ZY, et al. Mir-218 modulate hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation through pten/akt/pi3k pathway and hoxa10. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:4039–44.
Chang RM, Yang H, Fang F, Xu JF, Yang LY. MicroRNA-331-3p promotes proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting ph domain and leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatase. Hepatology. 2014;60:1251–63.
Cho WC. MicroRNAs: potential biomarkers for cancer diagnosis, prognosis and targets for therapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010;42:1273–81.
Giordano S, Columbano A. MicroRNAs: new tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma? Hepatology. 2013;57:840–7.
Qiu F, Yang L, Zhang L, Yang X, Yang R, Fang W, et al. Polymorphism in mature microRNA-608 sequence is associated with an increased risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Gene. 2015;565:180–6.
Pardini B, Rosa F, Naccarati A, Vymetalkova V, Ye Y, Wu X, et al. Polymorphisms in microRNA genes as predictors of clinical outcomes in colorectal cancer patients. Carcinogenesis. 2015;36:82–6.
Di Leva G, Croce CM. Mirna profiling of cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013;23:3–11.
Henrique R, Luis AS, Jeronimo C. The epigenetics of renal cell tumors: from biology to biomarkers. Front Genet. 2012;3:94.
Redova M, Svoboda M, Slaby O. MicroRNAs and their target gene networks in renal cell carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;405:153–6.
Zhang Y, Schiff D, Park D, Abounader R. MicroRNA-608 and microRNA-34a regulate chordoma malignancy by targeting egfr, bcl-xl and met. PLoS One. 2014;9, e91546.
Tokarz P, Blasiak J. The role of microRNA in metastatic colorectal cancer and its significance in cancer prognosis and treatment. Acta Biochim Pol. 2012;59:467–74.
Adamali H, Armstrong ME, McLaughlin AM, Cooke G, McKone E, Costello CM, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor enzymatic activity, lung inflammation, and cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186:162–9.
Tas F, Karabulut S, Serilmez M, Ciftci R, Duranyildiz D. Serum levels of macrophage migration-inhibitory factor (MIF) have diagnostic, predictive and prognostic roles in epithelial ovarian cancer patients. Tumour Biol: J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med. 2014;35:3327–31.
Tan L, Ye X, Zhou Y, Yu M, Fu Z, Chen R, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer tissues and impairs insulin secretion function of beta-cell. J Transl Med. 2014;12:92.
Richard V, Kindt N, Decaestecker C, Gabius HJ, Laurent G, Noel JC, et al. Involvement of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and its receptor (CD74) in human breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 2014;32:523–9.
Pei XJ, Wu TT, Li B, Tian XY, Li Z, Yang QX. Increased expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and dj-1 contribute to cell invasion and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Med Sci. 2014;11:106–15.
Oliveira CS, de Bock CE, Molloy TJ, Sadeqzadeh E, Geng XY, Hersey P, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor engages pi3k/akt signalling and is a prognostic factor in metastatic melanoma. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:630.
Ren Y, Tsui HT, Poon RT, Ng IO, Li Z, Chen Y, et al. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor: roles in regulating tumor cell migration and expression of angiogenic factors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2003;107:22–9.
Hira E, Ono T, Dhar DK, El-Assal ON, Hishikawa Y, Yamanoi A, et al. Overexpression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor induces angiogenesis and deteriorates prognosis after radical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2005;103:588–98.
Xia JT, Li W, Liu YJ, Chen LZ, Wu ZF, Zhang LJ, et al. Correlations of expressions of macrophage migration inhibitor factor and cyclin D1 with tumor size and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2007;15:918–21.
Huang XH, Jian WH, Wu ZF, Zhao J, Wang H, Li W, et al. Small interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated knockdown of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) suppressed cyclin D1 expression and hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation. Oncotarget. 2014;5:5570–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All samples were obtained with informed consent, and the study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of No. 401 Hospital of PLA.
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Kejia Wang and Qing Liang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Liang, Q., Wei, L. et al. MicroRNA-608 acts as a prognostic marker and inhibits the cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Tumor Biol. 37, 3823–3830 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4213-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4213-5