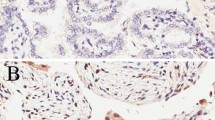
Abstract
Radiotherapy is one of the main treatments for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, but there are still no biomarkers to differentiate patients who will benefit from radiation. Although treatment with a combination of radiotherapy with chemotherapy, and/or surgery improves the prognosis of patients, no biomarkers can distinguish between the responses obtained with the combined therapies. Therefore, in this study, we selected patients treated with radiotherapy alone to evaluate survivin as a predictor for radiotherapy. One hundred two biopsy samples collected by endoscopy were immunostained by survivin antibody. Positive staining for survivin was obtained in 60.8% tumor samples. Survivin expression, metastasis, and clinical stage correlated significantly with overall survival. In multivariate analysis, survivin was an independent prognostic factor for predicting overall survival of patients with esophageal cancer. Moreover, in esophageal cancer cell lines, overexpression of survivin reduced the percentage of cell death induced by radiation. Our data indicate that survivin could be a potential predictor to define those patients with esophageal squamous carcinoma who would benefit from radiotherapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Zhang S, Lei Z, Li G, Zou X, Zhao P, Chen W. A report of cancer incidence and mortality from 34 cancer registries in China, 2006. China Cancer. 2010;19:356–65. in Chinese.
Fukuda K, Sakakura C, Miyagawa K, Kuriu Y, Kin S, Nakase Y, et al. Differential gene expression profiles of radioresistant oesophageal cancer cell lines established by continuous fractionated irradiation. Br J Cancer. 2004;91:1543–50.
Ogawa R, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, Kimura M, Mitsui A, Mori Y, et al. Identification of candidate genes involved in the radiosensitivity of esophageal cancer cells by microarray analysis. Dis Esophagus. 2008;21:288–97.
Chen MF, Fang FM, Lu CH, Lu MS, Chen WC, Lee KD, et al. Significance of nuclear accumulation of Foxo3a in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;71:1220–9.
Metzger R, Heukamp L, Drebber U, Bollschweiler E, Zander T, Hoelscher AH, et al. CUL2 and STK11 as novel response-predictive genes for neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy in esophageal cancer. Pharmacogenomics. 2010;11:1105–13.
Yang L, Cao Z, Li F, Post DE, Van Meir EG, Zhong H, et al. Tumor-specific gene expression using the survivin promoter is further increased by hypoxia. Gene Ther. 2004;11:1215–23.
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC. A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med. 1997;3:917–21.
Altieri DC. Survivin, versatile modulation of cell division and apoptosis in cancer. Oncogene. 2003;22:8581–9.
Wang Q, Wu PC, Roberson RS, Luk BV, Ivanova I, Chu E, et al. Survivin and escaping in therapy-induced cellular senescence. Int J Cancer. 2011;128:1546–58.
Stauber RH, Mann W, Knauer SK. Nuclear and cytoplasmic survivin: molecular mechanism, prognostic, and therapeutic potential. Cancer Res. 2007;67:5999–6002.
Altieri DC. Validating survivin as a cancer therapeutic target. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:46–54.
Rosato A, Pivetta M, Parenti A, Iaderosa GA, Zoso A, Milan G, et al. Survivin in esophageal cancer: an accurate prognostic marker for squamous cell carcinoma but not adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2006;119:1717–22.
Shariat SF, Karakiewicz PI, Godoy G, Karam JA, Ashfaq R, Fradet Y, et al. Survivin as a prognostic marker for urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: a multicenter external validation study. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:7012–9.
Altieri DC. Survivin, cancer networks and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:61–70.
Lei Y, Geng Z, Guo-Jun W, He W, Jian-Lin Y. Prognostic significance of survivin expression in renal cell cancer and its correlation with radioresistance. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010;344:23–31.
Freier K, Pungs S, Sticht C, Flechtenmacher C, Lichter P, Joos S, et al. High survivin expression is associated with favorable outcome in advanced primary oral squamous cell carcinoma after radiation therapy. Int J Cancer. 2007;120:942–6.
Shirai K, Suzuki Y, Oka K, Noda SE, Katoh H, Suzuki Y, et al. Nuclear survivin expression predicts poorer prognosis in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 2009;91:353–8.
Zhu HX, Wang YH, Zhou CQ, Zhang G, Bai JF, Quan LP, et al. Expression of survivin and its significance in esophageal cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2005;27:22–4. In Chinese.
Zhu HX, Liu S, Zhou CQ, Zhou XB, Zhang F, Quan LP, et al. Anti-apoptosis gene survivin promotes cell growth and transformation. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2002;82:338–40. in Chinese.
Lewis KD, Samlowski W, Ward J, Catlett J, Cranmer L, Kirkwood J, et al. A multi-center phase II evaluation of the small molecule survivin suppressor YM155 in patients with unresectable stage III or IV melanoma. Invest New Drugs. 2011;29:161–6.
Giaccone G, Zatloukal P, Roubec J, Floor K, Musil J, Kuta M, et al. Multicenter phase II trial of YM155, a small-molecule suppressor of survivin, in patients with advanced, refractory, non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4481–6.
Tanioka M, Nokihara H, Yamamoto N, Yamada Y, Yamada K, Goto Y, et al. Phase I study of LY2181308, an antisense oligonucleotide against survivin, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011;68:505–11.
Ikeguchi M, Kaibara N. Survivin messenger RNA expression is a good prognostic biomarker for oesophageal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2002;87:883–7.
Takeno S, Yamashita S, Takahashi Y, Ono K, Kamei M, Moroga T, et al. Survivin expression in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: its prognostic impact and splice variant expression. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2010;37:440–5.
Grabowski P, Kühnel T, Mühr-Wilkenshoff F, Heine B, Stein H, Höpfner M, et al. Prognostic value of nuclear survivin expression in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2003;88:115–9.
Vallböhmer D, Kuhn E, Warnecke-Eberz U, Brabender J, Hoffmann AC, Metzger R, et al. Failure in downregulation of intratumoral survivin expression following neoadjuvant chemoradiation in esophageal cancer. Pharmacogenomics. 2008;9:681–90.
Warnecke-Eberz U, Hokita S, Xi H, Higashi H, Baldus SE, Metzger R, et al. Overexpression of survivin mRNA is associated with a favorable prognosis following neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy in esophageal cancer. Oncol Rep. 2005;13:1241–6.
Capalbo G, Dittmann K, Weiss C, Reichert S, Hausmann E, Rödel C, et al. Radiation-induced survivin nuclear accumulation is linked to DNA damage repair. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;77:226–34.
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Mingrong Wang for the EC9706 cell line. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation (30370732, 81021061), Capital Foundation for Medical Research and Development (2007–2022), National Nonprofit Institute Research Grant of CAMS (JK2007B11) and 863 Project Grant 2006AA02A403, People's Republic of China.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, H., Wang, Q., Hu, C. et al. High expression of survivin predicts poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma following radiotherapy. Tumor Biol. 32, 1147–1153 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-011-0217-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-011-0217-y