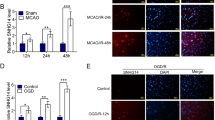
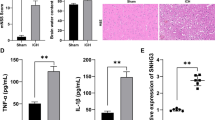
Abstract
Background
Cerebral apoplexy is currently the main cause of mortality and disability globally. LncRNAs play important roles in the pathophysiological process of cerebral apoplexy and the effect of LncRNA SNHG14 on cerebral apoplexy remain unclear.
Objective
Here, we investigated the biological function of LncRNA SNHG14 in cerebral apoplexy and underlying molecular mechanisms.
Results
Patients with cerebral apoplexy and normal volunteers were collected. Mouse hippocampal (HT-22) cells were then placed into a hypoxic incubator with 1% O2, 5% CO2, and 94% N2 for cerebral apoplexy. LncRNA SNHG14 was overexpressed in patients with cerebral apoplexy. LncRNA SNHG14 was found to induce inflammation in vitro model of cerebral apoplexy via the inhibition of miR-124-3p/TRAF6 axis. In addition, the down-regulation of LncRNA SNHG14 reduced inflammation in vitro model of cerebral apoplexy via the induction of miR-124-3p/TRAF6 axis.
Conclusion
LncRNA SNHG14 plays a crucial role in inflammation of cerebral apoplexy by miR-124-3p/TRAF6 axis, thereby it may be a promising therapeutic target for cerebral apoplexy.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajoolabady A, Wang S, Kroemer G et al (2021) Targeting autophagy in ischemic stroke: from molecular mechanisms to clinical therapeutics. Pharmacol Ther. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107848
Chen L, Kong L, Wei X et al (2019) β-arrestin 2 negatively regulates NOD2 signalling pathway through association with TRAF6 in microglia after cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury. J Cell Mol Med 23:3325–3335
Dou Y, Tian X, Zhang J, Wang Z, Chen G (2018) Roles of TRAF6 in central nervous system. Curr Neuropharmacol 16:1306–1313
Fathy N, Kortam MA, Shaker OG, Sayed NH (2021) Long Noncoding RNAs MALAT1 and ANRIL gene variants and the risk of cerebral ischemic stroke: an association study. ACS Chem Neurosci 12:1351
Gu Y, Sainburg LE, Kuang S et al (2021) Brain activity fluctuations propagate as waves traversing the cortical hierarchy. Cereb Cortex 31:3986
Hill MD (2021) In imaging-selected ischemic stroke with unknown onset, alteplase increases favorable outcomes and death at 90 d. Ann Intern Med 174:42
Hu C, Li C, Ma Q et al (2021) Inhibition of long noncoding RNA SNHG15 ameliorates hypoxia/ischemia-induced neuronal damage by regulating miR-302a-3p/STAT1/NF-κB axis. Yonsei Med J 62:325–337
Huo Y, Zhang K, Zhang T, Han Y, Hu Z (2021) MiR-124-3p alleviates the dezocine tolerance against pain by regulating TRAF6 in a rat model. NeuroReport 32:44–51
Jia Y, Yi L, Li Q, Liu T, Yang S (2021) LncRNA MALAT1 aggravates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis via the miR-195a-5p/HMGA1 axis. Biol Res 54:8
Kuang Y, Zheng X, Zhang L et al (2020) Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce autophagy in stroke mice by extracellular vesicle transfer of miR-25. J Extracell Vesicles 10:e12024
Li K, Shen L, Zheng P et al (2021) Identification of MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers for detecting ischemic stroke. Genes Genom 5:1
Lv H, Li J, Che Y (2021) miR-31 from adipose stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promotes recovery of neurological function after ischemic stroke by inhibiting TRAF6 and IRF5. Exp Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113611
Ma J, Cao X, Chen F et al (2021) Exosomal microRNAs contribute to cognitive impairment in hypertensive patients by decreasing frontal cerebrovascular reactivity. Front Neurosci 15:614220
Neurology branch of Chinese Medical Association, cerebrovascular disease group of Neurology branch of Chinese Medical Association (2018) Chinese guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute ischemic stroke, 2018. Chin J Neurol 51(9):666–682
Peng L, Zhou Y, Jiang N et al (2020) DJ-1 exerts anti-inflammatory effects and regulates NLRX1-TRAF6 via SHP-1 in stroke. J Neuroinflamm 17:81
Pu Z, Xu M, Yuan X, Xie H, Zhao J (2020) Circular RNA circCUL3 accelerates the warburg effect progression of gastric cancer through regulating the STAT3/HK2 axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 22:310–318
Reynen S, Schlossbauer M, Hubauer U et al (2021) Urinary N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide: prognostic value in patients with acute chest pain. ESC Heart Fail 8:2293
Shvedova M, Islam MR, Armoundas AA, Anfinogenova ND, Wrann CD, Atochin DN (2021x) Modified middle cerebral artery occlusion model provides detailed intraoperative cerebral blood flow registration and improves neurobehavioral evaluation. J Neurosci Methods 358:109179
Vasudeva K, Dutta A, Munshi A (2021) Role of lncRNAs in the development of ischemic stroke and their therapeutic potential. Mol Neurobiol 5:1–17
Wang F, Wang Q, Liu B et al (2021a) The long noncoding RNA synage regulates synapse stability and neuronal function in the cerebellum. Cell Death Differ 24:1
Wang X, HuangFu C, Zhu X et al (2021b) Exosomes and exosomal microRNAs in age-associated stroke. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570161119666210208202621
Xue Q, Yang L, Wang H, Han S (2021) Silence of long noncoding RNA SNHG14 alleviates ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury by regulating miR-124-3p/MMP2 axis. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8884438
Yan W, Sun W, Fan J et al (2020) Sirt1-ROS-TRAF6 signaling-induced pyroptosis contributes to early injury in ischemic mice. Neurosci Bull 36:845–859
Zhang G, Li T, Chang X, Xing J (2021a) Long noncoding RNA SNHG14 promotes ischemic brain injury via regulating miR-199b/AQP4 axis. Neurochem Res 46:1280–1290
Zhang B, Shen J, Zhong Z, Zhang L (2021b) PKM2 aggravates cerebral ischemia reperfusion-induced neuroinflammation via TLR4/MyD88/TRAF6 signaling pathway. NeuroImmunoModulation 28:29
Zhang Z, Zou X, Zhang R et al (2021c) Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal miR-146a-5p reduces microglial-mediated neuroinflammation via suppression of the IRAK1/TRAF6 signaling pathway after ischemic stroke. Aging (albany NY) 13:3060–3079
Zhuo Y, Chen W, Li W et al (2021) Ischemic-hypoxic preconditioning enhances the mitochondrial function recovery of transplanted olfactory mucosa mesenchymal stem cells via miR-181a signaling in ischemic stroke. Aging (albany NY) 13:11234
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University Research Fund (No. 2014B24).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FL contributed to data analysis, drafting or revising the article, gave final approval of the version to be published, and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Fang Li declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All the samples were obtained following patients’ written consent and approval by the Ethics Committee of The First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F. LncRNA SNHG14 promoted inflammation of cerebral apoplexy by miR-124-3p/TRAF6 axis. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 18, 233–241 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-021-00197-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-021-00197-8