Abstract
Background
Inflammation and oxidative stress-induced molecular death are one of the important causes for lung injury in critically ill patients. LKB1 is an important protein kinase in the body and has regulated inflammation and oxidative stress. However, LKB1 control inflammation and oxidative stress in lung injury were unclear.
Objective
We aimed to investigate the function and mechanism of Liver kinase B1 (LKB1) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced lung injury.
Result
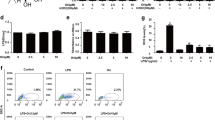
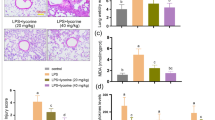
LKB1 prevented lung injury, and weakened correlation oxidative stress and inflammatory reaction in LPS-induced mice model of lung injury. Up-regulation of LKB1 reduced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and it-induced oxidative stress, and weakened inflammatory reactions in LPS-induced lung injury A549 cells. Down-regulation of LKB1 increased ROS production and it-induced oxidative stress, and enhanced inflammatory reactions in LPS-induced lung injury A549 cells. LKB1 induced phosphorylation (p)-AMPK protein expression, and suppressed the protein expression of NLRP3 in LPS-induced mice model of lung injury and in LPS-induced lung injury A549 cells. This experiment demonstrated the inhibition of AMPK or activation of NLRP3 inflammasome reversed the anti-inflammation function of LKB1 in LPS-induced lung injury. Meanwhile, ROS-induced oxidative stress also participated in the anti-inflammation effects of LKB1 in LPS-induced lung injury.
Conclusion
Therefore, our results indicate that LKB1 reduced inflammation and oxidative stress by regulating the AMPK/NLRP3 signaling pathway in LPS-induced lung injury.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ak H, Gulsen I, Karaaslan T, Alaca İ, Candan A, Koçak H, Atalay T, Çelikbilek A, Demir İ, Yılmaz T (2015) The effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on inflammatory cytokines after acute spinal cord injury. Turk J Trauma Emerg Surg 21:96–101
Chengke L, Weiwei L, Xiyang W, Ping W, Xiaoyang P, Zhengquan X, Hao Z, Penghui Z, Wei P (2013) Effect of infliximab combined with methylprednisolone on expressions of NF-kappaB, TRADD, and FADD in rat acute spinal cord injury. Spine 38:E861-869
Comegna M, Succoio M, Napolitano M, Vitale M, D’Ambrosio C, Scaloni A, Passaro F, Zambrano N, Cimino F, Faraonio R (2014) Identification of miR-494 direct targets involved in senescence of human diploid fibroblasts. FASEB J 28:3720–3733
Hsieh SM, Wang YH, Chang SC, Huang TS (2009) Low dose HIV-1 Tat improves the defective nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activity of dendritic cells from persons with spinal cord injury. Cell Immunol 257:105–110
Hu HQ, Sun LG, Guo WJ (2016) Decreased miRNA-146a in glioblastoma multiforme and regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis by target Notch1. Int J Biol Mark 31:e270-275
Impellizzeri D, Ahmad A, Di Paola R, Campolo M, Navarra M, Esposito E, Cuzzocrea S (2015) Role of Toll like receptor 4 signaling pathway in the secondary damage induced by experimental spinal cord injury. Immunobiology 220:1039–1049
Kang N, Hai Y, Yang J, Liang F, Gao CJ (2015) Hyperbaric oxygen intervention reduces secondary spinal cord injury in rats via regulation of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:1141–1153
Kang L, Yang C, Song Y, Zhao K, Liu W, Hua W, Wang K, Tu J, Li S, Yin H, Zhang Y (2017) MicroRNA-494 promotes apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation in degenerative human nucleus pulposus cells. Oncotarget 8:27868–27881
Kim Y, Jo SH, Kim WH, Kweon OK (2015b) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of intravenously injected adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells in dogs with acute spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther 6:229
Kim DI, Lee H, Lee BS, Kim J, Jeon JY (2015a) Effects of a 6-week indoor hand-bike exercise program on health and fitness levels in people with spinal cord injury: a randomized controlled trial study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 96:2033–20402031
Kuang X, Huang Y, Gu HF, Zu XY, Zou WY, Song ZB, Guo QL (2012) Effects of intrathecal epigallocatechin gallate, an inhibitor of Toll-like receptor 4, on chronic neuropathic pain in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 676:51–56
Liang Q, Wu Q, Jiang J, Wang C, Smith MD, Lu H, Wang Q, Nagarkatti P, Fan D (2011) Characterization of sparstolonin B, a Chinese herb-derived compound, as a selective Toll-like receptor antagonist with potent anti-inflammatory properties. J Biol Chem 286:26470–26479
Luo H, Yang R, Li C, Tong Y, Fan L, Liu X, Xu C (2017) MicroRNA-139-5p inhibits bladder cancer proliferation and self-renewal by targeting the Bmi1 oncogene. Tumour Biol J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med 39:1010428317718414
Mi L, Li Y, Zhang Q, Zhao C, Peng Y, Yang G, Zheng X (2015b) MicroRNA-139–5p regulates C2C12 cell myogenesis through blocking Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem Cell Biol 93:8–15
Mi L, Chen Y, Zheng X, Li Y, Zhang Q, Mo D, Yang G (2015a) MicroRNA-139-5p suppresses 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation through notch and IRS1/PI3K/Akt insulin signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem 116:1195–1204
Pfarr N, Sinn HP, Klauschen F, Flechtenmacher C, Bockmayr M, Ridinger K, von Winterfeld M, Warth A, Lorenz K, Budczies J, Penzel R, Lennerz JK, Endris V, Weichert W, Stenzinger A (2016) Mutations in genes encoding PI3K-AKT and MAPK signaling define anogenital papillary hidradenoma. Genes Chromosom Cancer 55:113–119
Pontillo A, Brandao L, Guimaraes R, Segat L, Araujo J, Crovella S (2010) Two SNPs in NLRP3 gene are involved in the predisposition to type-1 diabetes and celiac disease in a pediatric population from northeast Brazil. Autoimmunity 43:583–589
Schoultz I, Verma D, Halfvarsson J, Törkvist L, Fredrikson M, Sjöqvist U, Lördal M, Tysk C, Lerm M, Söderkvist P, Söderholm JD (2009) Combined polymorphisms in genes encoding the inflammasome components NALP3 and CARD8 confer susceptibility to Crohn’s disease in Swedish men. Am J Gastroenterol 104:1180–1188
Wang M, Xiu L, Diao J, Wei L, Sun J (2015) Sparstolonin B inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 769:79–85
Wang J, Yu Z, Wang C, Tian X, Huo X, Wang Y, Sun C, Feng L, Ma J, Zhang B, Yang Q, Ma X, Xu Y (2017) Dehydrocostus lactone, a natural sesquiterpene lactone, suppresses the biological characteristics of glioma, through inhibition of the NF-kappaB/COX-2 signaling pathway by targeting IKKbeta. Am J Cancer Res 7:1270–1284
Xu JM, Tao LJ, Fu D, Lv ZP, Li L, Dai RP (2008) Activation of interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) signaling in the spinal cord in the rats with experimental cardiac injury. Int J Cardiol 128:413–418
Zhan MN, Yu XT, Tang J, Zhou CX, Wang CL, Yin QQ, Gong XF, He M, He JR, Chen GQ, Zhao Q (2017) MicroRNA-494 inhibits breast cancer progression by directly targeting PAK1. Cell Death Dis 8:25 e29
Zhang YK, Liu JT, Peng ZW, Fan H, Yao AH, Cheng P, Liu L, Ju G, Kuang F (2013) Different TLR4 expression and microglia/macrophage activation induced by hemorrhage in the rat spinal cord after compressive injury. J Neuroinflamm 10:112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guarantor of integrity of the entire study: YY; MZ. Study concepts: YY; MZ. Study design: YY; MZ. Definition of intellectual content: YY; MZ. Literature research: YY; MZ. Clinical studies: YY; LZ; YC; NF; JT; HX. Experimental studies: YY; MZ. Data acquisition: YC; HX. Data analysis: YC; HX. Statistical analysis: MZ; NF; JT. Manuscript preparation: YY; MZ; LZ. Manuscript editing: YY; MZ; LZ. Manuscript review: YY; MZ; LZ.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Yifeng Yue, Liwu Zong, Yongmin Chen, Nianhai Feng, Junxia Tang, Hongyu Xu and Meiling Zhao declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Zibo Central Hospital.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, Y., Zong, L., Chen, Y. et al. Liver kinase B1 (LKB1) reduced inflammation and oxidative stress by regulating the AMPK/NLRP3 signaling pathway in LPS-induced lung injury. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 17, 385–395 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-021-00142-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-021-00142-9