Abstract
Backgrounds
Interleukin (IL)-18, a member of the IL-1 family, has been implicated in the development of a variety of inflammatory skin diseases. The binding of double-stranded (ds) DNA to absent in melanoma (AIM) 2 induces the oligomerization of apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a caspase recruitment domain (ASC) and the recruitment of pro-caspase-1, which leads to the activation of caspase-1, subsequently resulting in the secretion of IL-1β and IL-18. Curcumin is a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound in Curcuma longa and is also well known to have anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. In the current study, we focused on the inhibitory effect of curcumin on ASC oligo-merization in human keratinocytes.
Methods
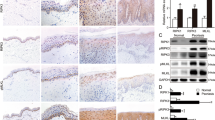
The IL-18 level was measured by using an ELISA kit. The protein levels of AIM2 inflammasome components, such as AIM2, ASC, and pro-caspase-1, were determined by using a western blot. The level of ASC oligomerization was also determined by using a western blot.
Results
Our results show pre-treatment with curcumin attenuated poly (dA:dT)-induced secretion of IL-18 in IFN-γ-primed human keratinocytes. Pre-treatment with 10 µM curcumin was also found to inhibit ASC oligomerization in IFN-γ-primed cells.
Conclusion
These collective results show that curcumin inhibits the poly (dA:dT)-induced secretion of IL-18 via the suppression of ASC oligomerization in IFN-γ-primed human keratinocytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakanishi, K., Yoshimoto, T., Tsutsui, H. & Okamura, H. Interleukin-18 regulates both Th1 and Th2 responses. Annu Rev Immunol 19, 423–474 (2001).
Lee, J. H., Cho, D. H. & Park, H. J. IL-18 and Cutaneous Inflammatory Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 16, 29357–29369 (2015).
Fernandes-Alnemri, T., Yu, J. W., Datta, P., Wu, J. & Alnemri, E. S. AIM2 activates the inflammasome and cell death in response to cytoplasmic DNA. Nature 458, 509–513 (2009).
Hornung, V. et al. AIM2 recognizes cytosolic dsDNA and forms a caspase-1-activating inflammasome with ASC. Nature 458, 514–518 (2009).
de Koning, H. D. et al. Strong induction of AIM2 expression in human epidermis in acute and chronic inflammatory skin conditions. Exp Dermatol 21, 961–964 (2012).
Kopfnagel, V., Wittmann, M. & Werfel, T. Human keratinocytes express AIM2 and respond to dsDNA with IL-1beta secretion. Exp Dermatol 20, 1027–1029 (2011).
Yun, M., Seo, G., Lee, J.-Y., Chae, G. T. & Lee, S.-B. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuates the AIM2-induced secretion of IL-1β in human epidermal keratinocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 467, 723–729 (2015).
Lee, K. M., Kang, J. H., Yun, M. & Lee, S. B. Quercetin inhibits the poly (dA:dT)-induced secretion of IL-18 via down-regulation of the expressions of AIM2 and pro-caspase-1 by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT1 pathway in IFN-gamma-primed human keratinocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503, 116–122 (2018).
Bauernfeind, F. et al. Cutting edge: reactive oxygen species inhibitors block priming, but not activation, of the NLRP3 inflammasome. J Immunol 187, 613–617 (2011).
Hewlings, S. J. & Kalman, D. S. Curcumin: A Review of Its’ Effects on Human Health. Foods 6, E92 (2017).
Gupta, S. C., Patchva, S. & Aggarwal, B. B. Therapeutic roles of curcumin: lessons learned from clinical trials. Aaps J 15, 195–218 (2013).
Yin, H. et al. Curcumin Suppresses IL-1beta Secretion and Prevents Inflammation through Inhibition of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. J Immunol 200, 2835–2846 (2018).
Tozser, J. & Benko, S. Natural Compounds as Regulators of NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated IL-1beta Production. Mediators Inflamm 2016, 5460302 (2016).
Kong, F. et al. Curcumin Represses NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB and P2X7R Signaling in PMA-Induced Macrophages. Front Pharmacol 7, 369 (2016).
Petrilli, V. et al. Activation of the NALP3 inflammasome is triggered by low intracellular potassium concentration. Cell Death Differ 14, 1583–1589 (2007).
Fernandes-Alnemri, T. et al. The AIM2 inflammasome is critical for innate immunity to Francisella tularensis. Nat Immunol 11, 385–393 (2010).
Ablasser, A. et al. RIG-I-dependent sensing of poly (dA:dT) through the induction of an RNA polymerase III-transcribed RNA intermediate. Nat Immunol 10, 1065–1072 (2009).
Pfeffer, L. M. The role of nuclear factor kappaB in the interferon response. J Interferon Cytokine Res 31, 553–559 (2011).
Khan, M. A., Gahlot, S. & Majumdar, S. Oxidative stress induced by curcumin promotes the death of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (HuT-78) by disrupting the function of several molecular targets. Mol Cancer Ther 11, 1873–1883 (2012).
Coll, R. C., Robertson, A., Butler, M., Cooper, M. & O’Neill, L. A. The cytokine release inhibitory drug CRID3 targets ASC oligomerisation in the NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasomes. PLoS One 6, e29539 (2011).
Jin, T. et al. Structures of the HIN domain:DNA complexes reveal ligand binding and activation mechanisms of the AIM2 inflammasome and IFI16 receptor. Immunity 36, 561–571 (2012).
Wang, P. H. et al. Inhibition of AIM2 inflammasome activation by a novel transcript isoform of IFI16. EMBO Rep 19, e45737 (2018).
Fernandes-Alnemri, T. et al. The pyroptosome: a supra-molecular assembly of ASC dimers mediating inflammatory cell death via caspase-1 activation. Cell Death Differ 14, 1590–1604 (2007).
Liu, H., Danthi, S. J. & Enyeart, J. J. Curcumin potently blocks Kv1.4 potassium channels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 344, 1161–1165 (2006).
Arechiga-Figueroa, I. A., Delgado-Ramirez, M., Moran-Zendejas, R. & Rodriguez-Menchaca, A. A. Modulation of Kv2.1 channels inactivation by curcumin. Pharmacol Rep 67, 1273–1279 (2015).
Banderali, U. et al. Curcumin blocks Kv11.1 (erg) potassium current and slows proliferation in the infant acute monocytic leukemia cell line THP-1. Cell Physiol Bio-chem 28, 1169–1180 (2011).
Hwang, I. et al. Non-transcriptional regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome signaling by IL-4. Immunol Cell Biol 93, 591–599 (2015).
Prasad, S., Tyagi, A. K. & Aggarwal, B. B. Recent developments in delivery, bioavailability, absorption and metabolism of curcumin: the golden pigment from golden spice. Cancer Res Treat 46, 2–18 (2014).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from Korea Centers for Disease Control & Prevention, Korea Ministry of Health & Welfare (5-2018-A0082-00005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
Yujin Lee, Junghoon Kang, Mihee Yun and Seong-Beom Lee declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
The article does not contain any studies with human and animal and this study was performed following institutional and national guidelines.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y., Kang, J., Yun, M. et al. Curcumin inhibits poly(dA:dT)-induced IL-18 secretion by inhibiting the ASC oligomerization in human keratinocytes. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 15, 399–406 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-019-0043-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-019-0043-7