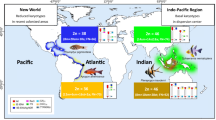
Abstract
Cardinal fishes (Apogonidae) belong to the numerically dominating reef fish families. Many species are kept in the aquarium and are popular as small, peaceful, and colorful fish. The taxonomic status of this family remains debatable. Up to the present, there are 366 valid species. However, only 15 species were studied cytogenetically including one by molecular cytogenetics. Here we report characterization of four cardinal fishes, namely Fibramia lateralis, Pterapogon kauderni, Sphaeramia nematotera and S. orbicularis from the Gulf of Thailand using different cytogenomic approaches. Chromosome preparations from kidney were studied by conventional staining, Ag-NOR banding and molecular cytogenetics by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) using 18S rDNA and microsatellite d(CA)15 probes. Whereas, all species had the same diploid chromosome number as 2n = 46, but there were differences in the fundamental number (NF) and chromosome structure: F. lateralis (NF = 54; 8a + 38t), S. nematotera (NF = 74; 14sm + 14a + 18t), S. orbicularis (NF = 68; 8sm + 14a + 24t) and P.kauderni (NF = 92; 4 m + 14sm + 28a). In all four species, NORs and 18S rDNA signals were detected adjacent to the telomere on the short arm of an acrocentric chromosome pair, but on different chromosome pairs, as 2, 10, 7 and 13 in F. lateralis, S. nematotera,S. orbicularis and P.kauderni, respectively. Also, microsatellite d(CA)15 sequences showed specific hybridization patterns along the chromosomes of the four studied species. Accordingly, all four Apogonidae species studied were clearly distinguishable by cytogenetic and molecular hybridization procedures. Further studies with more species are needed to explore their systematic status in the family




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida-Toledo LF, Ozouf-Costaz C, Foresti F, Bonillo C, Porto-Foresti F, Daniel-Silva MFZ. Conservation of the 5S-bearing chromosome pair and co–localization with major rDNA clusters in five species of Astyanax (Pisces, Characidae). Cytogenet Genome Res. 2002;97:229–33. https://doi.org/10.1159/000066609.
Alvarez MC, Otis J, Amores A, Guise K. Short-term cell culture technique for obtaining chromosomes in marine and freshwater fish. J Fish Biol. 1991;39:817–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1991.tb04411.x.
Arai R. Fish karyotypes a check list. Tokyo: Springer Press; 2011.
Araújo WC, Martínez PA, Molina WF. Mapping of ribosomal DNA by FISH, EcoRI digestion and replication bands in the cardinalfish Apogon americanus(Perciformes). Cytologia. 2010;75:109–17. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.75.109.
Chaiyasut K. Cytogenetics and Cytotaxonomy of the Family Zephyranthes. Department of Botany, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok. 1989; [In Thai]
Cioffi MB, Bertollo LAC. Distribution and evolution of repetitive DNAs in fish. Repetitive DNA Karger Genome Dyn Basel. 2012;7:197–221. https://doi.org/10.1159/000337950.
Cioffi MB, Martins C, Bertollo LAC. Comparative chromosome mapping of repetitive sequences. Implications for genomic evolution in the fish. Hopliasmalabaricus BMCGenet. 2009;10:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-10-34.
Cioffi MB, Bertollo Martins C, LAC. . Chromosomal spreading of associated transposable elements and ribosomal DNA in the fish Erythrinuserythrinus. Implications for genome change and karyoevolution in fish. BMC Evol Biol. 2010;10:271. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-10-271.
Cioffi MB, Bertollo LAC, Villa MA, de Oliveira EA, Tanomtong A, Yano CF, Supiwong W, Chaveerach A. Genomic organization of repetitive DNA elements and its implications for the chromosomal evolution of Channid fishes (Actinopterygii, Perciformes). PLoS ONE. 2015;10(6):e0130199. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0130199.
Cross I, Merlo A, Manchado M, Infante C, Cañavate JP. Rebordinos L. Cytogenetic characterization of the sole Solea senegalensis (Teleostei: Pleuronectiformes: Soleidae): Ag-NOR, (GATA)n, (TTAGGG)n and ribosomal genes by one-color and two-color FISH. Genetica. 2006;128:253–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-005-5928-9.
Eschmeyer WN, Fong JD. Species by family/subfamily. On-line Updated 30 April 2018, ]Accessed 23 May 2018] http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/SpeciesByFamily.asp.
Eschmeyer WN, Fricke R, Laan R. van der (eds). Catalog of fishes: Genera, Species, References. On-line Updated 2 July 2018 [Accessed 3 July 2018]http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp.
Fontana F, Lanfredi M, Congiu L, Leis M, Chicca M, Rossi R. Chromosomal mapping of 18S–28S and 5S rRNA genes by two-colour fluorescent in situ hybridization in six sturgeon species. Genome. 2003;46:473–7. https://doi.org/10.1139/g03-007.
Getlekha N, Cioffi MB, Maneechot N, Bertollo LAC, Supiwong W, Tanomtong A. Contrasting evolutionary paths among Indo-Pacific Pomacentrus species promoted by extensive pericentric inversions and genome organization of repetitive sequences. Zebrafish. 2018;15(1):45–54. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2017.1484.
Getlekha N, Cioffi MB, Yano CF, Maneechot N, Bertollo LAC, Supiwong W, et al. Chromosome mapping of repetitive DNAs in sergeant major fishes (Abudefdufinae, Pomacentridae): a general view on the chromosomal conservatism of the genus. Genetica. 2016;144(5):567–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-016-9925-y.
Getlekha N, Molina WF, Cioffi MB, Yano CF, Maneechot N, Bertollo LAC, Supiwong W, Tanomtong A. Repetitive DNAs highlight the role of chromosomal fusions in the karyotype evolution of Dascyllus species (Pomacentridae, Perciformes). Genetica. 2016;144(2):203–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-016-9890-5.
Hatanaka T, Galetti PM Jr. Mapping of the 18S and 5S ribosomal RNA genes in the fish Prochilodus argenteus Agassiz, 1829 (Characiformes, Prochilodontidae). Genetica. 2004;122:239–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-004-2039-y.
Howell WM, Black DA. Controlled silver–staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: a 1-step method. Experientia. 1980;36:1014–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01953855.
Hsu TC, Patak S, Chen TR. The possibility of latent centromeres and a proposed nomenclature system for total chromosome and whole arm translocations. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1975;15:41–9. https://doi.org/10.1159/000130497.
Johnson GD, Gill AC, Paxton JR, Eschmeyer WN, editors. Encyclopedia of Fishes. San Diego: Academic Press; 1998.
Kasiroek W, Indananda C, Luangoon N, Pinthong K, Supiwong W, Tanomtong A. First chromosome analysis of the Humpback cardinalfish, Fibramia lateralis (Perciformes, Apogonidae). Cytologia. 2017;82(1):9–15. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.82.9.
Kasiroek W, Indananda C, Pinthong K, Supiwong W, Tanomtong A. NOR polymorphism and chromosome analysis of Banggai cardinalfish, Pterapogonkauderni (Perciformes, Apogonidae). Cytologia. 2017;82(1):17–23. https://doi.org/10.1508/cytologia.82.17.
Kubat Z, Hobza R, Vyskot B, Kejnovsky E. Microsatellite accumulation in the Y chromosome of Silene latifolia. Genome. 2008;51:350–6. https://doi.org/10.1139/G08-024.
Mabuchi K, Fraser TH, Song H, Azuma Y, Nishida M. Revision of the systematics of the cardinalfishes (Percomorpha: Apogonidae) based on molecular analyses and comparative reevaluation of morphological characters. Zootaxa. 2014;3846(2):151–203. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3846.2.1.
Maneechot N, Yano CF, Bertollo LAC, Getlekha N, Molina WF, Ditcharoen S, et al. Genomic organization of repetitive DNAs highlights chromosomal evolution in the genus Clarias (Clariidae, Siluriformes). Mol Cytogenet. 2016;9:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13039-016-0215-2.
Murofushi M. A study of karyotype classification and karyotype evolution in marine teleosts. Rep Mishima Res Inst Sci Liv Nihon Univ . 1986;9:95–157.
Murofushi M, Oishi M, Nawa N. Karyological studies in Apogonsemilineatus. Rep Mishima Res Inst Sci Liv Nihon Univ. 1980;3:47–50.
Nelson JS. Fishes of the World. 4th ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 2006.
Ojima Y, Kojima T. Chromosomal polymorphisms in Apogonidae fishes. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 1985;61:79–82.
Pinkel D, Straume T, Gray J. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America.1986; 83: 29–34.
Rishi KK. A preliminary report on the karyotypes of eighteen marine fishes. Res Bull Punjab Univ. 1973;24:161–2.
Rivlin KA, Dale G, Rachlin JW. Karyotypic analysis of three species of cardinalfish (Apogonidae)and its implications for the taxonomic status of the genera Apogon and Phaeoptyx. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;463:211–3. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb21549.x.
Rivlin KA, Rachlin JW, Dale G. Intraspecific chromosomal variation in Apogonbinotatus(Perciformes: Apogonidae)from the Florida Keys and St.Croix.Ann. N. Y. Acad Sci. 1987;494:263–5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb29542.x.
Rivlin KA, Rachlin JW, Warkentine BE. G-Banding of the chromosomes of Apogonmaculates and A. pseudomaculatus (Perciformes:Apogonidae). Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;529:160–3. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb51448.x.
Rooney DE. Human cytogenetics: constutitional analysis: a practical approach. 3rd ed. London: Oxford University Press; 2001.
Rosa R, Bellafronte E, Moreira-Filho O, Margarido VP. Constitutive heterochromatin, 5S and 18S rDNA genes in Apareiodon sp. (Characiformes, Parodontidae) with a ZZ/ZW sex chromosome system. Genetica. 2006;128:159–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-005-5700-1.
Schmidt M. Chromosome banding in Amphibia. II. Constitutive heterochromatin and nucleolus organizer regions in Ranidae, Microhylidae and Racophoridae. Chromosoma. 1978;68:131–48.
Supiwong W, Jiwyam W, Sreeputhorn K, Maneechot N, Bertollo LAC, Cioffi MB, Getlekha N, et al. First reports on classical and molecular cytogenetics of archerfish, Toxoteschatareus(Perciformes: Toxotidae). Nucleus (India). 2017;60(3):349–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-017-0216-5.
Supiwong W, LiehrT Cioffi MB, Chaveerach A, KosyakovaN Fan X, Tanee T, Tanomtong A. Comparative cytogenetic mapping of rRNA genes among naked catfishes: implications for genomic evolution in the Bagridae family. Genet Mol Res. 2014;13(4):9533–42. https://doi.org/10.4238/2014.November.12.2.
Supiwong W, LiehrT Cioffi MB, Chaveerach A, KosyakovaN Pinthong K, Tanee T, Tanomtong A. Chromosomal evolution in naked catfishes (Bagridae, Siluriformes): a comparative chromosome mapping study. Zool Anz. 2014;253:316–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcz.2014.02.004.
Suzuki H, Kurihara Y, Kanemisha Y, Moriwaki K. Variation in the distribution of silver-staining nucleolar organizer regions on the chromosomes of the wild mouseMus musculus. Mol Biol Evol. 1990;7:271–82. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040598.
Turpin R, Lejeune J. Les chromosomes humains. Paris: Gauthier-Pillars; 1965.
Volff NJ. Sex determination in fish. Genome Biol. 2002. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2002-3-9-reports0052.
Wasko AP, Galetti PM Jr. Mapping 18S ribosomal genes in fish of the genus Brycon (Characidae) by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Genet Mol Biol. 2000;23(1):135–8. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572000000100025.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Research grant of Burapha University through National Research Council of Thailand (Grant No. 158/2560), Unit of Excellence 2021 on Genetic diversity assessment of widely distributed aquatic animals and herpetology from Thailand (UoE64003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The Animal Ethics Committee of Burapha University based on the Ethic of Animal Experimentation of National Research Council of Thailand, ID#19/ 2558.
Consent to participate
Yes.
Consent for publication
Yes.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Corresponding Editor: RN Chatterjee
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kasiroek, W., Phimphan, S., Pinthong, K. et al. Comparative cytogenomic analysis of Cardinal fishes (Perciformes, Apogonidae) from Thailand. Nucleus 65, 57–66 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-021-00352-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-021-00352-5