Abstract
In this study, a cDNA library was constructed from the total RNA of sweet potato leaves. A total of 789 copies of the cDNA were cloned in Escherichia coli by employing the pGEM-T Easy vector. Sequencing was carried out by Solgent Co. (Korea). As many as 579 expressed sequence tag–simple sequence repeat (EST-SSR) markers were designed (73.38%) from the known cDNA nucleotide base sequences. The lengths of the developed EST-SSR markers ranged from 100 to 499 bp (average length 238 bp). Their motif sequence types were varied, with most being dinucleotides and pentanucleotides, and the most commonly found motifs were CAGAAT (29.0%) and TCT (2.8%). Based on these SSR-containing sequences, 619 pairs of high-quality SSR primers were designed using WebSat and Primer3web. The total number of primers designed was 144. Polymorphism was evident in 82 EST-SSR markers among 20 Korean sweet potato cultivars tested and in 90 EST-SSR markers in the two parents of a mapping population, Yeseumi and Annobeny. In this study, the hexaploid sweet potato (2n = 6x = 90) EST-SSR markers were developed in the absence of full-sequence data. Moreover, by acting as a molecular tag for particular traits, the EST-SSR marker can also simultaneously identify information about the corresponding gene. These EST-SSR markers will allow the molecular analysis of sweet potato to be done more efficiently. Thus, we can develop high-quality sweet potato while overcoming the challenges from climate change and other unfavorable conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Sweet potato [Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.] is a hexaploid (2n = 6x = 90) plant that belongs to the family Convolvulaceae (Ting and Kehr 1953; Martin 1970). The tuberous root of sweet potato, which is involved in carbohydrate storage and vegetative propagation, is a unique organ that has value in biological research of organogenesis and evolution as well as importance in agriculture. In the future, more variations of sweet potato will be needed for its breeding, because despite its importance, this hexaploid crop is difficult to breed owing to the complexity of its genetics and the lack of genomic resources (Kriegner et al. 2003; Cervantes-Flores et al. 2008). Traditionally, phenotypic markers have been used to provide descriptors for identifying sweet potato cultivars (Huamán and Zhang 1997), but they are unreliable owing to their paucity and vulnerability to environmental influence. Molecular markers have great potential to speed up the process of developing improved cultivars; however, a little effort has been devoted to the development and application of molecular marker technology for the genetic improvement of sweet potato (Kriegner et al. 2003). Genetic markers offer a number of applications for sweet potato genetic improvement. The randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) technique developed in 1990 is a powerful molecular marker technique in genetics and plant breeding (Welsh and McClelland 1990; Williams et al. 1990). RAPD markers have been used on sweet potato to study genetic segregation and linkage (Thompson et al. 1997), construct DNA fingerprints (Connolly et al. 1994), and identify a gene for root-knot nematode resistance (Ukoskit et al. 1997). The amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) technique developed in 1995 (Vos et al. 1995) is based on the selective PCR amplification of small restriction fragments (80–400 bp) from a total digest of genomic DNA. In sweet potato, AFLP markers have been used to study genetic linkage maps (Kriegner et al. 2003; Cervantes-Flores et al. 2008) and to assess genetic diversity (Zhang et al. 2000). Expressed sequence tags (ESTs) can be used as a cost-effective and valuable source for the development of molecular markers, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and simple sequence repeats (SSRs). DNA SSRs are widely distributed in both noncoding and transcribed sequences, and are commonly known as genomic-SSRs and EST-SSRs (Morgante et al. 2002). SSRs are useful for many applications in plant genetics and breeding, such as for high-density linkage map construction, genetic diversity analysis, cultivar identification, and marker-assisted selection. However, it is still expensive, labor intensive, and time-consuming to develop genomic SSR markers. In contrast, EST-SSRs can be rapidly developed from an EST database at lower cost. Moreover, EST-SSRs can also lead to direct gene tagging for quantitative trait locus mapping of agronomically important traits and increase the efficiency of marker-assisted selection (Gupta and Rustgi 2004). In addition, EST-SSRs show a higher level of transferability to closely related species than do genomic SSR markers (Scott et al. 2000; Eujayl et al. 2004; Zhang et al. 2005; Saha et al. 2006) and can serve as anchor markers for comparative mapping and evolutionary studies (Varshney et al. 2005a, b). Breeding practices for improving the quality of sweet potato is ongoing worldwide, and the recent molecular markers developed for sweet potato have demonstrated good potential to be used in genetic selection (Wang et al. 2010).
Materials and methods
Plant materials
In this study, the 20 Korean sweet potato cultivars and two parents of a mapping population, Yeseumi and Annobeny, were provided by the Rural Development Administration (Jeollabuk, Korea) (Table 1).
DNA and RNA extraction
Total RNA was extracted from leaf tissue of sweet potato using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. In brief, RLT buffer (Qiagen) containing β-mercaptoethanol was thoroughly mixed with the sample. The mixture was then transferred to a QIAshredder spin column and centrifuged for 5 min. The supernatant was transferred to a new 1.5 mL tube and an equal volume of 70% ethyl alcohol was added. The mixture was immediately applied to an RNeasy spin column that was then centrifuged for 1 min at 13,000 rpm. The flow-through was discarded and the column was washed by adding 500 μL of RPE buffer (Qiagen) followed by centrifugation for 1 min at 13,000 rpm. The flow-through was again discarded and the washing process was repeated. Finally, the RNA was suspended in 30 μL of RNase-free water. The concentration of genomic DNA was checked using a Nano Drop 2000 spectrophotometer. The genomic DNA was extracted from leaf tissue of sweet potato using a modified cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide (CTAB) method. Samples of 20–100 mg of leaves were placed, respectively, in a 2 mL tube, containing a tungsten ball and frozen liquid nitrogen, for 5 min. The samples were then ground into powder using a TissueLyser apparatus (Qiagen) at 20 vibrations per second for 30 s. Next, 700 μL of 2× CTAB buffer (2% CTAB, 0.1 M Tris, pH 8.0, 1.4 M NaCl, 1% polyvinylpyrrolidone) was added to the tubes. The samples were then vortexed, after which the tubes were incubated in a water bath at 65 °C for 20 min. After removal from the water bath, 700 μL of phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol PCI (25:24:1) was added to the samples and the tubes were shaken for 20 min at room temperature before centrifugation. Next, 500 μL of the supernatant was removed to a new 1.5 mL tube and 350 μL of isopropanol was added. The tubes were then shaken for 5 min, followed by freezing at −72 °C for 2 h. Subsequently, the samples were melted slowly and centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 min. After discarding the supernatant, the pellet was dried at room temperature after washing two times in 70% ethanol. Finally, 20 μL of distilled water was added to each tube and the concentration of genomic DNA was checked using a Nano Drop 2000 spectrophotometer.
Construction of the cDNA library
The cDNA library was synthesized using a cDNA synthesis kit (TaKaRa, Shiga, Japan). In brief, 2000 ng of template RNA was added to a mixture composed of 4 μL of 5× 1st strand synthesis buffer, 1 μL of dNTP mixture (10 mM), 1 μL of RNase inhibitor (20 U/μL), 2 μL of oligo(dT)18 primer (1 μg/μL), and 1 μL of M-MLV reverse transcriptase, in a total volume of 20 μL. The mixture was then subjected to the following first-strand cDNA reaction conditions: room temperature for 10 min, 42 °C for 1 h, and 80 °C for 5 min. Next, the mixture was mixed with 30 μL of 5× 2nd strand synthesis buffer and 3 μL of dNTP mixture (10 mM), after which the volume was adjusted to 89 μL with nuclease-free water. Then, 2 μL of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I (20 U/μL) and 2 μL of E. coli RNase H/E. coli DNA ligase mixture were added, and the mixture was incubated at 16 °C for 2 h and 70 °C for 10 min. Subsequently, 4 μL of T4 DNA ligase (1 U/μL) was added to the solution and incubation was carried out at 37 °C for 10 min. The reaction was stopped by the addition of 12 μL of stop solution (0.2 M ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and 2 mg/mL glycogen, pH 8.0). To purify the cDNA, an equal volume of phenol:chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) was then added to the solution, after which the mixture was vortex-mixed and then centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 min. The upper layer was transferred to a new 1.5 mL tube and an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1) was added. The tube was stirred for 1 min and then centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 min. The upper layer was transferred to a new 1.5 mL tube and an equal volume of 4 M ammonium acetate was added, followed by an equal volume of isopropanol. Following incubation at −20 °C for 30 min, the mixture was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was subsequently removed, 1 mL of ethyl alcohol (70%) was added to the pellet, and the suspension was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 5 min. The cDNA was finally suspended in nuclease-free water. The cDNA was A-tailed in a total 10 μL reaction volume by adding 1 μL of 10× buffer, 0.6 μL of MgCl2 (25 mM), 0.4 μL of dATP (5 mM/μL), and 1 μL of Taq polymerase (5 U/μL). The mixture was incubated at 70 °C for 30 min and then purified using ethyl alcohol.
cDNA Library transformation to the vector
The cDNA library was ligated to the pGEM-T Easy vector (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) by mixing 50 ng of pGEM-T Easy Vector, 5 μL of 2× ligation buffer and 1 U of T4 DNA ligase in a 10 µL reaction volume. After ligation at room temperature for 1 h, 2 μL of the product and 50 μL of E. coli DH5α competent cells were mixed and incubated on ice for 20 min, followed by heat shock at 42 °C for 45 s and cooling on ice for 2 min. Then, 950 μL of Luria–Bertani (LB) broth was added and the cells were incubated at 37 °C for 90 min with shaking at 200 rpm. Subsequently, the culture was plated on LB agar containing 100 ppm ampicillin, 0.5 mM isopropyl β-d-1-thiogalactopyranoside, and 80 μg/mL X-Gal for 12 h at 37 °C. The positive colonies identified after blue-white selection were cultured in 5 mL of LB broth at 37 °C for 16 h with shaking at 180 rpm. Following incubation, the culture was centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 10 min and the plasmid DNA was extracted using a QIAprep Spin Miniprep Kit (Qiagen). After removing the supernatant, the cell pellet was suspended in 250 μL of P1 buffer and transferred to a 1.5 mL tube. Next, 250 μL of P2 buffer and 350 μL of N3 buffer were added before centrifugation at 13,000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was transferred to a QIAprep spin column that was then centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 1 min. After discarding the flow-through, 500 μL of PB buffer was added to the column, which was then centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 1 min. The column was washed with 750 μL of PE buffer and the plasmid DNA was retrieved in 30 μL of nuclease-free water after a final centrifugation of the column at 13,000 rpm for 1 min.
DNA Sequencing and Primer Design
The plasmid DNA sequence was analyzed by SolGent (SolGent Co., Daejeon, Korea), which verified that the cDNA was inserted into the pGEM-T Easy vector. After analysis of the DNA sequence, cDNA consensus was identified using the basic local alignment search tool (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi). The EST-SSR markers were designed using the microsatellite analysis program WebSat and Primer3web version 4.0.0. The SSR sites analyzed were used to prepare the forward and reverse primers. Primer design was based on the following core criteria: (1) primer length ranging from 18 to 27 bp; (2) melting temperature between 55 and 62 °C with 60 °C as the optimum; (3) PCR product size ranging from 150 to 500 bp; and (4) GC% content between 20 and 60%, with an amplification rate larger than 80%.
PCR amplification and polymorphism analysis
PCR was conducted using a UNO II thermocycler (Biometra GmbH, Göttingen, Germany). As a template, 30 ng of sweet potato genomic DNA was added to 2.5 mM 10× buffer (500 mM KCl; 100 mM Tris–HCl, pH 8.3; 15 mM MgCl2), 20 pmol dNTP mixture, 20 pmol SSR marker primer, and 1 U of Taq DNA polymerase. The initial denaturation was carried out at 96 °C for 5 min, and denaturation was at 96 °C for 1 min. The annealing temperature ranged from 54.5 to 61.5 °C for 30 s, and extension was at 72 °C for 1 min. The final extension temperature was 72 °C for 5 min. After the PCR was complete, 5 µL of the product was loaded onto a QIAxcel capillary gel electrophoresis system (Qiagen) for analysis.
Results
Construction of cDNA library and treatment by restriction enzymes
Total RNA was isolated from sweet potato tissue for design of the cDNA library. Electrophoresis analysis showed that the cDNA library amplicon size range was varied. A total of 789 cDNAs were cloned in E. coli by employing the pGEM-T Easy vector. To confirm the ligation of the plasmid and the cDNA, the extracted plasmid from E. coli was cut with a restriction enzyme (EcoRI) and analyzed by 1.0% agarose gel electrophoresis.
Frequency and distribution of EST-SSR markers in sweet potato
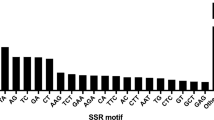
A total of 789 ESTs with an average length of 283 bp were used to evaluate the presence of SSR motifs. The length of contigs ranged from 100 to 499 bp, with those >250 bp accounting for 75.7%. A total of 617 SSRs were identified from 579 unique ESTs. Of these, 31 ESTs contained more than one SSR. All the SSRs showed that the ratio of their unit sizes was not evenly distributed. Among the 617 SSRs, the hexanucleotide repeat motifs were the most abundant (512, 82.98%), followed by penta- (69, 11.18%), tri- (28, 4.53%), di- (6, 0.97%), and tetranucleotide (2, 0.32%) repeat motifs (Table 2). As shown in Table 3, the 10–12-bp-long SSRs accounted for 95.5% of the total SSRs, with the remaining sequences being of 14–20 bp in length (28 SSRs, 4.5%). The maximum length of the dinucleotide repeat (TA/TA) and pentanucleotide repeat (GCGAG/CTCGC) was 20 bp, respectively. In addition, a total of 94 SSR motifs were identified of which 4, 4, 2, 56, and 28 were di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, and hexanucleotide repeats, respectively. The CAGAAT/ATTCTG hexanucleotide repeat was the most abundant motif detected in our designed primer (42, 29.0%), followed by the motifs TCT/AGA (4, 2.8%), TAATT/AATTA (3, 2.1%), GAG/CTC (2, 1.4%), GCGGA/TCCGC (2, 1.4%), AGAATC/GATTCT (2, 1.4%), CTCCTG/CAGGAG (2, 1.4%), and TTGCAG/CTGCAA (2, 1.4%). The frequency of the remaining 84 types of motifs accounted for 59.1% (Fig. 1).
Primer design and evaluation of EST-SSR markers in cultivated sweet potato
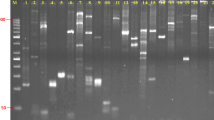
To ensure the uniqueness of the newly designed EST-SSR primer pairs, 579 potential unique SSR-containing sequences were analyzed. Based on these SSR-containing sequences, 619 pairs of high-quality SSR primers were designed using WebSat (http://www.wsmartins.net/websat/) and Primer3web version 4.0.0 (http://bioinfo.ut.ee/primer3/). The total number of designed primers was 144. Of these, 4, 8, 2, 59, and 71 were for di-, tri-, tetra-, penta- and hexanucleotide repeats, respectively (Fig. 2). After being tested in 20 Korean sweet potato cultivars, 119 primer pairs (82.6%) were successfully amplified. Of these 119 working primer pairs, only 76 amplified PCR products were of the expected sizes. Twenty-four of the other forty-three primers produced larger than expected PCR products and nineteen gave smaller than expected results. The 144 primers were used for further validation in the Yeseumi and Annobeny cultivars, and 106 primer pairs (73.6%) were successfully amplified. Examples of the PCR products amplified in Yeseumi and Annobeny, and in the 20 cultivars, are shown in Fig. 2.
Polymorphic primer pairs and number of designed primer pairs. The figure was indicated number of primer pairs designed (black columns), primer pairs amplified (gray columns), polymorphic loci in two parents Yeseumi and Annobeny (dotted white columns), and polymorphic loci in the 20 sweet potato cultivars (white columns)
Polymorphism of EST-SSR markers in cultivated sweet potato
The polymorphism assessment was examined in 20 Korean sweet potato cultivars, as well as Yeseumi and Annobeny. Among the 119 effective SSR primer pairs amplified from the 20 cultivars, 82 (68.9%) were polymorphic (observed for 3 di-, 6 tri-, 1 tetra-, 32 penta-, and 40 hexanucleotide repeats). Among the 106 effective SSR primer pairs amplified from cultivars Yeseumi and Annobeny, 90 (84.9%) were polymorphic (observed for 3 di-, 5 tri-, 2 tetra-, 36 penta-, and 44 hexanucleotide repeats) (Fig. 3).
SSR primer pairs for amplification of PCR products. A: PCR products amplified by 20 primer pairs from Yeseumi (lanes 1) and Annobeny (lanes 2). B: PCR products amplified by 2 primer pairs from twenty sweet potato cultivars. DNA samples from left to right are Yulmi (lanes 1), Jeonmi (lanes 2), Gogeonmi (lanes 3), Jungmi (lanes 4), Sincheonmi (lanes 5), Geonhwangmi (lanes 6), Yeonmi (lanes 7), Geonmi (lanes 8), Yeonjami (lanes 9), Sinjami (lanes 10), Sinyulmi (lanes 11), Helseumi (lanes 12), Geonpungmi (lanes 13), Yeseumi (lanes 14), Hayanmi (lanes 15), Jinhongmi (lanes 16), Juhwangmi (lanes 17), Dahomi (lanes 18), Simgeonmi (lanes 19), and Yeonhwangmi (lanes 20). Standard size markers are given on left side
Discussion
In this study, we developed EST-SSR markers from the genome sequence of sweet potato. In general, molecular analysis in sweet potato is carried out using SSR markers and inter-simple sequence repeat markers (Hu et al. 2003; Koussao et al. 2014). However, SSR markers do not represent gene function. Recently, the development of an EST-SSR marker in sweet potato was reported, using a next-generation sequencing (Wang et al. 2010) method; namely, isolation of microsatellite markers from genomic sequences. Compared with the traditional methods, such as construction of an SSR-enriched DNA library followed by cloning and sequencing using the Sanger method, next-generation sequencing has the advantages of time and cost savings (Abdelkrim et al. 2009; Santana et al. 2009; Malausa et al. 2011; Zalapa et al. 2012). Nevertheless, although studies using next-generation sequencing have resulted in more than 59 million sequencing reads, it was reported that only 92 primer pairs were successfully employed (Wang et al. 2010). In our study, a total of 789 potential unique EST sequences (about 174.7 kb) were used for searching SSRs, where 579 ESTs (73.4%) contained SSR motifs, generating 617 unique SSRs. Among the 144 designed primers, 119 (82.6%) were successfully amplified in sweet potato, which is a high efficiency rate. In this study, the hexanucleotide repeats were the most frequent motif type, followed by penta-, tri-, di-, and tetranucleotides (Table 2). However, in another report that used a total of 87,492 potential unique EST sequences (about 58.7 Mb) to search for SSRs in sweet potato; of which, 7163 ESTs (8.2%) contained SSR motifs, generating 8294 unique SSRs, the trinucleotide repeat was found to be the most abundant, followed by di-, tetra-, penta-, and hexanucleotides (Wang et al. 2011). In our study, 82 EST-SSR markers among the 20 sweet potato cultivars were polymorphic, whereas 90 EST-SSR markers were polymorphic among the Yeseumi and Annobeny cultivars. We had developed fixed EST-SSR markers in the absence of DNA marker data at sweet potato. This would necessitate a comparison of our fixed EST-SSR markers in more Korean and other cultivars. The development of EST-SSR markers has gained traction in recent years. Qureshi et al. (2004) developed 84 EST-SSR primers of Gossypium arboreum var. indium using 9948 sequence data, and Kim et al. (2010) used 30 EST-SSR markers for the analysis of Rosa hybrida L. Oh et al. (2010) reported the phylogenetic analysis of Daucus carota var. sativa as well as the analysis of various characteristic molecular markers, using 50 markers based on EST sequences. Moreover, besides acting as a molecular tag for particular traits, EST-SSR markers can also simultaneously identify information about the corresponding gene. Thus, by developing EST-SSR markers, the molecular analysis of sweet potato could be done more efficiently. EST-SSR markers can also be used in the construction of sweet potato maps. Thus, we can develop high-quality sweet potato while overcoming the challenges from climate change and other unfavorable conditions.
References
Abdelkrim J, Robertson BC, Stanton JA, Gemmell NJ (2009) Fast, cost-effective development of species-specific microsatellite markers by genomic sequencing. Biotechniques 46:185–192
Cervantes-Flores JC, Yencho GC, Kriegner A, Pecota KV, Faulk MA, Mwanga RO, Sosinski BR (2008) Development of a genetic linkage map and identification of homologous linkage groups in sweetpotato using multiple-dose AFLP markers. Mol Breeding 21:511–532
Connolly AG, Godwin ID, Cooper M, DeLacy IH (1994) Interpretation of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA marker data for fingerprinting sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) genotypes. Theor Appl Genet 88:332–336
Eujayl I, Sledge MK, Wang L, May GD, Chekhovskiy K, Zwonitzer JC, Mian MAR (2004) Medicago truncatula EST-SSRs reveal cross-species genetic markers for Medicago spp. Theor Appl Genet 108:414–422
Gupta PK, Rustgi S (2004) Molecular markers from the transcribed/expressed region of the genome in higher plants. Funct Integr Genomics 4:139–162
Hu J, Nakatani M, Lalusin AG, Kuranouchi T, Fujimura T (2003) Genetic analysis of sweetpotato and wild relatives using inter-simple sequence repeats (ISSRs). Breed Sci 53:297–304
Huamán Z, Zhang DP (1997) Sweetpotato. In: Fuccillo D, Sears L, Stapleton P (eds) Biodiversity in trust. Cambridge Univ Press, Cambridge, pp 29–38
Kim JK, Ahn DC, Oh HJ, Kim KH, Choi YM, Oh SY, Kang NJ, Jeong BR, Kim ZH, Park YH (2010) Skewed inheritance of EST-SSR alleles in reciprocal crosses of cut roses. Kor J Hort Sci Technol 28:618–626
Koussao S, Gracen V, Asante I, Danquah EY, Ouedraogo JT, Baptiste TJ, Vianney TM (2014) Diversity analysis of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas [L.] Lam) germplasm from Burkina Faso using morphological and simple sequence repeats markers. Afr J Biotechnol 13:729–742
Kriegner A, Cervantes JC, Burg K, Mwanga RO, Zhang D (2003) A genetic linkage map of sweetpotato [Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.] based on AFLP markers. Mol Breeding 11:169–185
Malausa T, Gilles A, Meglecz E, Blanquart H, Duthoy S, Costedoat C, Dubut V, Pech N, Castagnone-Sereno P, Delye C, Feau N, Frey P, Gauthier P, Guillemaud T, Hazard L, Corre V, Lung-Escarmant B, Male PJ, Ferreira S, Martin JF (2011) High-throughput microsatellite isolation through 454 GS-FLX titanium pyrosequencing of enriched DNA libraries. Mol Ecol Resour 11:638–644
Martin FW (1970) Self and interspecific incompatibility in the Convolvulaceae. Bot Gaz 131:139–144
Morgante M, Hanafey M, Powell W (2002) Microsatellites are preferentially associated with nonrepetitive DNA in plant genomes. Nat Genet 30:194–200
Oh GD, Hwang EM, Shim EJ, Jeon SJ, Park YD (2010) EST profiling for seed-hair characteristic and development of EST-SSR and SNP markers in carrot. Kor J Hort Sci Technol 28:1025–1038
Qureshi SN, Saha S, Kantety RV, Jenkins JN, Saha S (2004) Molecular biology and physiology: EST-SSR: a new class of genetic markers in cotton. J Cotton Sci 8:112–123
Saha MC, Cooper JD, Mian MR, Chekhovskiy K, May GD (2006) Tall fescue genomic SSR markers: development and transferability across multiple grass species. Theor Appl Genet 113:1449–1458
Santana QC, Coetzee MP, Steenkamp ET, Mlonyeni OX, Hammond GN, Wingfield MJ, Wingfield BD (2009) Microsatellite discovery by deep sequencing of enriched genomic libraries. Biotechniques 46:217–223
Scott KD, Eggler P, Seaton G, Rossetto M, Ablett EM, Lee LS, Henry RJ (2000) Analysis of SSRs derived from grape ESTs. Theor Appl Genet 100:723–726
Thompson PG, Hong LL, Ukoskit K (1997) Genetic linkage of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers in sweetpotato. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 122:79–82
Ting YC, Kehr AE (1953) Meiotic studies in the sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas Lam.). Heredity 44:207–211
Ukoskit K, Thompson PG, Watson CE, Lawrence GW (1997) Identifying a randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) marker linked to a gene for root-knot nematode resistance in sweetpotato. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 122:818–821
Varshney RK, Graner A, Sorrells ME (2005a) Genic microsatellite markers in plants: features and applications. Trends Biotechnol 23:48–55
Varshney RK, Sigmund R, Börner A, Korzun V, Stein N, Sorrells ME, Langridge P, Graner A (2005b) Interspecific transferability and comparative mapping of barley EST-SSR markers in wheat, rye and rice. Plant Sci 168:195–202
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, Lee TVD, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wang Z, Fang B, Chen J, Zhang X, Luo Z, Huang L, Chen X, Li Y (2010) De novo assembly and characterization of root transcriptome using Illumina paired-end sequencing and development of cSSR markers in sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas). BMC Genom 11:726. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-11-726
Wang Z, Li J, Luo Z, Huang L, Chen X, Fang B, Li Y, Chen J, Zhang X (2011) Characterization and development of EST-derived SSR markers in cultivated sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas). BMC Plant Biol 11:139. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-11-139
Welsh J, McClelland M (1990) Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:7213–7218
Williams JG, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Zalapa JE, Cuevas H, Zhu H, Steffan S, Senalik D, Zeldin E, McCown B, Harbut R, Simon P (2012) Using next-generation sequencing approaches to isolate simple sequence repeat (SSR) loci in the plant sciences. Am J Bot 99:193–208
Zhang D, Cervantes J, Huamán Z, Carey E, Ghislain M (2000) Assessing genetic diversity of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) cultivars from tropical America using AFLP. Genet Resour Crop Evol 47:659–665
Zhang LY, Bernard M, Leroy P, Feuillet C, Sourdille P (2005) High transferability of bread wheat EST-derived SSRs to other cereals. Theor Appl Genet 111:677–687
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Kyungpook National University Research Fund, 2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JH., Kim, JH., Jo, WS. et al. Characterization and development of EST-SSR markers in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam). 3 Biotech 6, 243 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0565-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0565-9