Abstract
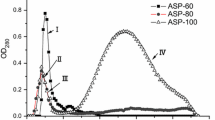
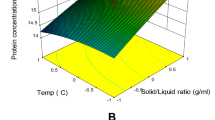
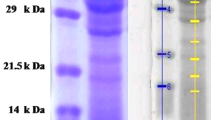
This study aimed to explore the potency of Gonggong sea snail’s (GSS) extract as an antimicrobial peptide (AMP) source. The results showed that the GSS meat extracts exhibited potential antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. A peptide band with a molecular weight < 5 kDa was obtained for the characterization of AMP candidates after separating the selected extract using SDS-PAGE, and the sequences were acquired by LC–ESI–MS analysis. The results of the bioinformatics analysis showed that the AMP candidate had a molecular weight of 1.4 kDa, which consisted of 12 amino acid residues (RHPDYSVALLLR), with an α-helix structure, isoelectric point pH (pI) of 9.53, net charge + 1, a total hydrophobic ratio at 49.9%, protein-binding potential (Boman index) of 2.17 kcal/mol, and hydrophobicity of + 13.67 kcal/mol. Furthermore, MIC and MBC values of the extract and the < 10 kDa fraction on both bacteria ranged from 0.50–1.03 mg/ml. The GSS meat extract could reach the intracellular site of E. coli, while in S. aureus, it was localized in the cell membrane. These results can be baseline information for developing AMPs in natural bio-preservative exploration as food additives and pharmaceuticals.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AMP:
-
Antimicrobial peptide
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- FITC:
-
Fluorescein-5-isothiocyanate
- LB:
-
Lysogeny broth
- MBC:
-
Minimum bactericidal concentration
- MHA:
-
Mueller–Hinton agar
- MIC:
-
Minimum inhibitory concentration
- MWCO:
-
Molecular weight cut off
- RNA:
-
Ribonucleic acid
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- TFA:
-
Trifluoroacetic acid
- Tris:
-
Tris(hydroxymethyl) aminomethane
- LC–ESI–MS:
-
Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
References
Abarrategui CL, McBeth C, Mandal SM, Sun ZJ, Heffron G, Men’endez AA, Migliolo L, Acosta OR, Villarino MG, Nolasco DO, Falcão R, Cherobim MD, Dias SC, Brandt WL, Starnbach M, Franco OL, Gonz´alez A (2015) Cm-p5: an antifungal hydrophilic peptide derived from the coastal mollusk Cenchritis muricatus (Gastropoda:Littorinidae). The FASEB J 29(8):3315–25. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.14-269860
Amini S (1986) Preliminary study of gonggong (Strombus canarium) in coastal waters of Bintan Island-Riau. Jurnal Penelitian Perikanan Laut 36:23–29
Arularasan S, Lyla PS, Kesavan K, Khan SA (2010) Recieps for the mesogastropod - Strombus canarium. Adv J Food Sci Technol 2(1):31–35
Asoodeh A, Azam AG, Chamani J (2012) Identification and characterization of novel antibacterial peptides from skin secretions of Euphlyctis cyanophlyctis. Int J Pept Res Ther 18:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-011-9284-6
Baeriswyl V, Heinis C (2013) Phage selection of cyclic peptide antagonists with increased stability toward intestinal protease. Protein Eng Des Sel 26(1):81–89. https://doi.org/10.1093/protein/gzs085
Ben said L, Fliss I, Offret C, Beaulieu L (2019) Antimicrobial peptides: the new generation of food additives. In: Melton L, Shahidi F, Varelis P (Eds) Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry, vol. 3 pp. 576–582. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-100596-5.21718-6.
Bringans S, Eriksen S, Kendrick T, Gopalakrishnakone P, Livk A, Lock R, Lipscombe R (2008) Proteomic analysis of the venom of Heterometrus longimanus (Asian black scorpion). Proteomics 8:1081–1096. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.200700948
De Zoysa M, Nikapitiya C, Whang I, Lee JS, Lee J (2009) Abhisin: a potential antimicrobial peptide derived from histone H2A of disk abalone (Haliotis discus discus). Fish Shellfish Immunol 27(5):639–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2009.08.007
Fjell C, Hiss JA, Hancook REW, Schneider G (2012) Designing microbial peptide: form follows function. Nat Rev Drug Discov 11(1):37–51. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3591
Ganesan AR, Mohanram MSG, Balasubramanian B, Kim IH, Seedevi P, Mohan K, Kanagasabai S, Arasu NV, Al-Dhabi NA, Ignacimuthu S (2020) Marine invertebrates’ proteins: A recent update on functional property. J King Saud Univ 32:1496–1502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2019.12.003
Gonelimali FD, Lin J, Miao W, Xuan J, Charles F, Chen M, Hatab SR (2018) Antimicrobial properties and mechanism of action of some plant extracts against food pathogens and spoilage microorganisms. Front Microbiol 9:1639. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01639
Lee H, Lim SI, Shin SH, Lim Y, Koh JW, Yang S (2019) Conjugation of cell-penetrating peptides to antimicrobial peptides enhances antibacterial activity. ACS Omega 4(13):15694–15701. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b02278
Li Z, Yuan Y, Meng M, Li S, Deng B, Wang Y (2020) The transcriptome analysis of the whole-body of the gastropod mollusk Limax flavus and screening of putative antimicrobial peptide and protein. Genomics 112:3991–3999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.06.046
Magrone T, Russo MA, Jirillo E (2018) Antimicrobial peptides: phylogenic sources and biological activities first of two parts. Curr Pharm Des 24(10):1043–1053. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612824666180403123736
Mahlapuu M, Björn C, Ekblom J (2020) Antimicrobial peptides as therapeutic agents: opportunities and challenges. Crit Rev Biotechnol 40(7):978–992. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2020.1796576
Muzahar VL (2013) Chemical characterization, sensory and spawning rate of gonggong (Strombus sp.) as icon Kepulauan Riau Province. J Maritime Dynamic 2:20–29
Nam BH, Seo JK, Lee MJ, Kim YO, Kim DG, An CM, Park NG (2015) Functional analysis of Pacific oyster (Crassostrea gigas) β-thymosin: focus on antimicrobial activity. Fish Shellfish Immunol 45(1):167–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2015.03.035
Nurilmala M, Ochiai Y (2016) Molecular characterization of southern bluefin tuna myoglobin (Thunnus maccoyii). Fish Physiol Biochem 42(5):1407–1416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-016-0228-0
Osorio D, Rondon-Villarreal P, Torres R (2015) Peptides: a package for data mining of antimicrobial peptide. The R J 7(1):4–14
Ovchinnikova TV, Balandin SV, Aleshina GM, Tagaev AA, Leonova YF, Krasnodembsky ED, Men’sheninKokryakov AVVN (2006) Aurelin, a novel antimicrobial peptide from jellyfish Aurelia aurita with structural features of defensins and channel-blocking toxins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348(2):514–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.07.078
Park CB, Kim HS, Kim SC (1998) Mechanism of action of the antimicrobial peptide buforin II: buforin II kills microorganisms by penetrating the cell membrane and inhibiting cellular functions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 244(1):253–257. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1998.8159
Pushpanathan M, Gunasekaran P, Rajendhran J (2013) Antimicrobial peptides: versatile biological properties. Int J Pept 2013:675391. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/675391
Sathyan N, Philip R, Chaithanya ER, Kumar PRA (2012) Identification and molecular characterization of molluskin, a histone-H2A-derived antimicrobial peptide from molluscs. ISRN Mol Biol 2012:219656. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/219656
Suartini IGAA, Agustini NLP, Setiasih NLE, Putriningsih S, Nurwidana DL (2016) Aktivitas biologis imunoglobulin yolk anti parvovirus setelah perlakuan suhu. Buletin Veteriner Udayana 8(1):79–85
Tachapuripunya V, Roytrakul S, Chumnanpuen P, E-kobon T (2021) Unveiling putative functions of mucus proteins and their tryptic peptides in seven gastropod species using comparative proteomics and machine learning-based bioinformatitcs predictions. Molecules 26:3475. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113475
Tam JP, Lu YA, Yang JL (2002) Antimicrobial dendrimeric peptides. Eur J Biochem 269(3):923–932. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0014-2956.2001.02728.x
Tidona F, Criscione A, Guastella AM, Zuccaro A, Bordonaro S, Marletta D (2009) Bioactive peptides in dairy products. Italian J Anim Sci 8:315–340. https://doi.org/10.4081/ijas.2009.315
Vermeer LS, Lan Y, Abbate V, Ruh E, Bui TT, Wilkinson LJ, Kanno T, Jumagulova E, Kozlowska J, Patel J, McIntyre CA, Yam WC, Siu G, Atkinson RA, Lam JK, Bansal SS, Drake AF, Mitchell GH, Mason AJ (2012) Conformational flexibility determines selectivity and antibacterial, antiplasmodial, and anticancer potency of cationic α-helical peptides. J Biol Chem 287(41):34120–34133. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.359067
Viruly L (2011) The utilization of sea snail gonggong (Strombus canarium) from Bintan Island of Riau Archipelago as natural seasoning. Master Thesis, Bogor Agricultural University, Bogor, Indonesia.
Wang G, Mishra B, Lau K, Lushnikova T, Golla R, Wang X (2015) Antimicrobial peptides in 2014. Pharmaceuticals (basel) 8(1):123–150. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph8010123
Wang G, Li X, Wang Z (2016) APD3: the antimicrobial peptide database as a tool for research and education. Nucleic Acids Res 44(D1):D1087–D1093. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1278
Yin LM, Edwards MA, Li J, Yip CM, Deber CM (2012) Roles of hydrophobicity and charge distribution of cationic antimicrobial peptides in peptide-membrane interactions. J Biol Chem 287(10):7738–7745. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.303602
Zainol MI, Yusoff KM, Yusof MYM (2013) Antibacterial activity of selected Malaysian honey. BMC Complement Altern Med 13:129. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-13-129
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Ministry of Higher Education-Republic of Indonesia, the Southeast Asian Food and Agricultural Science and Technology (SEAFAST) Center-Bogor Agricultural University, Faculty of Marine Science and Fisheries-Raja Ali Haji Maritime University and the scientific support for the work (Muzahar, Hasan Nashrullah, and Agus A. Hakim).
Funding
This research was funded by Directorate General of Research Empowerment and Development, the Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher Education of Republic Indonesia through PDUPT Program (Grant No 4133/IT3.L1/PN/2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LV: Conceptualization; Methodology; Formal Analysis; Investigation; Visualization; Writing- original draft preparation; Writing: review and editing; MTS: Conceptualization; Methodology; Writing—review and editing; Supervision; MN: Conceptualization; Methodology; Writing—review and editing; Supervision; SS: Visualization; Writing – original draft; Writing: review and editing; NA: Conceptualization; Methodology; Writing—review and editing; Supervision; Funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Viruly, L., Suhartono, M.T., Nurilmala, M. et al. Identification and characterization of antimicrobial peptide (AMP) candidate from Gonggong Sea Snail (Leavistrombus turturella) extract. J Food Sci Technol 60, 44–52 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05585-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05585-z