Abstract
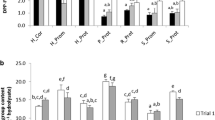
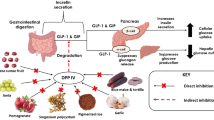
Inhibition of DPP-4 and stimulation of GLP-1 secretion are therapeutic strategies for controlling glycaemia in type 2 diabetes. The present study assessed the DPP-4 inhibitory activity and GLP-1 secretory action of pigmented and non-pigmented rice (Oryza sativa L.), along with an extruded food product. Cereal-based extruded food products, with or without passion fruit powder, were prepared from red rice using a twin extruder. Optimal extrusion conditions were determined using a CCD of response surface methodology resulting in optimal conditions to be 97.5 °C, a screw speed of 250 rpm, feed moisture of 25.2% and addition of 11.25% passion fruit powder. Samples were sequentially extracted in n-hexane, ethanol (50%) and water. Ethanol/water (50:50) extracts of rice bran significantly inhibited DPP-4 activity by 70.48 ± 1.06%, comparing favourably with RR (42.55 ± 0.84%), PRR (35.91 ± 1.27%) and PA (29.14 ± 1.23%). DPP-4 inhibitory activity was retained in both extruded products albeit at reduced levels. GLP-1 secretion was stimulated mostly by extruded products extracted with n-hexane or ethanol which upregulated basal secretion by 6.1-fold and 4.2-fold, respectively. ICP-MS results showed that extruded food items have a lower arsenic content. In conclusion, there are potential opportunities for the nutraceuticals and functional food products using pigmented red rice.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All datasets generated for this study are included in the manuscript. Further if any more data are required, it can be provided from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Statistical analysis was conducted using Graph Pad Prism version 5 (Graph Pad Software, USA). All experiments were carried out in triplicate. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM and statistical comparisons were assessed using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. A p-value less than 0.05 was deemed statistically significant.
Abbreviations
- DPP-4:
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide
- ICP-MS:
-
Inductively coupled plasma-mass-spectrometry
- DMA:
-
Dimethyl arsenic acid
- As III:
-
Arsenite
- As V:
-
Arsenate
- MMA:
-
Monomethyl arsonic acid
- SEM:
-
Standard error of the mean
- STC-1:
-
Secretin tumor cell line
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium
- HEPES:
-
N-2-Hydroxyethylpiperazine-N'-2-Ethanesulfonic Acid
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunoassay.
- RB:
-
Rice bran
- RR:
-
Red rice
- PRR:
-
Polished red rice
- WR:
-
White rice
- OE:
-
Optimized extrudate
- CE:
-
Controlled extrudate
References
Ajanal M, Gundkalle M, Nayak S (2012) Estimation of total alkaloid in Chitrakadivati by UV-Spectrophotometer”. Anc Sci Life 31(4):198–201
Al-masri IM, Mohammad MK, Tahaa MO (2009) Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV) is one of the mechanisms explaining the hypoglycemic effect of berberine. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 24:1061–1106
Bandyopadhyay K, Misra G, Ghosh S (2008) Preparation and characterization of protein hydrolysates from Indian defatted rice bran meal. J Oleo Sci 57:47–52
Capuano A, Sportiello L, Maiorino MI, Rossi F, Giugliano D, Esposito K (2013) (2013) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes therapy-focus on alogliptin. Drug Des Devel Ther 7:989–1001
Chemat F, Vian AM, Cravotto G (2012) Green extraction of natural products: concept and principles. Intern J Mol Sci 13:8615–8627. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13078615
Chia-Ling J, Chuan-Chuan H, Yu-Shan T, Meng-Chun P-Y, Kuo-Chiang CH (2015) The development of bioactive peptides from dietary proteins as a dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the management of type 2 diabetes. Bio Med 5(3):9–15
Choi SH, Kim JS, Lee JY, Jeon JS, Kim JW, Russo RE, Gonzalez J, Yoo JH, Kim KS, Yang JS, Park KS (2014) Analysis of arsenic in rice grains using ICP-MS and fs LA-ICP-MS. J Anal at Spectrom (JAAS) 29:1233–1237
Codex General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Food and Feed, Codex Standard, 2012.
D’Amato M, Forte G, Caroli S (2004) Identification and quantification of major species of arsenic in rice. J AOAC Intern 87:238–243
FSANZ. (2006). Contaminants and natural toxicants. Standard 1.4.1. Available:< http://www.foodstandards.gov.au/_srcfiles/fsc_1_4_1_Contaminants_v78.pdf >. Accessed 2006.
Fujiwara K, Tsuru D (1978) New chromogenic and fluorogenic substrates for pyrrolidonyl peptidase. J Biochem 83:1145–1149
Gillespie AL, Pan X, Marco-Ramell A, Meharg C, Green BD (2017) Detailed characterisation of STC-1 cells and the pGIP/Neo sub-clone suggests the incretin hormones are translationally regulated. Peptides 96:20–30
Giorda CB, Nada E, Tartaglino B (2014) Pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy of DPP4 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and renal or hepatic impairment. a systematic review of the literature. Endocrine 46:406–419
Gupta V, Kalra S (2011) Choosing a gliptin. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 15(4):298–308
Hand KV, Bruen CM, O’Halloran F, Giblin L (2010) Acute and chronic effects of dietary fatty acids on cholecystokinin expression, storage and secretion in enteroendocrine STC-1 cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 54:S93–S103
Harper J M (1989). Food Extruders and Their Applications; Mercier C, Linko P, Harper JM, Eds.;American Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA,1–15.
Hatanaka T, Inoue Y, Arima J, Kumagai Y, Usuki K, Kawakami K, Kimura M, Mukaihara T (2012) Production of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptides from defatted rice bran. Food Chem 134:797–802
Hatanaka T, Uraji M, Fujita A, Awakami K (2015) Anti-oxidant activities of rice-derived peptides and their inhibitory effects on Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV. Intern J Peptidase Res Ther 21(4):479–485
Heitkemper DT, Vela NP, Stewart KR, Westphal CS (2001) Determination of total and speciated arsenic in rice by ion chromatography and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Anal Spectrom 16(4):299–306
Kumar A, Girish GM, Jones DD, Hanna MA (2008) Modelling residence time distribution in a twin-screw extruder as a series of ideal steady-state flow reactors. J Food Eng 84:441–448
Mahdi-Pour B, Jothy SL, Latha LY, Chen Y, Sasidharan S (2012) Antioxidant activity of methanol extracts of different parts of Lantana camara. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2(12):960–965
Mayorga P, Moyano A, Anawar HM, Garcia-Sanchez A (2013) Uptake and accumulation of arsenic in different organs of carrot irrigated with as-rich water. Clean-Soil, Air, Water 41(6):587–592
Nagendra PMN, Sanjay KR, Shravya KM, Vismaya MN, Nanjunda SS (2011) Health benefits of rice bran - a review. J Nutr Food Sci 1:3. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9600.1000108
Nguyen DH, Ta NTA, Bui AV, Do TH, Nguyen HC (2019) Evaluation of the use of different solvents for phytochemical constituents, antioxidants, and in vitro anti-inflammatory activities of severinia buxifolia. J Food Quality. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8178294
Parrado J, Miramontes E, Jover M, Gutierrez JF, Terán LC, Bautista J (2006) Preparation of a rice bran enzymatic extract with potential use as functional food. Food Chem 98:742–748
Pathak R, Bridgeman MB (2010) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors in the management of diabetes. Pharmacy Therapeutics. 35(9):509–513
Purnomo Y, Sumitro S (2018) Inhibitory activity of Urena lobata leaf extract on dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4): is It different in vitro and in vivo ? Medicinal Plants – Intern. J Phytomed Related Ind. https://doi.org/10.5958/0975-6892.2018.00016.3
Samyor D, Deka SC, Das AB (2016) Evaluation of physical, thermal, pasting characteristics and mineral profile of pigmented and non -pigmented rice cultivars. J Food Process Preserv 40(2):174–182
Samyor D, Deka SC, Das AB (2018) Effect of extrusion conditions on the physicochemical and phytochemical properties of red rice and passion fruit powder based extrudates. J Food Sci Technol 55(12):5003–5013
Samyor D, Deka SC, Das AB (2020) Physicochemical and phytochemical properties of foam mat dried passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) powder and comparison with fruit pulp. J Food Sci Technol 58:787–796
Shao Y, Bao J (2015) Polyphenols in whole rice: Genetic diversity and health benefits. Food Chem 180:86–97
Signes-Pastor AJ, Meharg CM (2016) Inorganic arsenic in rice-based products for infants and young children. Food Chem 191:128–134
Sivamaruthi BS, Kesika P, Chaiyasut C (2018) A comprehensive review on anti-diabetic property of rice bran. Asian Pacif J Tropic Biomed 8(1):79–84
Suzuki KT, K T, (2002) Arsenic round the world: A review. Talanta 58(1):201–235
Zendjabil M (2016) Biological diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Curr Res Transl Med 64:49–52
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Newton Bhabha PhD Placement Programme (F.No.BT/IN/UK/DBT-BC/
2015-16) in collaboration with Dept. of Biotechnology, India and British Council, U.K for providing financial support to D.S.
Funding
Newton Bhabha PhD Placement Programme (F.No.BT/IN/UK/DBT-BC/2015–16) in collaboration with Dept. of Biotechnology, India and British Council, U.K for a period of 6 months.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DS, ABD and I (SCD) designed the experiments for optimization of process parameters using Design Expert 7 Version software. DS, DC, MC and BDG analysed and interpreted the data. DS drafted the manuscript and BDG and I edited the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samyor, D., Calderwood, D., Carey, M. et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitory activity and glucagon-like peptide (GLP-1) secretion in arsenically safe pigmented red rice (Oryza sativa L.) and its product. J Food Sci Technol 59, 4016–4024 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05444-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05444-x