Abstract
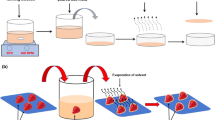
A bio-nanocomposite film is a polymer blend with nanofiller dispersed in a biopolymer matrix. The aim of this study is to investigate the functional, gas sensing and antimicrobial properties of bio-nanocomposite films incorporated with chicken skin gelatin/ tapioca starch/zinc oxide at different pH levels (pH 4, 6, 7 and 8). Bio-nanocomposite films were prepared using a casting technique followed by the characterization of their functional, gas sensing and antimicrobial properties. Film formulations with pH at different levels showed increased thickness, colour and water vapour permeability (WVP) (p < 0.05). In addition, the increase of pH in films in chicken skin gelatin bio-nanocomposite films increased the tensile strength (TS), while decreasing the elongation at break (EAB). The highest response for ammonia gas in chicken skin gelatin bio-nanocomposite films was obtained at pH 7, with quick response time (τres) within 10 s. The inhibition zone of Staphylococcus aureus in chicken skin gelatin bio-nanocomposite films increased with increasing pH levels. Overall, chicken skin gelatin bio-nanocomposite films with a pH level of 8 were found to have the optimal formulation, with the highest values in thickness, and TS, with the lowest values for WVP and EAB. In conclusion, bio-nanocomposite chicken skin gelatin films with an alkaline pH are a superior packaging material.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Benjakul S, Prodpran T, Agustini TW (2012) Physico-mechanical and antimicrobial properties of gelatin film from the skin of unicorn leatherjacket incorporated with essential oils. Food Hydrocoll 28(1):189–199
Al-Hassan AA, Norziah MH (2012) Starch–gelatin edible films: water vapor permeability and mechanical properties as affected by plasticizers. Food Hydrocoll 26(1):108–117
Alias SA, Sarbon NM (2019) Rheological, physical, and mechanical properties of chicken skin gelatin films incorporated with potato starch. NPJ Sci of Food 3(1):1–9
AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemist) (2006) official methods of analysis of AOAC international. Soxhlet extraction method.18th. Ref. 963.15. USA
Arfat YA, Benjakul S, Prodpran T (2016) Physico-mechanical characterization and antimicrobial properties of fish protein isolate/fish skin gelatin-zinc oxide (ZnO) nanocomposite films. Food Bioprocess Technol 9:101–112
Arham R, Mulyati MT, Metusalach M, Salengke S (2016) Physical and mechanical properties of agar based edible film with glycerol plasticizer. Int Food Res J 23(4):16–69
Azeredo HMC, Mattoso LHC, McHugh TH (2011) Nanocomposites in food packaging–a review. INTECH Open Access. Publisher
Chinabhark K, Benjakul S, Prodpran T (2007) Effect of pH on the properties of protein-based film from bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenus) surimi. Bioresour Technol 98(1):221–225
Espitia PJP, Soares NDFF, Teófilo RF, dos Reis Coimbra JS, Vitor DM, Batista RA, Medeiros EAA (2013) Physical–mechanical and antimicrobial properties of nanocomposite films with pediocin and ZnO nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 94(1):199–208
Gioffrè M, Torricelli P, Panzavolta S, Rubini K, Bigi A (2012) Role of pH on stability and mechanical properties of gelatin films. J Bioact Compat Polym 27(1):67–77
Hamaguchi PY, WuYin W, Tanaka M (2007) Effect of pH on the formation of edible films made from the muscle proteins of Blue marlin (Makaira mazara). Food Chem 100(3):914–920
Khairul WM, Daud AI, Hanifaah NAM, Arshad S, Razak IA, Zuki HM, Erben MF (2017) Structural study of a novel acetylide-thiourea derivative and its evaluation as a detector of benzene. J Mol Struct 1139:353–361
Korposh SO, Takahara N, Ramsden JJ, Lee SW, Kunitake T (2006) Nano-assembled thin film gas sensors. 1. Ammonia detection by a porphyrin-based multilayer film. J Polym Environ 21(3):211–215
Kumar P, Sandeep KP, Alavi S, Truong VD, Gorga RE (2010) Preparation and characterization of bio-nanocomposite films based on soy protein isolate and montmorillonite using melt extrusion. J Food Eng 100(3):480–489
Lee SW, Said NS, Sarbon MN (2020) The effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the physical, mechanical and antimicrobial properties of gelatin/tapioca starch composite films as food packaging materials. J Food Sci Technol (in press)
Loo PYC, Sarbon MN (2020) Functional properties of edible chicken skin gelatin film incorporated with tapioca starch. Food Biosci 35:100589
Ma L, Yang H, Ma M, Zhang X, Zhang Y (2018) Mechanical and structural properties of rabbit skin gelatin films. Int J Food Prop 21(1):1203–1218
Martucci JF, Ruseckaite RA (2010) Biodegradable three-layer film derived from bovine gelatin. J Food Eng 99(3):377–393
Medvedova A, Valik L (2012) Staphylococcus aureus: characterisation and quantitative growth description in milk and artisanal raw milk cheese production. InTech 4:71–102
Muller J, González-Martínez C, Chiralt A (2017) Combination of poly (lactic) acid and starch for biodegradable food packaging. J Mater Sci 10(8):952–967
Nagarajan M, Benjakul S, Prodpran T, Songtipya P (2015) Effects of pHs on properties of bio-nanocomposite based on tilapia skin gelatin and Cloisite Na+. Int J Biol Macromol 75:388–397
Nazmi NN, Isa MIN, Sarbon NM (2017) Preparation and characterization of chicken skin gelatin/cmc composite film as compared to bovine gelatin film. Food Biosci 19:149–155
Nostro A, Cellini L, Di Giulio M, D’Arrigo M, Marino A, Blanco AR, Bisignano G (2012) Effect of alkaline pH on staphylococcal biofilm formation. APMIS 120(9):733–742
Nur Hazirah MASP, Isa MIN, Sarbon NM (2016) Effect of xanthan gum on the physical and mechanical properties of gelatin-carboxymethyl cellulose film blends. Food Packag Shelf Life 9:55–63
Othman SH (2014) Bio-nanocomposite materials for food packaging applications: types of biopolymer and nano-sized filler. Agric Sci Procedia 2:296–303
Robertson G (2013) Crimes against humanity: the struggle for global justice. The New Press, New York
Sahraee S, Milani JM, Ghanbarzadeh B, Hamishehkar H (2017) Effect of corn oil on physical, thermal, and antifungal properties of gelatin-based nanocomposite films containing nano chitin. LWT Food Sci Technol 76:33–39
Said NS, Sarbon NM (2019) Protein-based active film as antimicrobial food packaging: a review in active antimicrobial food packaging, (Ed) Isil Var, IntechOpen, pp 1–18. ISBN: 978-1-78985-004-8
Sarbon NM, Badii F, Howell NK (2013) Preparation and characterisation of chicken skin gelatin as an alternative to mammalian gelatin. Food Hydrocoll 30(1):143–151
Shankar S, Rhim JW (2019) Effect of Zn salts and hydrolyzing agents on the morphology and antibacterial activity of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Environ Chem Lett 17(2):1105–1109
Shankar S, Jaiswal L, Rhim JW (2016) Gelatin-based nanocomposite films: potential use in antimicrobial active packaging. In Antimicrob Food Packag 22:339–348
Shapi’i RA, Othman SH (2016) Effect of concentration of chitosan on the mechanical, morphological and optical properties of tapioca starch film. Int Food Res J 23:S187
Soo PY, Sarbon NM (2018) Preparation and characterization of edible chicken skin gelatin film incorporated with rice flour. Food Packag Shelf Life 15:1–8
Tongdeesoontorn W, Mauer LJ, Wongruong S, Sriburi P, Rachtanapun P (2011) Effect of carboxymethyl cellulose concentration on physical properties of biodegradable cassava starch-based films. Chem Cent J 5(1):6–15
Tongnuanchan P, Benjakul S, Prodpran T, Songtipya P (2011) Characteristics of film based on protein isolate from red tilapia muscle with negligible yellow discoloration. Int J Biol Macromol 48(5):758–767
Weng W, Zheng H, Su W (2014) Characterization of edible films based on tilapia (Tilapia zillii) scale gelatin with different extraction pH. Food Hydrocoll 41:19–26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azizun, N., Khairul, W.M., Daud, A.I. et al. Effect of pH on functional, gas sensing and antimicrobial properties of bio-nanocomposite gelatin film for food packaging application. J Food Sci Technol 58, 3338–3345 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04893-6
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04893-6