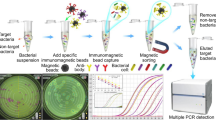
Abstract
L. monocytogenes continues to be a major health issue in Europe, as well as worldwide. Faster methods, not only for detection, but also for sample preparation are of great interest particularly for this slow-growing pathogen. Immunomagnetic separation has been previously reported to be an effective way to concentrate bacteria, and remove inhibitors. In the present study, different commercial antibodies were evaluated to select the most appropriate one, in order to develop a highly specific method. Additionally, magnetic nanoparticles, instead of microparticles, were selected due to their reported advantages (higher surface-volume ration and faster kinetics). Finally, the separation protocol, with a calculated capture efficiency of 95%, was combined with real-time PCR for highly sensitive detection of the concentrated bacteria. The optimized IMS-qPCR allowed to reduce hands-on time in the sample treatment, without affecting the overall performance of the method as a very low limit of detection was still obtained (9.7 CFU/ 25 g) with values for sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive and negative predictive values of 100%, resulting in a kappa index of concordance of 1.00. These results were obtained in spiked food samples of different types (chicken, fish, milk, hard and fresh cheese), further demonstrating the applicability of the optimized methodology presented.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman DG (1991) Practical statistics for medical research. Chapman and Hall, New York
Anderson A, Pietsch K, Zucker R et al (2011) Validation of a duplex real-time PCR for the detection of Salmonella spp. in different food products. Food Anal Methods 4:259–267
Auvolat A, Besse NG (2016) The challenge of enumerating Listeria monocytogenes in food. Food Microbiol 53:135–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2015.09.003
Bergis H, Lombard B, EURL for Listeria monocytogenes (2018) EURL Lm Guidance Document to evaluate the competence of laboratories implementing challenge tests and durability studies related to Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat foods. https://ec.europa.eu/food/sites/food/files/safety/docs/biosafety_fh_mc_guidance-comp-labs.pdf
Bi Y, Shu M, Zhong C et al (2020) A novel sds rinse and immunomagnetic beads separation combined with real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid and sensitive detection of Salmonella in ready-to-eat duck meat. Food Anal Methods. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01735-1
Cho A-R, Dong H-J, Seo K-H, Cho S (2014) Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detecting Listeria monocytogenes prfA in milk. Food Sci Biotechnol 23:467–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0064-x
Cho IH, Ku S (2017) Current technical approaches for the early detection of foodborne pathogens: challenges and opportunities. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102078
Day JB, Hammack TS (2019) Bio-Plex suspension array immuno-detection of Listeria monocytogenes from cantaloupe and packaged salad using virulence protein inducing activated charcoal enrichment media. J Food Microbiol 84:103225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2019.05.009
EFSA and ECDC (European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control) (2018) The European Union Summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses and zoonotic agents and food-borne outbreaks in 2017. EFSA J 16:5500. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2014.3547
Garrido-Maestu A, Azinheiro S, Carvalho J et al (2017a) Combination of microfluidic loop-mediated isothermal amplification with gold nanoparticles for rapid detection of Salmonella spp. in food samples. Front Microbiol 8:1–8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02159
Garrido-Maestu A, Azinheiro S, Carvalho J et al (2018) development and evaluation of loop-mediated isothermal amplification, and recombinase polymerase amplification methodologies, for the detection of Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat food samples. Food Control 86:27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.11.006
Garrido-Maestu A, Chapela M-J, Peñaranda E, Cabado AG (2015) Re-evaluation of Enhanced qPCR Prevalidated Method for Next-day Detection of Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Escherichia coli O157 and Listeria monocytogenes. Food Biotechnol 29:317–335. https://doi.org/10.1080/08905436.2015.1091977
Garrido-Maestu A, Fuciños P, Azinheiro S et al (2017b) Systematic loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for rapid detection and characterization of Salmonella spp., Enteritidis and Typhimurium in food samples. Food Control 80:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.05.011
Garrido-Maestu A, Azinheiro S, Carvalho J et al (2019) Combination of immunomagnetic separation and real-time recombinase polymerase amplification (IMS-qRPA) for specific detection of Listeria monocytogenes in smoked salmon samples. J Food Sci In Press. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14662
Garrido A, Chapela MJ, Román B et al (2013) A new multiplex real-time PCR developed method for Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes detection in food and environmental samples. Food Control 30:76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.06.029
Gómez-Hens A, Fernández-Romero JM, Aguilar-Caballos MP (2008) Nanostructures as analytical tools in bioassays. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 27(394):406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2008.03.006
Hice SA, Clark KD, Anderson JL, Brehm-Stecher BF (2018) Capture, concentration and detection of Salmonella in foods using magnetic ionic liquids and recombinase polymerase amplification. Anal Chem 11:850. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04751
Hudson JA, Lake RJ, Savill MG et al (2001) Rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes in ham samples using immunomagnetic separation followed by polymerase chain reaction. J Appl Microbiol 90:614–621. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.2001.01287.x
Kaclíková E, Kuchta T, Kay H, Gray D (2001) Separation of Listeria from cheese and enrichment media using antibody-coated microbeads and centrifugation. J Microbiol Methods 46:63–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-7012(01)00255-X
Kawasaki S, Horikoshi N, Okada Y et al (2005) Multiplex PCR for simultaneous detection of Salmonella spp., Listeria monocytogenes, and Escherichia coli O157: H7 in meat samples. J Food Prot 68:551–556
Kim JY, Lee J-L (2016) Development of a multiplex real-time recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) assay for rapid quantitative detection of Campylobacter coli and jejuni from eggs and chicken products. Food Control 73:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.10.041
Koo OK, Aroonnual A, Bhunia AK (2011) Human heat-shock protein 60 receptor-coated paramagnetic beads show improved capture of Listeria monocytogenes in the presence of other Listeria in food. J Appl Microbiol 111:93–104. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.05040.x
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
Mao Y, Huang X, Xiong S et al (2016) Large-volume immunomagnetic separation combined with multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria ivanovii in lettuce. Food Control 59:601–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.06.048
Ohtsuka K, Tanaka M, Ohtsuka T et al (2010) Comparison of detection methods for Escherichia coli O157 in beef livers and carcasses. Foodborne Pathog Dis 7:1563–1567. https://doi.org/10.1089/fpd.2010.0585
Park JY, Park K, Ok G, Chang HJ, Park TJ, Choi SW, Lim MC (2020) Detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 using automated immunomagnetic separation and enzyme-based colorimetric assay. Sensors 20(5):1395
Prado M, Espiña B, Fernandez-Argüelles MT et al (2016) Detection of foodborne pathogens using nanoparticles. Advantages and trends. Antimicrob Food Packag. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-800723-5.00014-0
Ricci A, Allende A, Bolton D et al (2018) Listeria monocytogenes contamination of ready-to-eat foods and the risk for human health in the EU. EFSA J. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5134
Rodríguez-Lázaro D, Pla M, Scortti M et al (2005) A novel real-time PCR for Listeria monocytogenes that monitors analytical performance via an internal amplification control. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:9008–9012
Rossmanith P, Krassnig M, Wagner M, Hein I (2006) Detection of Listeria monocytogenes in food using a combined enrichment/real-time PCR method targeting the prfA gene. Res Microbiol 157:763–771
Suh SH, Jaykus L-A, Brehm-Stecher B (2013) Advances in separation and concentration of microorganisms from food samples. In: Sofos J (ed) Advances in microbial food safety. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 173–192
Tomas D, Rodrigo A, Hernandez M, Ferrus MA (2009) Validation of real-time PCR and Enzyme-Linked fluorescent assay-based methods for detection of Salmonella spp. in chicken feces samples. Food Anal Methods 2:180–189
Uyttendaele M, Van Hoorde I, Debevere J (2000) The use of immuno-magnetic separation (IMS) as a tool in a sample preparation method for direct detection of L. monocytogenes in cheese. Int J Food Microbiol 54:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-1605(99)00196-8
Valderrama WB, Dudley EG, Doores S, Cutter CN (2016) Commercially available rapid methods for detection of selected food-borne pathogens. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 56:1519–1531. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2013.775567
Välimaa A-L, Tilsala-Timisjärvi A, Virtanen E (2015) Rapid detection and identification methods for Listeria monocytogenes in the food—a review. Food Control 55:103–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.02.037
Varshney M, Yang L, Su X-L, Li Y (2005) Magnetic nanoparticle-antibody conjugates for the separation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in ground beef. J Food Prot 68:1804–1811
Wei S, Park B-J, Kim S-H et al (2019) Detection of Listeria monocytogenes using Dynabeads® anti-Listeria combined with real-time PCR in soybean sprouts. LWT 99:533–539
Yang H, Qu L, Wimbrow AN et al (2007) Rapid detection of Listeria monocytogenes by nanoparticle-based immunomagnetic separation and real-time PCR. Int J Food Microbiol 118:132–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.06.019
Zeng J, Wei H, Zhang L et al (2014) Rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in raw oysters using immunomagnetic separation combined with loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Int J Food Microbiol 174:123–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.01.004
Zilelidou E, Karmiri CV, Zoumpopoulou G et al (2016) Listeria monocytogenes strains underrepresented during selective enrichment with an ISO method might dominate during passage through simulated gastric fluid and in vitro infection of Caco-2 cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:6846–6858. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02120-16
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the project Nanotechnology Based Functional Solutions (NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000019), supported by Norte Portugal Regional Operational Programme (NORTE2020), under the PORTUGAL 2020 Partnership Agreement, through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), and by NANOIMMUNOTECH S.L. in the framework of the project Smart Factory for Safe Foods (SF4SF) supported by FEDER Innterconecta 2015 (EXP-00082964/ ITC-20151195).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Alejandro Garrido-Maestu*, Sarah Azinheiro, Joana Carvalho, Begoña Espiña and Marta Prado declare that they do not have conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent (in case humans are involved)
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garrido-Maestu, A., Azinheiro, S., Carvalho, J. et al. Evaluation and implementation of commercial antibodies for improved nanoparticle-based immunomagnetic separation and real-time PCR for faster detection of Listeria monocytogenes. J Food Sci Technol 57, 4143–4151 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04450-1
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04450-1