Abstract
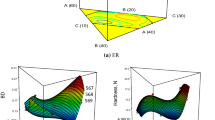
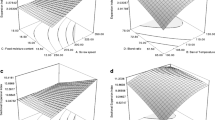
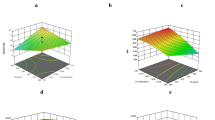
Whole pearl millet, finger millet and decorticated soy bean blended (millet soy) extrudates formulations were designed using a linear programming (LP) model to minimize the total cost of the finished product. LP formulated composite flour was extruded through twin screw food extruder at different feed rate (6.5–13.5 kg/h), screw speed (200–350 rpm, constant feed moisture (14% wb), barrel temperature (120 °C) and cutter speed (15 rpm). The physical, functional, textural and pasting characteristics of extrudates were examined and their responses were studied. Expansion index (2.31) and sectional expansion index (5.39) was found to be was found maximum for feed rate and screw speed combination 9.5 kg/h and 250 rpm. However, density (0.25 × 10−3 g/mm3) was maximum for 9.5 kg/h and 300 rpm combination. Maximum color change (10.32) was found for 9.5 kg/h feed rate and 200 rpm screw speed. The lower hardness was obtained for the samples extruded at lowest feed rate (6.5 kg/h) for all screw speed and feed rate at 9.5 kg/h for 300–350 rpm screw speed. Peak viscosity decreases with all screw speed of 9.5 kg/h feed rate.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adesina AA, Sowbhagya CM, Bhattacharya S, Zakiuddin AS (1998) Maize-soy based ready to eat extruded snack food. J Food Sci Technol 35:40–43
Arsham H (2003) http://home.ubalt.edu/ntsbarsh/Research/LpSolvers.htm Dec, 2009
Balasubramanian S, Singh N (2007) Effect of extrusion process variables and legumes on corn extrudates behaviour. J Food Sci Technol 44:330–333
Barnes HA, Hutton JF, Walters K (1990) Extensional viscosity. In an introduction to rheology. Elsevier Science, London, pp 75–96
Barrett AH, Peleg M (1992) Extrudate cell structure-texture relationships. J Food Sci 57:1253–1257
Bhattacharya M, Hanna MA (1987) Textural properties of extrusion cooked corn starch. Lebensm Wiss Technol 20:195–201
Calder B (2000) Personal communication, snack foods processing short course, food protein research and development center. Texas A & M University, College Station
Camire ME, Camire A, Krumhar K (1990) Chemical and nutritional changes in foods during extrusion. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 29:35–57
Cheman YB, Mohamad NB, Karim A, Tan TK (1992) Evaluation of flour highprotein rice-soy snack formulations. J Food Sci Technol 27:715–719
Chiang BY, Johnson JA (1977) Gelatinization of starch in extruded products. Cereal Chem 54:436–443
Chinnaswamy R, Bhattacharya KR (1983) Studies on expanded rice. Physicochemical basis of varietal differences. J Food Sci 48:1600–1604
Davidson VJ, Paton D, Diosady LL, Larocque G (1984) Degradation of wheat starch in a single-screw extruder: characteristics of starch polymers. J Food Sci 49:453–458
Deffenbaugh LB, Walker CE (1990) Use of the rapid visco-analyzer to measure starch pasting properties. Part II: Effects of emulsifiers and sugar emulsifier interactions. Starke 42:89–95
Deliza R, Macfie HJH, Hedderley D (1996) Information affects consumer assessment of sweet and bitter solutions. J Food Sci 61:1080–1084
Desrumaux A, Bouvier JM, Burri J (1999) Corn grits particle size and distribution effects on the characterstics of expanded extrudates. J Food Sci 63:857–863
Drewnowski A (1997) Taste preferences and food intake. Annu Rev Nutr 17:237–253
Eastman J, Orthoefer F, Solorio S (2001) Using extrusion to create breakfast cereal products. Cereal Foods WorldAm Assoc Cereal Chem 46:468–471
Euromonitor International (2001) Report: savory snacks market in the US. Euromonitor International, Chicago
Fan J, Mitchell JR, Blanshard JMV (1996) The effect of sugars on the extrusion of maize grits: I. The role of the glass transition in determining product density and shape. Int J Food Sci Technol 31:55-65
Fardet A, Abecassis J, Hoebler C, Baldwin PM, Buleon A, Berot S, Barry JL (1999) Influence of technological modifications of the protein network from pasta on in vitro Starch Degradation. J Cereal Sci 30:133–145
Gomez MH, Aguilera JM (1984) A physicochemical model for extrusion of corn starch. J Food Sci 49:40–43, 63
Guha M, Ali SZ, Bhattacharya S (1998) Effect of barrel temperature and screw speed on rapid viscoanalyser pasting behaviour of rice extrudate. Int J Food Sci Technol 33:259–266
Guy R, Horne AW (1988) Extrusion and co-extrusion of cereals. In: Blanshard JMV, Mitchell JV (eds) Food Structure—Its creation and evaluation. Butterworths, London, pp 331–339
Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) (1989) Nutrient requirements and recommended dietary allowances for Indians. ICMR, New Delhi, p 129
Kim YS, Wiesenborn DP, Orr PH, Grant LA (1995) Screening potato starch for novel properties using differential scanning calorimetry. J Food Sci 60:1060–1065
Lai HM (2001) Effects of hydrothermal treatment on the physicochemical properties of pregelatinized rice flour. Food Chem 72:455–463
Launay B, Lisch JM (1984) Twin-screw extrusion cooking of starches: flow behavior of starch pastes, expansion and mechanical properties of extrudates. In: Jowitt R (ed) Extrusion cooking technology. Applied Science Pub., Ltd., London, pp 159–160
Liang XM, KING JM (2003) Pasting and crystalline property differences of commercial and isolated rice starch and added amino acids. J Food Sci 68:832–838
Lin S, Huff HE, HSIEH F (2002) Extrusion process parameters, sensory characteristics, and structural properties of a high moisture soy protein meat analog. J Food Sci 67:1066–1071
Lo TE, Moreira RG, Castell ME (1998) Modelling product quality during twin screw food extrusion. Am Soc Agrl Eng 98:4106–1729
Mercier C (1977) Effect of extrusion-cooking on potato starch using a twin screw French extruder. Starch/Stäerke 29:48–52
Moore G (1994) Snack food extrusion. In: Frame ND (ed) The technology of extrusion cooking. Blackie Academic and Professional, London, pp 100–143
Onwulata CI, Konstance RP, Smith PW, Holsinger VH (2001) Co extrusion of dietary fiber and milk proteins in expanded corn products. Lebensm Wiss Technol 34:424–429
Parker JK, Hassell GM, Mottram DS, Guy RC (2000) Sensory and instrumental analyses of volatile generated during the extrusion cooking of oat flours. J Agric Food Chem 48:3497–3499
Peri C, Barbieri R, Casiraghi EM (1983) Physical chemical and nutritional quality of extruded corn germ flour and milk protein blend. J Food Technol 18:43–52
Politz ML, Timpa JD, Wasserman BP (1994) Quantitative measurement of extrusion-induced starch fragmentation products in maize flour using automated gel permeation chromatography. Cereal Chem 71:532–536
Riaz M (1997) Technology of producing snack food by extrusion. Research Department Technical Bulletin XIX(2), AIB
Schweizer TF, Reimann S, Solms J, Eliasson AC, Asp G (1986) Influence of drum drying and twin screw extrusion cooking wheat carbohydrates. II. Effect of lipids on physical properties, dehydration and complex formulation of starch in wheat flour. J Cereal Sci 4:249–260
Singh N, Smith AC (1997) A comparison of wheat starch, whole wheat meal and oat flour in the extrusion cooking process. J Food Eng 34:15–32
Singh N, Sharma B, Singh B (2000) Effect of sodium bicarbonate and monoglycerides on the extrusion behaviour of maize grits. J Food Eng 46:61–66
Wiesenborn DP, Orr PH, Casper HH, Tacke BK (1994) Potato starch paste behaviour as related to some physical/chemical properties. J Food Sci 59:644–648
Yeh AI, Jaw YM (1999) Effects of feed rate and screw speed on operating characteristics and extrudate properties during single-screw extrusion cooking of rice flour. Cereal Chem 76:236–242
Zobel HF (1984) Gelatinization of starch and mechanical properties of starch pastes. In: Whistler RL, BeMiller JN, Paschall EF (eds) Starch: chemistry and technology, 2nd edn. Academic, London, pp 285–309
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balasubramanian, S., Singh, K.K., Patil, R.T. et al. Quality evaluation of millet-soy blended extrudates formulated through linear programming. J Food Sci Technol 49, 450–458 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0297-0
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0297-0