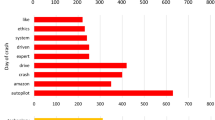
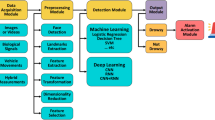
Abstract
Significant advances in embedded technologies hold promise to characterize and monitor driver’s state of alertness and detect critical levels of driver drowsiness in real-time. While some enduring solutions have been available as prototypes for a while, many of these technologies are now in the development, validation testing, or even commercialization stages. Several studies have reviewed some available fatigue and/or drowsiness detection solutions. This paper builds on previous studies and aims to provide up-to-date yet complete review on emerging driver drowsiness and alertness monitoring technologies. The contribution of this paper is to identify and review the key objective driver state monitoring technologies namely (i) driving behavioural (vehicle-based), (ii) driver behavioural (video-based), and (iii) driver physiological signals measure based technologies. Each technology is presented with a detailed description of associated detection methods and measuring metrics along with the current research activities and market products in this era. An evaluation of these technologies is also provided in term of intrusiveness, accuracy of detection, and practical use point of view. Therefore, the paper highlights open issues with these emerging systems which need further investigation in the future. We think that this study contribute to a better understanding of sleepiness at the wheel, and will help promote the implementation of accurate crash prevention technologies.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bitalino development kit. http://bitalino.com/ (2017)
Libelium mysignals development kit. http://www.my-signals.com/ (2017)
Shimmer development kit. http://www.shimmersensing.com (2017)
Abtahi, S., Hariri, B., Shirmohammadi, S.: Driver drowsiness monitoring based on yawning detection. In: 2011 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, pp 1–4 (2011)
Advanced Brain Monitoring, I.: B-alert eeg headset system. https://www.advancedbrainmonitoring.com/xseries/x10/ (2015)
Akerstedt, T., Bassetti, C., Cirignotta, F., Garcia-borreguero, D., Goncalves, M., Horne, J., Leger, D., Partinen, M., Penzel, T., Philip, P., Verster, J.C.: Sleepiness at the wheel. Institut National du Sommeil et de la Vigilance European Sleep Research Society (2013)
Akin, M., Kurt, M., Sezgin, M., Bayram, M.: Estimating vigilance level by using eeg and emg signals. Neural Comput. Appl. 17, 227–236 (2008)
Albrecht: Fas-100 driver assistant system. http://service.alan-electronics.de/archiv/fahrer-assistenz-systeme/FAS%20100/FAS100-anleitung.pdf (2009)
Alert, F.D.: Ford’s wake-up call for europe’s sleepy drivers. Volvo Cars. http://media.ford.com (2010)
AntiSleep: Driver alert system. SmartEye http://smarteye.se/applied-solutions/ (2016)
ANTneuro, I.: Eegosports: Ultra-mobile eeg & emg recording platform. https://www.ant-neuro.com/products/eego_sports (2017)
Anund, A., Kecklund, G., Vadeby, A., Hjälmdahl, M., ÅKerstedt, T.: The alerting effect of hitting a rumble strip—a simulator study with sleepy drivers. Accid. Anal. Prev. 40(6), 1970–1976 (2008)
Applied Physics, Lab., A.: Drowsy Driver Detection System. Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore (2000). https://www.jhuapl.edu/PressRelease/000628
Arnedt, J.T., Wilde, G.J.S., Munt, P.W., MacLean, A.W.: How do prolonged wakefulness and alcohol compare in the decrements they produce on a simulated driving task? Accid. Anal. Prev. 33(3), 337–344 (2001)
Artaud, P., Planque, S., Lavergne, C., C!Ara, H., Tarriere, C., Gueguen, B., et al.: An on-board system for detecting lapses of alertness in car driving. In: Proceedings: International Technical Conference on the Enhanced Safety of Vehicles, pp 350–359. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (1995)
Arun, S., Kenneth, S., Murugappan, M.: Drowsiness detection during different times of day using multiple features. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 36(2), 243–250 (2013)
Arun, S., Sundaraj, K., Murugappan, M.: Hypovigilance detection using energy of electrocardiogram signals. Accid. Anal. Prev. 12(71), 794–799 (2012)
Balasubramanian, V., Adalarasu, K.: Emg-based analysis of change in muscle activity during simulated driving. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 11(2), 151–158 (2007)
Barea, R., Boquete, L., Mazo, M., Lopez, E.: System for assisted mobility using eye movements based on electrooculography. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 10(4), 209–218 (2002)
Barr, L., Popkin, S., Howarth, H.: An evaluation of emerging driver fatigue detection measures and technologies. Tech. rep. US department of Transportation (2009)
Bekiaris, A.: Sensation project. http://www.sensation-eu.org/ (2005)
Bergasa, L.M., Nuevo, J., Sotelo, M.A., Barea, R., Lopez, M.E.: Real-time system for monitoring driver vigilance. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 7(1), 63–77 (2006)
Bhata, V.: No-nap anti sleep alarm. http://www.thenonap.com/general.html (2010)
BioSemi, B.: Activetwo: biopotential measurement system with active electrodes. https://www.biosemi.com/products.htm (2017)
Borghini, G., Astolfi, L., Vecchiato, G., Mattia, D., Babiloni, F.: Measuring neurophysiological signals in aircraft pilots and car drivers for the assessment of mental workload fatigue and drowsiness. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 44, 58–75 (2014)
Brandt, T., Stemmer, R., Rakotonirainy, A.: Affordable visual driver monitoring system for fatigue and monotony. In: IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37583), vol. 7, pp 6451–6456 (2004)
Brown, T., Johnson, R., Milavetz, C.: Identifying periods of drowsy driving using eeg. Ann. Adv. Automot. Med. 57, 99 (2013)
Brown, T., Lee, J., Schwarz, C., Fiorentino, D., McDonald, A.: Assessing the feasibility of vehicle-based sensors to detect drowsy driving. Tech Report, National Advanced Driving Simulator University of Iowa (2014)
Brunner, D., Vasko, R., Detka, C., Monahan, J., III, C.R., Kupfer, D.: Muscle artifacts in the sleep eeg: automated detection and effect on all-night eeg power spectra. J. Sleep Res. 5(3), 155–164 (1996)
Campagne, A., Pebayle, T., Muzet, A.: Correlation between driving errors and vigilance level: influence of the driver’s age. Physiol. Behav. 80(4), 515–524 (2004)
Cao, L., Li, J., Sun, Y., Zhu, H., Yan, C.: Eeg-based vigilance analysis by using fisher score and pca algorithm. In: International Conference on Progress in Informatics and Computing PIC, pp 175–179 (2010)
Chen, L.I, Zhao, Y., Zhang, J., Zou, J.Z.: Automatic detection of alertness/drowsiness from physiological signals using wavelet-based nonlinear features and machine learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 41(21), 7344–7355 (2015)
Chen, Z., Wu, C., Zhong, M., Lyu, N., Huang, Z.: Identification of common features of vehicle motion under drowsy distracted driving: a case study in Wuhan China. Accid. Anal. Prev. 81, 251–259 (2015)
Cheng, B., Zhang, W., Lin, Y., Feng, R., Zhang, X.: Driver drowsiness detection based on multisource information. Hum. Factors Ergon. Manuf. Serv. Ind. 22(5), 450–467 (2012)
Chieh, T.C., Mustafa, M.M., Hussain, A., Hendi, S.F., Majlis, B.Y.: Development of vehicle driver drowsiness detection system using electrooculogram (eog). In: 1st International Conference on Computers, Communications, Signal Processing with Special Track on Biomedical Engineering, pp 165–168 (2005)
Chin, T.L., Che, J.C., Bor, S.L., Shao, H.H., Chih, F.C., Wang, I.J.: A real-time wireless brain-computer interface system for drowsiness detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circ. Syst. 4, 214–222 (2010)
Cognionics, I.: Quick-20: wireless dry eeg headset. https://www.cognionics.net/quick-20 (2017)
Colic, A., Marques, O., Furht, B.: Driver Drowsiness Detection Systems and Solutions, vol. 6. Springer, Berlin (2014)
Correa, A.G., Orosco, L., Laciar, E.: Automatic detection of drowsiness in eeg records based on multimodal analysis. Med. Eng. Phys. 36(2), 244–249 (2014)
Coxworth, B.: Danish anti sleep pilot systems. In: Gizmag, p 17439 (2011)
DADS: Driver alertness detection system. Intercore, Inc. http://intercoreinc.com/ (2017)
Damousis, I.G., Tzovaras, D., Strintzis, M.G.: A fuzzy expert system for the early warning of accidents due to driver hypo-vigilance. Pers. Ubiquit. Comput. 13(1), 43–49 (2009)
Dasgupta, A., George, A., Happy, S.L., Routray, A., Shanker, T.: An on-board vision based system for drowsiness detection in automotive drivers. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Sci. Appl. Math. 5(2), 94–103 (2013)
Dinges, D.F.: An overview of sleepiness and accidents. J. Sleep Res. 4, 4–14 (1995)
Dong, Y., Hu, Z., Uchimura, K., Murayama, N.: Driver inattention monitoring system for intelligent vehicles: a review. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 12(2), 596–614 (2011)
DÓrazio, T., Leo, M., Guaragnella, C., Distante, A.: A visual approach for driver inattention detection. Pattern Recog. 40, 2341–2355 (2007)
Edenborough, N., Hammoud, R., Harbach, A., Ingold, A., Kisacanin, B., Malawey, P., Newman, T., Scharenbroch, G., Skiver, S., Smith, M., Wilhelm, A., Witt, G., Yoder, E., Zhang, H.: Driver state monitor from delphi. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), vol. 2, pp 1206–1207 (2005)
Edwards, D.J., Sirois, B., Dawson, T., Aguirre, A., Davis, B., Trutschel, U.: Evaluation of fatigue management technologies using weighted feature matrix method. In: Proceedings of the Fourth International Driving Symposium on Human Factors in Driver Assessment, Training and Vehicle Design, pp 146–152 (2007)
Emotiv, I.: Epoc+ research grade 14 channel mobile eeg. https://www.emotiv.com/epoc/ (2017)
Erwin, C., Volow, M., Gray, B.: Psychophysiologic Indices of Drowsiness. Tech. rep., SAE Technical Paper (1973)
Eskandarian, A., Mortazavi, A.: Evaluation of a smart algorithm for commercial vehicle driver drowsiness detection. In: 2007 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, pp 553–559 (2007)
Eskandarian, A., Sayed, R., Delaigue, P., Blum, J., Mortazavi, A.: Advanced driver fatigue research. Rep. FMCSA-RRR-07-001 Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (2007)
EyeAlert: Distracted driving and fatigue sentinels. http://www.eyealert.com/ (2017)
EyeSight: EyeSight driver assist technology. Subaru, http://www.subaru.com/engineering/eyesight.html (2016)
FaceLab: eye tracking system. Ekstrem Makina, http://www.ekstremmakina.com/EKSTREM/product/facelab/ (2013)
Fairclough, S.H., Graham, R.: Impairment of driving performance caused by sleep deprivation or alcohol: a comparative study. Hum. Factors 41(1), 118–128 (1999)
Fischer, P.: Wake up call! understanding drowsy driving and what states can do. Governors Highway Safety Association (2016)
Flores, M., Armingol, J., de la Escalera, A.: Driver drowsiness warning system using visual information for both diurnal and nocturnal illumination conditions. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 1, 3 (2010)
Flores, M.J., Armingol, J.M., Escalera, A.D.L.: Driver drowsiness detection system under infrared illumination for an intelligent vehicle. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 5(4), 241–251 (2011)
FMI Ltd, G.: Astid advisory system for tired drivers. https://fmiltd.co.uk/astid.html (2006)
FocusBand, I: ifocusband: wearable neurofeedback brain training headband. https://focusband.com/ (2017)
Forsman, P.M., Vila, B.J., Short, R.A., Mott, C.G., Dongen, H.P.V.: Efficient driver drowsiness detection at moderate levels of drowsiness. Accid. Anal. Prev. 50, 341–350 (2013)
Fu, C.L., Li, W.K., Chun, H.C., Tung, P.S., Chin, T.L.: Generalized eeg-based drowsiness prediction system by using a self-organizing neural fuzzy system. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. 59, 2044–2055 (2012)
Fukuda, J., Akutsu, E., Aoki, K.: An estimation of driver’s drowsiness level using interval of steering adjustment for lane keeping. JSAE Rev. 16(2), 197–199 (1995)
Furugori, S., Yoshizawa, N., Iname, C., Miura, Y.: Estimation of driver fatigue by pressure distribution on seat in long term driving. Rev. Automot. Eng. 26(1), 053–058 (2005)
GmbH, B.P.: Brainvision actichamp eeg recording plateform. https://www.brainproducts.com (2017)
GmbH, R.B.: Bosch driver drowsiness detection. https://www.bosch-mobility-solutions.com/ (2015)
Golz, M., Sommer, D., Trutschel, U., Sirois, B., Edwards, D.: Evaluation of fatigue monitoring technologies. Somnologie-Schlafforschung und Schlafmedizin 14(3), 187–199 (2010)
G.Tec Medical Engineering, G.: G.nautilus: wireless biosignal acquisition system. http://www.gtec.at (2017)
Gurudath, N., Riley, H.B.: Drowsy driving detection by eeg analysis using wavelet transform and k-means clustering. Procedia Comput. Sci. 34(1), 400–409 (2014)
Häkkänen, H., Summala, H., Partinen, M., Tiihonen, M., Silvo, J.: Blink duration as an indicator of driver sleepiness in professional bus drivers. Sleep 22(6), 798–802 (1999)
Hoddes, E., Zarcone, V., Smythe, H., Phillips, R., Dement, W.C.: Quantification of sleepiness: a new approach. Psychophysiology 10(4), 431–436 (1973)
Hori, T., Sugita, Y., Koga, E., Shirakawa, S., Inoue, K., Uchida, S., Kuwahara, H., Kousaka, M., Kobayashi, T., Tsuji, Y., Terashima, M., Fukuda, K., Fukuda, N.: Proposed supplements and amendments to ’a manual of standardized terminology, techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects’, the rechtschaffen & kales (1968) standard. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 55(3), 305–310 (2001)
Horne, J.A., Baulk, S.D.: Awareness of sleepiness when driving. Psychophysiology 41(1), 161–165 (2004)
Hostens, I., Ramon, H.: Assessment of muscle fatigue in low level monotonous task performance during car driving. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 15(3), 266–274 (2005)
Hu, S., Zheng, G.: Driver drowsiness detection with eyelid related parameters by support vector machine. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(4), 7651–7658 (2009)
Huggins, J.E., Guger, C., Ziat, M., Zander, T.O., Taylor, D., Tangermann, M., Soria-Frisch, A., Simeral, J., Scherer, R., Rupp, R., Ruffini, G., Robinson, D.K.R., Ramsey, N.F., Nijholt, A., Müller-Putz, G., McFarland, D.J., Mattia, D., Lance, B.J., Kindermans, P.J., Iturrate, I., Herff, C., Gupta, D., Do, A.H., Collinger, J.L., Chavarriaga, R., Chase, S.M., Bleichner, M.G., Batista, A., Anderson, C.W., Aarnoutse, E.J.: Workshops of the sixth international brain–computer interface meeting: brain–computer interfaces past, present, and future. Brain-Comput. Interfaces 4(1-2), 3–36 (2017)
Hyoki, K., Shigeta, M., Tsuno, N., Kawamuro, Y., Kinoshita, T.: Quantitative electro-oculography and electroencephalography as indices of alertness. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 106(3), 213–219 (1998)
Iber, C., Ancoli-Israel, S., Chesson, A., Quan, S.: The aasm manual for the scoring of sleep and associated events: rules, terminology and technical specifications. American Academy of Sleep Medicine (2007)
IDMT, F.: Eyetracker Driver Micro-Sleep Alerter. Fraunhofer. https://www.idmt.fraunhofer.de/en/institute.html(2015)
IMEC, I.: Eeg headset for emotion detection for wearable health solutions. https://www.imec-int.com/ (2017)
Ingre, M., Åkerstedt, T., Peters, B., Anund, A., Kecklund, G.: Subjective sleepiness, simulated driving performance and blink duration: examining individual differences. J. Sleep Res. 15(1), 47–53 (2006)
InSight: Sensomotoric instruments gmbh. SMI. http://www.smivision.com/en/gaze-and-eye-trackingsystems/services/smi-eye-tracking-roadshow.html (2017)
Interaxon, I.: Muse: immersive meditation wireless eeg device. https://choosemuse.com/ (2017)
Ji, Q., Zhu, Z., Lan, P.: Real-time nonintrusive monitoring and prediction of driver fatigue. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 53(4), 1052–1068 (2004)
Johns, M.: Optalert automotive video camera system. http://www.optalert.com/ (2002)
Johns, M.W.: A new method for measuring daytime sleepiness: the Epworth sleepiness scale. Sleep 14(6), 540–545 (1991)
Kang, H.B.: Various approaches for driver and driving behavior monitoring: a review. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, pp 616–623 (2013)
Katsis, C.D., Ntouvas, N.E., Bafas, C.G., Fotiadis, D.I.: Assessment of muscle fatigue during driving using surface emg. In: Inproceedings of the IASTED International Conference on Biomedical Engineering, vol. 262, pp 1–4 (2004)
Khushaba, R.N., Kodagoda, S., Lal, S., Dissanayake, G.: Driver drowsiness classification using fuzzy wavelet-packet-based feature-extraction algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 58(1), 121–131 (2011)
Kickstarter, I.: Steer: wearable device that will not let you fall asleep. https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/creativemode/steer-you-will-never-fall-asleep-while-driving?lang=fr (2018)
Krajewski, J., Sommer, D., Trutschel, U., Edwards, D., Golz, M.: Steering wheel behavior based estimation of fatigue. In: Proc. 5Th Int. Driving Symp. Human Factors Driver Assessment, pp 118–124 (2009)
Kurt, M.B., Sezgin, N., Akin, M., Kirbas, G., Bayram, M.: The ann-based computing of drowsy level. Expert Systems with Applications 36(2, Part 1), 2534–2542 (2009)
Lal, S.K.L., Craig, A.: A critical review of the psychophysiology of driver fatigue. Biol. Psychol. 55(3), 173–194 (2001)
Lawoyin, S.: Novel Technologies for the Detection and Mitigation of Drowsy Driving. Ph.D. thesis, Virginia Commonwealth University (2014)
Lee, B.G., Lee, B.L., Chung, W.Y.: Mobile healthcare for automatic driving sleep-onset detection using wavelet-based eeg and respiration signals. Sensors 14(10), 17915–17936 (2014)
Lee, B.G., Park, J.H., Pu, C.C., Chung, W.Y.: Mobile-based kernel-fuzzy-c-means-wavelet for driver fatigue prediction with cloud computing. In: IEEE SENSORS Proceedings, pp 1236–1239 (2014)
Lee, S., Shin, Y., Woo, S., Kim, K., Lee, H.N.: Review of wireless brain-computer interface systems. In: Brain-Computer Interface Systems-Recent Progress and Future Prospects, pp 215–238. Intech (2013)
Lew, M., Sebe, N., Huang, T., Bakker, E., Vural, E., Cetin, M., Ercil, A., Littlewort, G., Bartlett, M., Movellan, J.: Drowsy driver detection through facial movement analysis. In: Human-Computer Interaction, vol. 4796, pp 6–18. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Lexus, A.: Pre-collision system with driver attention monitor. https://www.lexus.com/models/GX/safety/pre-collision-system (2010)
Li, G., Chung, W.Y.: Detection of driver drowsiness using wavelet analysis of heart rate variability and a support vector machine classifier. Sensors 13(12), 16494–16511 (2013)
Li, W., He, Q.C., Fan, X.M., Fei, Z.M.: Evaluation of driver fatigue on two channels of eeg data. Neurosci. Lett. 506(2), 235–239 (2012)
Liang, W.C., Yuan, J., Sun, D.C., Lin, M.H.: Changes in physiological parameters induced by indoor simulated driving: effect of lower body exercise at mid-term break. Sensors 9(9), 6913–6933 (2009)
Liao, L.D., Lin, C.T., McDowell, K., Wickenden, A.E., Gramann, K., Jung, T.P., Ko, L., Chang, J.Y.: Biosensor technologies for augmented brain–computer interfaces in the next decades. Proc. IEEE 100(Special Centennial Issue), 1553–1566 (2012)
Lin, C.T., Chen, Y.C., Huang, T.Y., Chiu, T.T., Ko, L.W., Liang, S.F., Hsieh, H.Y., Hsu, S.H., Duann, J.R.: Development of wireless brain computer interface with embedded multitask scheduling and its application on real-time driver’s drowsiness detection and warning. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 55(5), 1582–2008 (2008)
Lin, C.T., Huang, K.C., Chuang, C.H., Ko, L.W., Jung, T.P.: Can arousing feedback rectify lapses in driving? prediction from eeg power spectra. J. Neural Eng. 10(5), 024–056 (2013)
Lin, C.T., Ko, L., Chung, I.F., Huang, T.Y., Chen, Y.C., Jung, T.P., Liang, S.F.: Adaptive eeg-based alertness estimation system by using ica-based fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 53(11), 2469–2476 (2006)
Lin, F.C., Ko, L.W., Chuang, C.H., Su, T.P., Lin, C.T.: Generalized eeg-based drowsiness prediction system by using a self-organizing neural fuzzy system. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 59(9), 2044–2055 (2012)
Liu, C.C., Hosking, S.G., Lenné, M.G.: Predicting driver drowsiness using vehicle measures: recent insights and future challenges. J. Safety Res. 40(4), 239–245 (2009)
Liu, C.C., Hosking, S.G., Lenné, M.G.: Predicting driver drowsiness using vehicle measures: recent insights and future challenges. J. Safety Res. 40(4), 239–245 (2009)
Liu, D., Sun, P., Xiao, Y., Yin, Y.: Drowsiness detection based on eyelid movement. In: 2010 Second International Workshop on Education Technology and Computer Science, vol. 2, pp 49–52 (2010)
Liu, J., Zhang, C., Zheng, C.: Eeg-based estimation of mental fatigue by using kpca-hmm and complexity parameters. Biomed. Signal. Process. Contr. 5, 124–130 (2010)
Liu, N.H., Chiang, C.Y., Hsu, H.M.: Improving driver alertness through music selection using a mobile eeg to detect brainwaves. Sensors 13(7), 8199–8221 (2013)
Mardi, Z., Ashtiani, S.N., Mikaili, M.: Eeg-based drowsiness detection for safe driving using chaotic features and statistical tests. J. Med. Signals Sens. 1(2), 130–137 (2011)
mBrainTrain, L.: Smarting: small simple and mobile eeg device. https://mbraintrain.com/smarting/ (2017)
McKernon, S.: A Literature Review on Driver Fatigue among Drivers in the General Public. Tech. rep., Land Transport New Zealand (2009)
MindMedia, N.: Nexus-4: entry-level system for biofeedback and neurofeedback. https://www.mindmedia.com/en/products/nexus-4/ (2017)
Mittal, A., Kumar, K., Dhamija, S., Kaur, M.: Head movement-based driver drowsiness detection: a review of state-of-art techniques. In: IEEE International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICETECH), pp 903–908 (2016)
Miyaji, M., Kawanaka, H., Oguri, K.: Driver’s cognitive distraction detection using physiological features by the Adaboost. In: IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, ITSC, pp 90–95 (2009)
Monk, T.H.: A visual analogue scale technique to measure global vigor and affect. Psychiatry Res. 27(1), 89–99 (1989)
Morales, J.M., Stasi, L.L.D., Díaz-Piedra, C., Morillas, C., Romero, S.: Real-time monitoring of biomedical signals to improve road safety. In: International Work-Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Pp. 89–97. Springer (2015)
Morris, D.M., Pilcher, J.J., III, F.S.S.: Lane heading difference an innovative model for drowsy driving detection using retrospective analysis around curves. Accid. Anal. Prev. 80, 117–124 (2015)
Murugappan, M., Wali, M.K., Ahmmad, R.B., Murugappan, S.: Subtractive fuzzy classifier based driver drowsiness levels classification using eeg. In: International Conference on Communications and Signal Processing (ICCSP), pp 159–164. IEEE (2013)
M.V.: Driver alertness detection system. Volvo Cars. http://www.media.volvocars.com (2017)
Neurocom, I.: Vigiton: driver vigilance telemetric control system. http://www.neurocom.ru/en2/product/vigiton.html (2013)
Neurocom, J.: Driver vigilance telemetric control system (dvtcs). http://www.neurocom.ru/en2/product/edvtcs.html (2008)
Neuroelectrics, N.: Enobio: wearable, wireless electrophysiology sensor system for the recording of eeg. https://www.neuroelectrics.com/products/enobio/enobio-8/ (2017)
NeuroScan, C.: Curry scan nuamps express for eeg and erp recording. https://compumedicsneuroscan.com/(2017)
NeuroScan, C.: Quik-cap electrode system. https://compumedicsneuroscan.com/quik-cap-electrode-system/(2017)
NeuroSky, I.: Mindwave: mobile 2 eeg brainwave sensing headset. https://store.neurosky.com/pages/mindwave(2015)
NeuroTherapeutics, I.: Versus: neuroperfomance assessment wireless eeg headset. https://www.emotiv.com/epoc/(2017)
Olimex, L.: Openeeg: open source hardware board. http://openeeg.sourceforge.net/doc/simpleEEG/ (2017)
OpenBCI, I.: Open source biosensing tools. https://openbci.com/ (2017)
Osram Opto Semiconductors, S.: Siemens infrared light-emitting diode (ir-led) for driver microsleep recognition. https://www.siemens.com (2010)
Otmani, S., Pebayle, T., Roge, J., Muzet, A.: Effect of driving duration and partial sleep deprivation on subsequent alertness and performance of car drivers. Physiol. Behav. 84(5), 715–724 (2005)
Papadelis, C., Chen, Z., Kourtidou-Papadeli, C., Bamidis, P.D., Chouvarda, I., Bekiaris, E., Maglaveras, N.: Monitoring sleepiness with on-board electrophysiological recordings for preventing sleep-deprived traffic accidents. Clin. Neurophysiol. 118(9), 1906–1922 (2007)
Patel, M., Lal, S., Kavanagh, D., Rossiter, P.: Applying neural network analysis on heart rate variability data to assess driver fatigue. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(6), 7235–7242 (2011)
Peng, Y., Boyle, L.N., Hallmark, S.L.: Driver’s lane keeping ability with eyes off road: insights from a naturalistic study. Accid. Anal. Prev. 50, 628–634 (2013)
Peters, R.D., Wagner, E.K., Alicandri, E., Fox, J.E., Thomas, M.L., Thorne, D.R., Sing, H.C., Balwinski, S.M.: Effects of partial and total sleep deprivation on driving performance. Public Roads 62(4) (1999)
Philip, P., Sagaspe, P., Moore, N., Taillard, J., Charles, A., Guilleminault, C., Bioulac, B.: Fatigue, sleep restriction and driving performance. Accid. Anal. Prev. 37(3), 473–478 (2005)
Picot, A., Charbonnier, S., Caplier, A.: Drowsiness detection based on visual signs: blinking analysis based on high frame rate video. In: 2010 IEEE Instrumentation Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings, pp 801–804 (2010)
Pratt, R.: Cognex’s safetrac in-vehicle safety system. https://www.cognex.com (2007)
Pratt, R.: Iteris safety direct and lane departure warning (ldw) system. https://www.iteris.com (2007)
QUSAR Sensing, I.: Dsi 10-20: wireless headset sensor interface. https://compumedicsneuroscan.com/quik-cap-electrode-system/ (2016)
Rosipal, R., Lewandowski, A., Dorffner, G.: In search of objective components for sleep quality indexing in normal sleep. Biol. Psychol. 94(1), 210–220 (2013)
ROSPA: Driver fatigue and road accidents: a literature review and position paper. Technical report, The Royal Society for the prevention of accidents, Birmingham U.K (2001)
Royal, D., Street, F., Suite, N.W.: National Survey of Distracted and Drowsy Driving Attitudes and Behavior. Technical report, National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (2002)
Sahayadhas, A., Sundaraj, K., Murugappan, M.: Detecting driver drowsiness based on sensors: a review. Sensors 12(12), 16937–16953 (2012)
Sanjaya, K., Lee, S., Katsuura, T.: Review on the application of physiological and biomechanical measurement methods in driving fatigue detection. Journal of Mechatronics, Electrical Power and Vehicular Technology 7(1) (2016)
Sayed, R., Eskandarian, A., Oskard, M.: Driver drowsiness detection using artificial neural networks. In: Transportation Research Board 80Th Annual Meeting, pp 1–13 (2001)
Shen, K.Q., Li, X.P., Ong, C.J., Shao, S.Y., Wilder-Smith, E.P.V.: Eeg-based mental fatigue measurement using multi-class support vector machines with confidence estimate. Clin. Neurophysiol. 119(7), 1524–1533 (2008)
Shen, W., Sun, H., Cheng, E., Zhu, Q., Li, Q.: Effective driver fatigue monitoring through pupil detection and yawing analysis in low light level environments. Int. J. Digit. Technol. Appl 6, 372–383 (2012)
Shin, H.S., Jung, S.J., Kim, J.J., Chung, W.Y.: Real time car driver’s condition monitoring system. In: IEEE Sensors, pp 951–954 (2010)
Sigari, M.H., Pourshahabi, M.R., Soryani, M., Fathy, M.: A review on driver face monitoring systems for fatigue and distraction detection. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 64(1), 73–100 (2014)
Slobinsky, N.: Mobileye vision-based driver assistance systems. https://www.mobileye.com/ (2009)
S.N.: Saab Driver Attention Warning System. Saabnetwork http://www.saabnet.com/tsn/press/071102.html(2015)
StopSleep, I.: Sleepiness prevention ring. https://www.stopsleep.fr/ (2017)
Subasi, A.: Automatic recognition of alertness level from eeg by using neural network and wavelet coefficients. Expert Syst. Appl. 28(4), 701–711 (2005)
Tansakul, W., Tangamchi, P.: Fatigue driver detection system using a combination of blinking rate and driving inactivity. Jounal of Automation and Control Engineering 4(1), 33–39 (2016)
Taylor, M.: No doze: Mercedes e-class alerts drowsy drivers. Autoweek Daily Drive, December 24 (2008)
Tefft, B.C.: Asleep at the wheel: the prevalence and impact of drowsy driving. Technical Report, American Automobile Association Foundation for Traffic Safety (2010)
Thiffault, P., Bergeron, J.: Monotony of road environment and driver fatigue: a simulator study. Accid. Anal. Prev. 35(3), 381–391 (2003)
Tsuchida, A., Bhuiyan, M.S., Oguri, K.: Estimation of drowsiness level based on eyelid closure and heart rate variability. In: 31St Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society: Engineering the Future of Biomedicine, EMBC, pp 2543–2546 (2009)
Volkswagen: Driver Alert System. Volkswagen Driver Assistance Experience, http://www.volkswagen.co.uk/technology/passive-safety/driver-alert-system (2016)
Volow, M., Erwin, C.: The Heart Rate Variability Correlates of Spontaneous Drowsiness Onset, Tech. rep., SAE Technical Paper (1973)
Vuckovic, A., Radivojevic, V., Chen, A.C.N., Popovic, D.: Automatic recognition of alertness and drowsiness from eeg by an artificial neural network. Med. Eng. Phys. 24(5), 349–360 (2002)
Vural, E.: Video based detection of driver fatigue. Ph.D. Thesis. Sabanci University. Istanbul Turkey (2009)
Wang, L., Wu, X., Ba, B., Dong, W.: A vision-based method to detect perclos features. Comput. Eng. Sci. 6, 0–17 (2006)
Xia, Q., Song, Y., Zhu, X.: The research development on driving fatigue based on perclos. Tech. Autom. Appl. 6, 0–13 (2008)
Xiao, F., Bao, C.Y., Yan, F.S.: Yawning detection based on gabor wavelets and lda. J. Beijing Univ. Technol 35, 409–413 (2009)
Yang, G., Lin, Y., Bhattacharya, P.: A driver fatigue recognition model based on information fusion and dynamic bayesian network. Inform. Sci. 180(10), 1942–1954 (2010)
Yeo, M.V.M., Li, X., Shen, K., Wilder-Smith, E.P.V.: Can svm be used for automatic eeg detection of drowsiness during car driving? safety science. Med. Eng. Phys. 47(1), 115–124 (2009)
Yin, B.C., Fan, X., Sun, Y.F.: Multiscale dynamic features based driver fatigue detection. Int. J. Pattern Recogn. Artif. Intell. 23, 575–589 (2009)
Young, L.R., Sheena, D.: Eye-movement measurement techniques. Am. Psychol. 30(3), 315 (1975)
Zhang, C., Wang, H., Fu, R.: Automated detection of driver fatigue based on entropy and complexity measures. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 15(1), 168–177 (2014)
Zhang, C., Zheng, C.X., Yu, X.L.: Automatic recognition of cognitive fatigue from physiological indices by using wavelet packet transform and kernel learning algorithms. Expert Syst. Appl. 36(3), 4664–4671 (2009)
Zhang, Z., Zhang, J.: A new real-time eye tracking based on nonlinear unscented kalman filter for monitoring driver fatigue. J. Contr. Theor. Appl. 8, 181–188 (2008)
Zhao, C., Zheng, C., Zhao, M., Liu, J., Tu, Y.: Automatic classification of driving mental fatigue with eeg by wavelet packet energy and kpca-svm. International Journal of Innovative Computing Information and Control 7(3), 1157–1168 (2011)
Zilberg, E., Xu, Z.M., Burton, D., Karrar, M., Lal, S.: Methodology and initial analysis results for development of non-invasive and hybrid driver drowsiness detection systems. In: The 2nd International Conference on Wireless Broadband and Ultra Wideband Communications, Auswireless, pp 16–16. IEEE (2007)
Acknowledgements
This work was part of WISSD Project carried out in Heudiasyc Lab. and was co-funded by the French Regional Program (Hauts-de-France), and the European Regional Development Fund through the program FEDER.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doudou, M., Bouabdallah, A. & Berge-Cherfaoui, V. Driver Drowsiness Measurement Technologies: Current Research, Market Solutions, and Challenges. Int. J. ITS Res. 18, 297–319 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13177-019-00199-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13177-019-00199-w