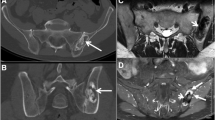
Abstract
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a critical disease which is presented by occlusion of peripheral arteries, while it could result in amputation of the involved limbs if it remained untreated before it would progress into tissue necrosis. It is usually diagnosed by CT angiography or conventional angiography, but its early diagnosis is challenging because its symptoms may be absent or like those of other diseases. In this case report, the authors showed that an atypical soft tissue uptake of lower limb incidentally found on a bone scintigraphy resulted in early diagnosis and successful treatment outcome of PAD.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasheets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Qenawy OK, Tantawy WH, Abdalla AKH, Sayed SAA. Comparative study between multi-detector CT angiography and digital subtraction angiography in evaluation of peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Egyptian J Radiol Nucl Med. 2015;46:1003–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrnm.2015.06.012.
Aboyans V, Ricco J-B, Bartelink M-LEL, Björck M, Brodmann M, Cohnert T, et al. 2017 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of peripheral arterial diseases, in collaboration with the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur Heart J. 2017;39(9):763–816. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehx095
Fowkes FGR, Murrary GD, Butcher I, Heald CL, Lee RJ, Chambless LE, et al. Ankle brachial index combined with Framingham Risk Score to predict cardiovascular events and mortality: a meta-analysis. J Am Med Ass. 2008;300(2):197–208. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.300.2.197.
Foley TR, Armstrong EJ, Waldo SW. Contemporary evaluation and management of lower extremity peripheral artery disease. Heart. 2016;102(18):1436–41. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2015-309076.
Jocius D, Vajauskas D, Skrebunas A, Gutauskas M, Tamosiunas AE. Ischemic muscle necrosis of lower extremities in peripheral arterial disease: the impact of 99mTc-MDP scintigraphy on patient management. Medicina. 2019;55(12):763. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina55120763.
Alvelo JL, Papademetris X, Mena-Hurtado C, Jeon S, Sumpio BE, Sinusas AJ, et al. Radiotracer imaging allows for noninvasive detection and quantification of abnormalities in angiosome foot perfusion in diabetic patients with critical limb ischemia and nonhealing wounds. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018;11(5): e006932. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.117.006932.
Kaye J, Hayward M. Soft tissue uptake on 99mTc methylene diphosphonate bone scan imaging: pictorial review. Australas Radiol. 2002;46(1):13–21. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1673.2001.00989.x.
Love C, Din AS, Tomas MB, Kalapparambath TP, Palestro CJ. Radionuclide bone imaging: an illustrative review. Radiographics. 2003;23(2):341–58. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.232025103.
Peller PJ, Ho VB, Kransdorf MJ. Extraosseous Tc-99m MDP uptake: a pathophysiologic approach. Radiographics. 1993;13(4):715–34. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiographics.13.4.8356264.
Masaoka S. Evaluation of arterial obstructive leg and foot disease by three-phase bone scintigraphy. Ann Nucl Med. 2001;15(3):281–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02987847.
Palot Manzil FF, Almodovar SE, Bhambhvani P. Looking beyond the indication: Bone scan for trauma providing unsuspected initial diagnosis of acute critical lower limb arterial compromise. J Nucl Med Technol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnmt.117.200618.
Schulman S, Konstantinides S, Hu Y, Tang LV. Venous thromboembolic diseases: diagnosis, management and thrombophilia testing: observations on NICE guideline [NG158]. Thromb Haemost. 2020;120(08):1143–6. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0040-1712913.
Maeseneer MD, Lenchik L, Everaert H, Marcelis S, Bossuyt A, Osteaux M, et al. Evaluation of lower back pain with bone scintigraphy and SPECT. Radiographics. 1999;19(4):901–12. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiographics.19.4.g99jl03901.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was designed by In Kook Chun. Material preparation and data collection were performed by Seong Jae Bae and In Kook Chun. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Seong Jae Bae and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Seong Jae Bae and In Kook Chun declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval and Consent to Participate
This article is a case report for which approval by an institutional review board of Kangwon National University Hospital is waived (reference number: KNUH-2022–01-017) and this study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the Helsinki declaration as revised in 2013.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bae, S.J., Chun, I.K. Incidentally Found Soft Tissue 99mTc-DPD Uptake on Bone Scintigraphy Was Useful in an Early Diagnosis of Peripheral Arterial Disease. Nucl Med Mol Imaging 56, 202–207 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-022-00750-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-022-00750-w