Abstract
Background
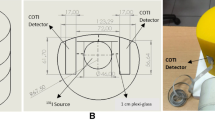
Technetium-99 m (99mTc) pertechnetate thyroid uptake rate can be measured with a gamma probe or gamma camera. This study was performed to compare their diagnostic accuracy for evaluating patients with thyrotoxicosis.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 99mTc pertechnetate thyroid uptake rate records of patients by both gamma probe and camera methods at a tertiary center in Korea from November 2019 to June 2020. We determined the normal reference ranges of thyroid uptake rate by two methods and compared both methods for differentiating Graves’ disease and thyroiditis in patients with thyrotoxicosis by receiver operating characteristic curve analysis.
Results
A total of 371 patients (euthyroid 89, Graves 167, and thyroiditis 115) were included. The normal reference range for thyroid uptake rate in euthyroid patients was 0.3–1.9% and 2.0–4.7% for the camera and probe methods, respectively. For differentiating Graves’ disease and thyroiditis, the area under the curve of the camera method (0.988) was significantly greater than that (0.975) of the probe method (p = 0.030). The sensitivity and specificity for the probe method were 92.2% and 91.3%, respectively, with a cut-off value of 3.0%. Those for the camera method were 93.4% and 94.8%, respectively, with a cut-off value of 0.7%.
Conclusion
99mTc pertechnetate thyroid uptake rate measured by the camera method had higher diagnostic accuracy than the probe method for evaluating patients with thyrotoxicosis. Considering the diagnostic accuracy and patient convenience, the thyroid uptake rate measured by the camera method would be a good substitute for the probe method.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
Hoff WVT, Pover GG, Eiser NM. Technetium-99 m in the diagnosis of thyrotoxicosis. Br Med J. 1972;4:203–6.
Atkins HL. Technetium-99m pertechnetate uptake and scanning in the evaluation of thyroid function. Semin Nucl Med. 1971;1:345–55.
Macauley M, Shawgi M, Ali T, Curry A, Howe K, Howell E, et al. Assessment of normal reference values for thyroid uptake of technetium-99m pertechnetate in a single centre UK population. Nucl Med Commun. 2018;39:834–8.
Ramos CD, Zantut Wittmann DE, Etchebehere EC, Tambascia MA, Silva CA, Camargo EE. Thyroid uptake and scintigraphy using 99mTc pertechnetate: standardization in normal individuals. Sao Paulo Med J. 2002;120:45–8.
Maisey MN, Natarajan TK, Hurley PJ, Wagner HN Jr. Validation of a rapid computerized method of measuring 99mTc pertechnetate uptake for routine assessment of thyroid structure and function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973;36:317–22.
Sahlmann CO, Siefker U, Lehmann K, Harms E, Conrad M, Meller J. Quantitative thyroid scintigraphy for the differentiation of Graves’ disease and hyperthyroid autoimmune thyroiditis. Nuklearmedizin. 2004;43:124–8.
Moon JH, Yi KH. The diagnosis and management of hyperthyroidism in Korea: consensus report of the Korean thyroid association. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2013;28:275–9.
Menon BK, Rao RD, Abhyankar A, Rajan MG, Basu S. Comparative evaluation of 24-hour thyroid 131I uptake between γ camera-based method using medium-energy collimator and standard uptake probe-based method. J Nucl Med Technol. 2014;42:194–7.
Robeson WR, Ellwood JE, Castronuovo JJ, Margouleff D. A new method to measure thyroid uptake with a gamma camera without routine use of a standard source. Clin Nucl Med. 2002;27:324–9.
Higgins HP, Ball D, Eastham S. 20-Min 99mTc thyroid uptake: a simplified method using the gamma camera. J Nucl Med. 1973;14:907–11.
Fadime D. Cut off value of technetium uptake in the differential diagnosis of Graves’ disease and subacute thyroiditis. Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol. 2020;8:54–7.
Wasilewska-Radwanska M, Stepien A, Pawlus J, Natkaniec K, Kraft O. Comparative studies of thyroid 99mTc uptake measured with gamma camera and scintillation probe. Pol J Environ Stud. 2006;15:2013–215.
Lee SM, Kim SK, Hahm JR, Jung JH, Kim HS, Kim S, et al. Differential diagnostic value of total T3/free T4 ratio in Graves’ disease and painless thyroiditis presenting thyrotoxicosis. Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27:121–5.
Sriphrapradang C, Bhasipol A. Differentiating Graves’ disease from subacute thyroiditis using ratio of serum free triiodothyronine to free thyroxine. Ann Med Surg. 2016;10:69–72.
Yoshimura Noh J, Momotani N, Fukada S, Ito K, Miyauchi A, Amino N. Ratio of serum free triiodothyronine to free thyroxine in Graves’ hyperthyroidism and thyrotoxicosis caused by painless thyroiditis. Endocr J. 2005;52:537–42.
Jeon MJ, Lee SH, Lee JJ, Han MK, Kim H-K, Kim WG, et al. Comparison of thyroid hormones in euthyroid athyreotic patients treated with levothyroxine and euthyroid healthy subjects. Int J Thyroidol. 2019;12:28–34.
Nelson JC, Renschler A, Dowswell JW. The normal thyroidal uptake of iodine. Calif Med. 1970;112:11–4.
Pittman JA Jr, Dailey GE 3rd, Beschi RJ. Changing normal values for thyroidal radioiodine uptake. N Engl J Med. 1969;280:1431–4.
Hamunyela RH, Kotze T, Philotheou GM. Normal reference values for thyroid uptake of technetium-99m pertechnetate for the Namibian population. J Endocrinol Metab Diabetes S Afr. 2013;18:142–7.
Lee H, Kim JH, Kang YK, Moon JH, So Y, Lee WW. Quantitative single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography for technetium pertechnetate thyroid uptake measurement. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:e4170.
Baskaran C, Misra M, Levitsky LL. Diagnosis of pediatric hyperthyroidism: technetium 99 uptake versus thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins. Thyroid. 2015;25:37–42.
Uchida T, Suzuki R, Kasai T, Onose H, Komiya K, Goto H, et al. Cut-off value of thyroid uptake of (99m)Tc-pertechnetate to discriminate between Graves’ disease and painless thyroiditis: a single center retrospective study. Endocr J. 2016;63:143–9.
2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid. 2016;26:1–133.
Burch HB, Cooper DS. ANNIVERSARY REVIEW: anti-thyroid drug therapy: 70 years later. Eur J Endocrinol. 2018;179:R261–74.
Kim JY, Kim JH, Moon JH, Kim KM, Oh TJ, Lee DH, et al. Utility of quantitative parameters from single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography in patients with destructive thyroiditis. Korean J Radiol. 2018;19:470–80.
Lee WW. Clinical applications of technetium-99m quantitative single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;53:172–81.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant number HI18C2383).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was designed by Jin-Sook Ryu. Material preparation and data collection were performed by Jonghwa Ahn, Seong-gil Jo, Jangwon Park, Min Ji Jeon, Won Gu Kim, Tae Yong Kim, Won Bae Kim, and Young Kee Shong. The data analysis was performed by Meihua Jin. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Meihua Jin and all authors commend on previous version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Author Meihua Jin, Author Jonghwa Ahn, Author Seong-gil Jo, Author Jangwon Park, Author Min Ji Jeon, Author Won Gu Kim, Author Tae Yong Kim, Author Won Bae Kim, Author Young Kee Shong, and Author Jin-Sook Ryu declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The present study was approved by institutional review board of the Asan Medical Center (IBR No: 2020–1708), and informed was waived due to retrospective study design. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the Helsinki declaration as revised in 2013 and its later amendments.
Consent for Publication and to Participate
Informed consent providing clearance for the use of stored material, data, and their publication after anonymization was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, M., Ahn, J., Jo, Sg. et al. Comparison of 99mTc Pertechnetate Thyroid Uptake Rates by Gamma Probe and Gamma Camera Methods for Differentiating Graves’ Disease and Thyroiditis. Nucl Med Mol Imaging 56, 42–51 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-021-00734-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-021-00734-2