Abstract
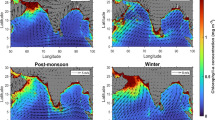
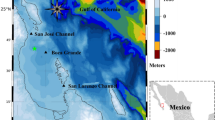
To understand the distribution of aluminum (Al) under the influence of mesocale eddies in the western South China Sea (SCS), sea level anomaly, geostrophic current, environmental parameters and reactive Al were investigated in the western SCS in August 2013. The highest reactive Al concentration ((180±64) nmol/L) was observed in the surface waters, indicating a substantial atmospheric input. Vertically, the reactive Al decreased from the surface high concentration to the subsurface minima at the depth of chlorophyll a (Chl a) maxima and then increased again with depth at most of the stations. The average concentration of reactive Al in the upper 100 m water column was significantly lower in the cyclonic eddy ((137±6) nmol/L) as compared with that in the noneddy waters ((180±21) nmol/L). By contrast, the average concentrations of Chl a and silicate in the upper 100 m water column were higher in the cyclonic eddy and lower in the anticyclonic eddy. There was a significant negative correlation between the average concentrations of reactive Al and Chl a in the upper 100 m water column. The vertical distribution of reactive Al and the negative correlation between reactive Al and Chl a both suggest that the reactive Al in the upper water column was significantly influenced by biological removal processes. Our results indicate that mesoscale eddies could regulate the distribution of reactive Al by influencing the primary production and phytoplankton community structure in the western SCS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arimoto R, Gao Y, Zhou M Y, et al. 1997. Atmospheric deposition of trace elements to the Western Pacific basin. In: Baker J E, ed. Atmospheric Deposition of Contaminants to the Great Lakes and Coastal Waters. Florida: SETAC Press, 209–225
Behrenfeld M J, Falkowski P G. 1997. Photosynthetic rates derived from satellite-based chlorophyll concentration. Limnol Oceanogr, 42(1): 1–20
Benitez-Nelson C R, Bidigare R R, Dickey T D, et al. 2007. Mesoscale eddies drive increased silica export in the subtropical Pacific Ocean. Science, 316(5827): 1017–1021
Berger C J, Lippiatt S M, Lawrence M G, et al. 2008. Application of a chemical leach technique for estimating labile particulate aluminum, iron, and manganese in the Columbia River plume and coastal waters off Oregon and Washington. J Geophys Res, 113(C2): doi: 10.1029/2007JC004703
Brown M T, Lippiatt S M, Lohan M C, et al. 2012. Trace metal distributions within a Sitka eddy in the northern Gulf of Alaska. Limnol Oceanogr, 57(2): 503–518
Chen Gengxin. 2010. Mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea: mean properties and spatio-temporal variability (in Chinese) [dissertation]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chou L, Wollast R. 1997. Biogeochemical behavior and mass balance of dissolved aluminum in the western Mediterranean Sea. Deep Sea Res II, 44(3–4): 741–768
Chow C H, Hu J H, Centurioni L R, et al. 2008. Mesoscale Dongsha Cyclonic Eddy in the northern South China Sea by drifter and satellite observations. J Geophys Res, 113(C4): C04018
Chuang M T, Chang S C, Lin N H, et al. 2013. Aerosol chemical properties and related pollutants measured in Dongsha Island in the northern South China Sea during 7-SEAS/Dongsha Experiment. Atmos Environ, 78: 82–92
Cohen D D, Garton D, Stelcer E, et al. 2004. Multielemental analysis and characterization of fine aerosols at several key ACE-Asia sites. J Geophys Res, 109(D19): D19S12
Dammshäuser A, Wagener T, Croot P L. 2011. Surface water dissolved aluminum and titanium: tracers for specific time scales of dust deposition to the Atlantic. Geophys Res Lett, 38(24): L24601
Dammshäuser A, Wagener T, Garbe-Schönberg D, et al. 2013. Particulate and dissolved aluminum and titanium in the upper water column of the Atlantic Ocean. Deep Sea Res I, 73: 127–139
Duce R A, Liss P S, Merrill J T, et al. 1991. The atmospheric input of trace species to the world ocean. Global Biogeochem Cycles, 5(3): 193–259
Gehlen M, Beck L, Calas G, et al. 2002. Unraveling the atomic structure of biogenic silica: evidence of the structural association of Al and Si in diatom frustules. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 66(9): 1601–1609
Gehlen M, Heinze C, Maier-Reimer E, et al. 2003. Coupled Al-Si geochemistry in an ocean general circulation model: a tool for the validation of oceanic dust deposition fields. Global Biogeochem Cycles, 17(1): 1028
Gelado-Caballero M D, Torres-Padrón M E, Hernández-Brito J J, et al. 1996. Aluminium distributions in Central East Atlantic waters (Canary Islands). Mar Chem, 51(4): 359–372
Giesbrecht T, Sim N, Orians K J, et al. 2013. The distribution of dissolved and total dissolvable aluminum in the Beaufort Sea and Canada Basin region of the Arctic Ocean. J Geophys Res, 118(12): 6824–6837
Han Qin, Moore J K, Zender C, et al. 2008. Constraining oceanic dust deposition using surface ocean dissolved Al. Global Biogeochem Cycles, 22(2): GB2003
Ho T Y, Chou W C, Wei C L, et al. 2010. Trace metal cycling in the surface water of the South China Sea: vertical fluxes, composition, and sources. Limnol Oceanogr, 55(5): 1807–1820
Hu Zifeng, Tan Yehui, Song Xingyu, et al. 2014. Influence of mesoscale eddies on primary production in the South China Sea during spring inter-monsoon period. Acta Oceanol Sin, 33(3): 118–128
Hydes D J. 1989. Seasonal variation in dissolved aluminium concentrations in coastal waters and biological limitation of the export of the riverine input of aluminium to the deep sea. Cont Shelf Res, 9(10): 919–929
Hydes D J, de Lange G J, de Baar H J W. 1988. Dissolved aluminium in the Mediterranean. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 52(8): 2107–2114
Kirkwood D S, Aminot A, Carlberg S. 1996. The 1994 quasimeme laboratory performance study: nutrients in seawater and standard solutions. Mar Pollut Bull, 32(8–9): 640–645
Kramer J, Laan P, Sarthou G, et al. 2004. Distribution of dissolved aluminium in the high atmospheric input region of the subtropical waters of the North Atlantic Ocean. Mar Chem, 88(3–4): 85–101
Li Faming, Ren Jingling, Yan Li, et al. 2013. The biogeochemical behavior of dissolved aluminum in the southern Yellow Sea: influence of the spring phytoplankton bloom. Chin Sci Bull, 58(2): 238–248
Li Jianbing, Ren Jingling, Zhang Jing, et al. 2008. The distribution of dissolved aluminum in the Yellow and East China Seas. J Ocean Univ China, 7(1): 48–54
McGillicuddy D J, Robinson A R, Siegel D A, et al. 1998. Influence of mesoscale eddies on new production in the Sargasso Sea. Nature, 394(6690): 263–266
Measures C I. 1999. The role of entrained sediments in sea ice in the distribution of aluminium and iron in the surface waters of the Arctic Ocean. Mar Chem, 68(1–2): 59–70
Measures C I, Brown M T, Vink S. 2005. Dust deposition to the surface waters of the western and central North Pacific inferred from surface water dissolved aluminum concentrations. Geochem Geophys Geosyst, 6(9): doi: 10.1029/2005GC000922
Measures C I, Edmond J M. 1988. Aluminum as a tracer of the deep outflow from the Mediterranean. J Geophys Res, 93(C1): 591–595
Measures C I, Edmond J M. 1990. Aluminium in the South-Atlantic: steady-state distribution of a short residence time element. J Geophys Res, 95(C4): 5331–5340
Measures C I, Hatta M, Fitzsimmons J, et al. 2015. Dissolved Al in the zonal N Atlantic section of the US GEOTRACES 2010/2011 cruises and the importance of hydrothermal inputs. Deep Sea Res II, 116: 176–186
Measures C I, Vink S. 2000. On the use of dissolved aluminum in surface waters to estimate dust deposition to the ocean. Global Biogeochem Cycles, 14(1): 317–327
Moore R M. 1981. Oceanographic distributions of zinc, cadmium, copper and aluminium in waters of the central arctic. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 45(12): 2475–2482
Moran S B, Moore R M. 1988. Evidence from mesocosm studies for biological removal of dissolved aluminium from sea water. Nature, 335(6192): 706–708
Moran S B, Moore R M. 1992. Kinetics of the removal of dissolved aluminum by diatoms in seawater: a comparison with thorium. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 56(9): 3365–3374
Narvekar P V, Singbal S Y S. 1993. Dissolved aluminium in the surface microlayer of the Eastern Arabian Sea. Mar Chem, 42(2): 85–94
Obata H, Nozaki Y, Okamura K, et al. 2000. Flow-through analysis of Al in seawater by fluorometric detection with the use of lumogallion. Field Anal Chem Technol, 4(6): 274–282
Obata H, Nozaki Y, Alibo D S, et al. 2004. Dissolved Al, In, and Ce in the eastern Indian Ocean and the Southeast Asian Seas in comparison with the radionuclides 210Pb and 210Po. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 68(5): 1035–1048
Orians K J, Bruland K W. 1986. The biogeochemistry of Aluminum in the Pacific-Ocean. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 78(4): 397–410
Parsons T R, Maita Y, Lalli C M. 1984. A Manual of Chemical and Biological Methods for Seawater Analysis. New York: Pergamon Press, 475–490
Paytan A, Mackey K R M, Chen Ying, et al. 2009. Toxicity of atmospheric aerosols on marine phytoplankton. Proc Natl Acad Sci U SA, 106(12): 4601–4605
Ren Jingling, Zhang Jing, Luo Jingqing, et al. 2001. Improved fluorimetric determination of dissolved aluminium by micelle-enhanced lumogallion complex in natural waters. Analyst, 126(5): 698–702
Ren Jingling, Zhang Jing. 2002. Studies on marine biogeochemistry of aluminum. Marine Environmental Science (in Chinese), 21(1): 68–74
Ren Jingling, Zhang Guoling, Zhang Jing, et al. 2011. Distribution of dissolved aluminum in the Southern Yellow Sea: Influences of a dust storm and the spring bloom. Mar Chem, 125(1–4): 69–81
Schüßler U, Balzer W, Deeken A. 2005. Dissolved Al distribution, particulate Al fluxes and coupling to atmospheric Al and dust deposition in the Arabian Sea. Deep Sea Res II, 52(14–15): 1862–1878
Stoffyn M. 1979. Biological control of dissolved aluminum in seawater: experimental evidence. Science, 203(4381): 651–653
Stoffyn M, Mackenzie F T. 1982. Fate of dissolved aluminum in the oceans. Mar Chem, 11(2): 105–127
Taylor S R. 1964. Trace element abundances and the chondritic earth model. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 28(12): 1989–1998
Tria J, Butler E C V, Haddad P R, et al. 2007. Determination of aluminium in natural water samples. Anal Chim Acta, 588(2): 153–165
Uematsu M, Wang Zifa, Uno I. 2003. Atmospheric input of mineral dust to the western North Pacific region based on direct measurements and a regional chemical transport model. Geophys Res Lett, 30(6): 1342
Uematsu M, Yoshikawa A, Muraki H, et al. 2002. Transport of mineral and anthropogenic aerosols during a Kosa event over East Asia. J Geophys Res, 107(D7): AAC 3-1–AAC 3–7
Wang S H, Hsu N C, Tsay S C, et al. 2012. Can Asian dust trigger phytoplankton blooms in the oligotrophic northern South China Sea. Geophys Res Lett, 39(5): L05811
Wang Zhaowei, Ren Jingling, Yan Li, et al. 2013. Preliminary study on scavenging mechanism of dissolved aluminum by phytoplankton. Acta Ecol Sin (in Chinese), 33(22): 7140–7147
Wang Guihua, Su Jilan, Chu P C. 2003. Mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea observed with altimeter data. Geophys Res Lett, 30(21): 2121
Wang Qiong, Tan Yehui, Zhou Linbin, et al. 2014. Research on dissolved aluminum in the central and southern South China Sea: can aluminum stimulate Pyrrophyta’s growth. J Trop Oceanogr (in Chinese), 33(2): 78–86
Xiu Peng, Chai Fei, Shi Lei, et al. 2010. A census of eddy activities in the South China Sea during 1993–2007. J Geophys Res, 115(C3): C03012
Xue Huijie, Chai Fei, Pettigrew N, et al. 2004. Kuroshio intrusion and the circulation in the South China Sea. J Geophys Res, 109(C2): C02017
Zhang J, Liu Sumei, Lü X, et al. 1993. Characterizing Asian wind-dust transport to the Northwest Pacific Ocean. Direct measurements of the dust flux for two years. Tellus B, 45(4): 335–345
Zhang Jing, Xu H, Ren Jingling. 2000. Fluorimetric determination of dissolved aluminium in natural waters after liquid-liquid extraction into n-hexanol. Anal Chim Acta, 405(1–2): 31–42
Zhong Chao, Xiao Wupeng, Huang Bangqin. 2013. The response of phytoplankton to mesoscale eddies in the western South China Sea. Advances in Marine Science (in Chinese), 31(2): 213–220
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Wang Junxing for helpful discussion during the preparation of this manuscript. We also appreciate the support from the captain and crews of the R/V Shiyan III.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences under contract No. XDA11020305; the National Basic Research Program (973 program) of China under contract No. 2015CB452903; the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest under contract No. 201403008; the National Project of Basic Sciences and Technology under contract No. 2017FY201404; the National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract Nos 41506150 and 41276162.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Zhou, L., Tan, Y. et al. Distribution of reactive aluminum under the influence of mesoscale eddies in the western South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 36, 95–103 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-017-1046-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-017-1046-7