Abstract
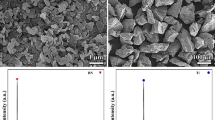
Boron carbide-reinforced copper metal matrix composites have been the subject of broad research because of their good mechanical, electrical and tribological properties. In the present research, Cu–B4C composites containing 5, 10 and 15 wt% of B4C have been fabricated by cold powder compaction followed by conventional sintering at 900 °C for 1 h under argon atmosphere. The fabricated composites are characterized by X-ray diffraction, optical microscopy and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). From microscopic study, we have found that B4C particles are homogeneously distributed in the copper matrix and there is good compatibility between B4C and Cu. The microstructure analyzed by FESEM shows that the interface between Cu matrix and B4C is clean and no interfacial product is formed. The effect of B4C particles and their weight fraction on microstructure, mechanical properties and electrical conductivity is also studied. The Vickers hardness value increases with increasing weight percentage of boron carbide in Cu matrix. The hardness value increases from 38 VHN for pure copper to 79 VHN for Cu-15 wt% B4C metal matrix composite (MMC). A maximum relative density of 82% is achieved for Cu-5 wt% B4C MMC. The maximum compressive strength of 315 MPa is achieved for Cu-15 wt% B4C MMC. The electrical conductivity of pure Cu is found to be 4.5 × 106 S/m, and it decreases to 1.92 × 106, 0.75 × 106 and 0.32 × 106 S/m for Cu-5 wt% B4C, Cu-10 wt% B4C and Cu-15 wt% B4C MMCs, respectively.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghahremani D, Ebadzadeh T, and Maghsodipour A, Ceram Int Part A 41 (2015) 1957.
Celebi Efe G, Ipek M, Zeytin S, and Bindal C, Compos Part B 43 (2012) 1813.
Nayak D, Ray N, Sahoo R, and Debata M, Tribol Trans 57 (2014) 908.
Schubert T, Trindade B, Weißgärber T, and Kieback B, Mater Sci Eng A 475 (2008) 39.
Tariolle S, Thévenot F, Aizenstein M, Dariel MP, Frumin N, and Frage N, J Solid State Chem 177 (2004) 400.
Moustafa S F, Abdel-Hamid Z, and Abd-Elhay A M, Mater Lett 53 (2002) 244.
Mansourzadeh S, Hosseini M, Salahinejad E, and Yaghtina A H, Pro Nat Sci Mater Inter 26 (2016) 613.
Yazdani A, and Salahinejad E, Mater Des 32 (2011) 3137.
Pozdniakov A V, Lotfy A, Qadir A, Shalaby E, Khomutov M G, Churyumov A Y, and Zolotorevskiy V S, Mater Sci Eng A 688 (2017) 1.
Zheng R, Chen J, Zhang Y, Ameyama K, and Ma C, Mater Sci Eng A 601 (2014) 20.
Altinsoy I, Efe F G C, Aytaş D, Kılıç M, Ozbek I, Bindal C, Period Eng Nat Sci 1 (2013) 34.
Sathiskumar R, Murugan N, Dinaharan I, and Vijay S J, Arch Metal Mater 59 (2014) 83.
Sathiskumar R, Murugan N, Dinaharan I, and Vijay S J, Mater Charac 84 (2013) 16.
Rama Rao S, and Padmanabhan G, Inter J Mater Biomat Appl 2 (2012) 18.
Shirvanimoghaddam K, Khayyam H, Abdizadeh H, Karbalaei Akbari M, Pakseresht A H, Ghasali E, and Naebe M, Mater Sci Eng A 658 (2016) 135–149.
Ahn B.-W., Kim J.-H., Hamad K., and Jung S.-B., J Alloys Compd 693 (2017) 688.
Akbari M, Shojaeefard M H, Asadi P, Khalkhali A, Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China 27 (2017) 2317.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prajapati, P.K., Chaira, D. Fabrication and Characterization of Cu–B4C Metal Matrix Composite by Powder Metallurgy: Effect of B4C on Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Electrical Conductivity. Trans Indian Inst Met 72, 673–684 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-018-1518-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-018-1518-2