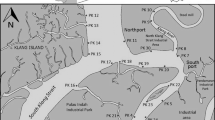
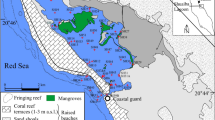
Abstract
Intertidal sediments of the inner and middle zone from the Bahía Blanca estuary were sampled for geochemical and environmental assessment of metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, Zn, Mn, Ni, Cr and Fe). Results indicate that both the organic matter content and the sediment grain size plays an important role in controlling the differential concentrations of the metals found in sediments from both zones. For most of the elements (except Mn), sediment metal concentrations were greater in the middle zone, although the concentrations did not exceed the maximums for quality of marine sediments. In this sense, anthropogenic impact (i.e., sewage drain) appears to be a key factor in the distribution of metals within the estuarine system. Comparing the levels obtained with quality levels (LEL and SEL), except Cu that showed levels slightly above the LEL, the rest of the concentrations of metals were lower to those levels. The low metal concentrations obtained within this highly impacted estuarine system suggest that the great volume of water that flooding the extensive flats in each tidal cycle has much importance. Although the potential risks of metals to the estuarine environment were low, taking into account the toxicity of some of these metals, continuity of monitoring is highly recommended.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta JA, Jansen B, Kalbitz K, Faz A, Martínez-Martínez S (2011) Salinity increases mobility of heavy metals in soils. Chemosphere 85:1318–1324. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.07.046
Andrade ML, Reyzabal ML, Marcet P, Montero MJ (2002) Industrial impact on marsh soils at the Bahia Blanca Ria, Argentina. J Environ Qual 31:532–538. doi:10.2134/jeq2002.0532
Biancalana MF, Menéndez MC, Berazategui AA, Fernández Severini MD, Hoffmeyer MS (2012) Sewage pollution effects on mesozooplankton structure in a shallow temperate estuary. Environ Monit Assess 184(6):3901–3913. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2232-2
Botté SE (2005) El rol de la vegetación en el ciclo biogeoquímico de metales pesados en Humedales del estuario de Bahía Blanca. Doctoral Thesis, Universidad Nacional del Sur (UNS), Bahía Blanca (Argentina), p 317
Botté SE, Freije RH, Marcovecchio JE (2007) Dissolved heavy metal (Cd, Pb, Cr, Ni) concentrations insurface water and porewater from Bahía Blanca estuary tidal flats. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:415–421. doi:10.1007/s00128-007-9231-6
Botté SE, Arlenghi J, Del Blanco LA, Asteasuain AA, Marcovecchio JE (2009) Variación entre pleamar y bajamar en la concentración de metales en el sedimento de planicie del Estuario de Bahía Blanca. I Reunión Argentina de Geoquímica de la Superficie, Córdoba
Botté SE, Freije RH, Marcovecchio JE (2010) Distribution of several heavy metals in tidal flats sediments within Bahía Blanca estuary (Argentina). Water Air Soil Pollut 210:371–388. doi:10.1007/s11270-009-0260-0
Chakraborty P, Sarkar A, Vudamala K, Naik R, Nath BB (2015) Organic matter—a key factor in controlling mercury distribution inestuarine sediment. Mar Chem 173:302–309. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2014.10.005
Chen Z, Saito Y, Kanai Y, Wei T, Li L, Yao H, Wang Z (2004) Low concentration of heavy metals in the Yangtze estuarine sediments, China: a diluting setting. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 60:91–100. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2003.11.021
Cifuentes O, Escudero D, Medus S, Devoto B (2012) Cadmium found in the Bahia Blanca estuary. Int Educ Sci Res J 2(10):61–79
Dewitt TH, Jones JK, Ozretich RJ, Swartz RC, Lamberson JO, Schults DW, Ditsworth GR, Smith LM, Hoselton L (1992) The influence of organic matter quality on the toxicity and partitioning of sediment-associated fluoranthene. Environ Toxicol Chem 11(2):197–208. doi:10.1002/etc.5620110209
Dean WE (1974) Determination of carbonate and organic matter in calcareous sediments and sedimentary rocks by loss on ignition: comparison with other methods. J Sediment Petrol 44:242–248. doi:10.1306/74D729D2-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D
Delgado J, Nieto JM, Boski T (2010) Analysis of the spatial variation of heavy metals in the Guadiana estuary sediments (SW Iberian Peninsula) based on GIS-mapping techniques. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 88:71–83. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2010.03.011
Du Laing G, Vandecasteele B, De Grauwe P, Moors W, Lesage E, Meers E, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2007) Factors affecting metal concentrations in the upper sediment layer of intertidal reed beds along the river Scheldt. J Environ Monit 9:449–455. doi:10.1039/b618772b
Du Laing G, De Vos R, Vandecasteele B, Lesage E, Tack FMG, Verloo MG (2008) Effect of salinity on heavy metal mobility and availability in intertidal sediments of the Scheldt estuary. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 77:589–602. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2007.10.017
Du Laing G, Rinklebe J, Vandecasteele B, Meers E, Tack FMG (2009) Trace metal behaviour in estuarine and riverine floodplain soils and sediments: a review. Sci Total Environ 407:3972–3985. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.07.025
Eggleton J, Thomas KV (2004) A review of factors affecting the release and bioavailability of contaminants during sediment disturbance events. Environ Int 30:973–980. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2004.03.001
Federal Register (1984) Definition and procedure for determination of the method detection limit. EPA, 40 CFR Part 136, Appendix B, Revision 1.11 1(11):198–199
Fernández Severini MD, Botté SE, Hoffmeyer M, Marcovecchio JE (2009) Spatial and temporal distribution of cadmium and copper in water and zooplankton in the Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 85:57–66. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2009.03.019
Ferrer L, Contardi E, Andrade SJ, Asteasuain R, Pucci AE, Marcovecchio JE (2000) Environmental cadmium and lead concentrations in the Bahía Blanca estuary (Argentina). Potential toxic effects of Cd and Pb on crab larvae. Oceanologia 42:493–504
Freije RH, Marcovecchio JE (2004) Oceanografía química. In: Piccolo MC, Hoffmeyer M (eds) Ecosistema del estuario de Bahía Blanca. Instituto Argentino de Oceanografía, Bahía Blanca, pp 69–78
Freije RH, Asteasuain RO, Schmidt AS, Zavatti JR (1981) Relación de la salinidad y temperature del agua con las condiciones hidrometeorológicas en la porción interna del estuario de Bahía Blanca. Contrib Cient IADO Nº57, p 12
Freije RH, Spetter CV, Marcovecchio JE, Popovich CA, Botté SE, Negrín V, Arias A, Delucchi F, Asteasuain RO (2008) Water chemistry and nutrients of the Bahía Blanca estuary. In: Neves R, Baretta JW, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zone management in South America. IST Press, Lisbon, pp 241–254
Gredilla A, Stoichev T, Fdez-Ortiz de Vallejuelo S, Rodriguez-Iruretagoiena A, de Morais P, Arana G, de Diego A, Madariaga JM (2015) Spatial distribution of some trace and major elements in sediments of the Cávado estuary (Esposende, Portugal). Mar Pollut Bull 99:305–311. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.07.040
Hu BH, Cui R, Li J, Wei H, Zhao J, Bai F, Song W, Ding X (2013) Occurrence and distribution of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Changhua River estuary and adjacent shelf (Hainan Island). Mar Pollut Bull 76:400–405. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.08.020
Ip CCM, Li XD, Zhang G, Wai OWH, Li YS (2007) Trace metal distribution in sediments of the Pearl River estuary and the surrounding coastal area, South China. Environ Pollut 147:311–323. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.06.028
Kim BSM, Salaroli AB, de Lima Ferreira PA, Rosemberg Sartoretto J, de Mahiques MM, Lopes Figueira RC (2016) Spatial distribution and enrichment assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from Baixada Santista, Southeastern Brazil. Mar Pollut Bul 103:333–338. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.12.041
Limbozzi F, Leitao TE (2008) Characterization of Bahía Blanca main existing pressures and their effects on the state indicators for surface and groundwater quality. In: Neves R, Baretta JW, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zone management in South America. IST Press, Lisboa
Management Consortium of the Port Bahía Blanca (2016) http://puertobahiablanca.com/estadisticaspuerto/2015/12/datosterminales1215.pdf
Marcovecchio JE, Botté SE, Delucchi F, Arias A, Fernández Severini MD, De Marco S, Tombesi N, Andrade S, Ferrer LD, Freije RH (2008) Pollution processes in Bahia Blanca estuarine environment. In: Neves R, Baretta JW, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zone management in South America. IST Press, Lisboa, pp 301–314
Martínez MV, Buzzi N, García F, Botté SE (2012) Dinámica de contaminantes inorgánicos en sedimentos intermareales en el estuario de Bahía Blanca. VIII Jornadas Nacionales de Ciencias del Mar, Comodoro Rivadavia
Negrin VL, Spetter CV, Asteasuain RO, Perillo GME, Marcovecchio JE (2011) Influence of flooding and vegetation on carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus dynamics in the pore water of a Spartina alterniflora salt marsh. J Environ Sci 23(2):212–221. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60395-6
Negrin VL, Spetter CV, Guinder VA, Perillo GME, Marcovecchio JE (2013) The role of Sarcocornia perennis and tidal flooding on sediment biogeochemistry in a South American wetland. Mar Biol Res 9(7):703–715. doi:10.1080/17451000.2013.765579
Perillo GM, Piccolo MC (1991) Tidal response in the Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina. J Coast Res 7(2):437–449
Pérez DE, Perillo GME (2002) Transporte de sedimentos del Arroyo Napostá Grande, Bahía Blanca, provincia de Buenos Aires. Asoc Argent Sedimentol 9(2):189–199
Perillo GME, Piccolo C, Parodi E, Freije RH (2001) Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina. In: Seeliger U, Kjerfve B, Mateus M (eds) Coastal marine ecosystems of Latin America, ecological studies, vol 144. Springer, Berlin, pp 205–217. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-04482-7
Persaud D, Jaagumagi R, Hayton A (1993) Guidelines for the protection and management of aquatic sediment quality in Ontario. Ontario Ministry of Environment and Energy, Ontario, p 30
Píccolo MC, Perillo GME (1990) Physical characteristics of the Bahía Blanca estuary (Argentina). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 31:303–317. doi:10.1016/0272-7714(90)90106-2
Piccolo MC, Perillo GME, Melo W (2008) The Bahía Blanca estuary: an integrated overview of its geomorphology and dynamics. In: Neves R, Baretta JW, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zone management in South America. IST Press, Lisboa, pp 219–229
PMI Report (2014) http://www.bahiablanca.gob.ar/equipos-de-trabajo/gestionambiental/comite-tecnico-ejecutivo/informes-medioambientales/informesmedioambientales-2014/
Popovich CA, Spetter CV, Marcovecchio JE, Freije RH (2008) Dissolved nutrient availability during winter diatom bloom in a turbid and shallow estuary (Bahía Blanca, Argentina). J Coast Res 24(1):95–102. doi:10.2112/06-0656.1
Pradit S, Wattayakorn G, Angsupanich S, Baeyens W, Leermakers M (2010) Distribution of trace elements in sediments and biota of Songkhla Lake, Southern Thailand. Water Air Soil Pollut 206:155–174. doi:10.1007/s11270-009-0093-x
Pratolongo P, Mazzon C, Zapperi G, Piovan MJ, Brinson MM (2013) Land cover changes in tidal salt marshes of the Bahía Blanca estuary (Argentina) during the past 40 years. Est Coast Shelf Sci 133:23–31. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2013.07.016
Rainbow PS (2007) Trace metal bioaccumulation: models, metabolic availability and toxicity. Environ Int 33:576–582. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2006.05.007
Ridgway J, Shimmield G (2002) Estuaries as repositories of historical contamination and their impact on shelf seas. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 55:903–928. doi:10.1006/ecss.2002.1035
Spetter CV, Buzzi NS, Fernández EM, Cuadrado DG, Marcovecchio JE (2015) Assessment of the physicochemical conditions sediments in a polluted tidal flat colonized by microbial mats in Bahía Blanca Estuary (Argentina). Mar Pollut Bull 91(2):491–505
Williams TP, Bubbs JM, Lester JN (1994) Metal accumulation within salt marsh environments: a review. Mar Pollut Bull 28(5):277–290. doi:10.1016/0025-326X(94)90152-X
Xu F, Qiu L, Cao Y, Huang J, Liu Z, Tian X, Li A, Yin X (2016) Trace metals in the surface sediments of the intertidal Jiaozhou Bay, China: sources and contamination assessment. Mar Pollut Bull 104:371–378. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.01.019
Zar JH (1996) Biostatistical analysis, 3rd edn. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Zhang W, Lu L, Hutchinson SM, Xu S, Chen Z, Gao X (2001) China’s Yangtze estuary: I. Geomorphic influence on heavy metal accumulation in intertidal sediments. Geomorphology 41:195–205. doi:10.1016/S0169-555X(01)00116-7
Zhang W, Feng H, Chang J, Qu J, Xie H, Yu L (2009) Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of Yangtze River intertidal zone: an assessment from different indexes. Environ Pollut 157:1533–1543. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2009.01.007
Zhao S, Feng C, Wang D, Liu Y, Shen Z (2013) Salinity increases the mobility of Cd, Cu, Mn, and Pb in the sediments of Yangtze estuary: relative role of sediments’ properties and metal speciation. Chemosphere 91:977–984. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simonetti, P., Botté, S.E. & Marcovecchio, J.E. Occurrence and spatial distribution of metals in intertidal sediments of a temperate estuarine system (Bahía Blanca, Argentina). Environ Earth Sci 76, 636 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6975-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6975-0