Abstract
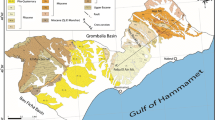
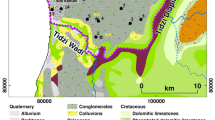
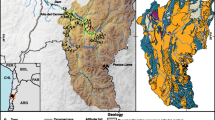
The recharge sources and groundwater degradation in the coastal plain of Oussja Ghar el Melah were investigated using geochemical and isotopes tools. We demonstrate that the water quality of shallow groundwater in the phreatic aquifer is impacted by long-term intensive irrigation. We show that the factors controlling the salinity and composition of groundwater are the return flow of the irrigation water, the water–rock interaction in the aquifer and salts formed on the surface by marine sprays. In the low plain where NO3 − content is of up to about 140 mg/L, groundwater is affected by diffuse pollution caused by intensive agricultural activities. In the upstream part of the plain and in the area situated in the SW, stable isotopes and tritium values indicate recent recharge by local precipitation.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelo CAJ, Postma D (1994) Geochemistry, groundwater and pollution. Balkema, Rotterdam
Barale V, Folving S (1996) Remote sensing of coastal interactions in the Mediterranean region. Ocean Coast Manag 30:217–233
Böhlke JK (2002) Groundwater recharge and agricultural contamination. Hydrogeol J 10:153–179
Burrolet PF, Dumon E (1952) Geological map of Porto Farina. ONM, Tunisia
Celle-Jeanton H, Zouari K, Travi Y, Daoud A (2001) Isotopic characterisation of the precipitation in Tunisia. Variations of the stable isotope compositions of rainfall events related to the origin of air masses. C R Acad Sci 333:625–631
Chelbi F, Paskoff R, Trousset P (1995) La baie d’Utique et son évolution depuis l’Antiquité: une réévaluation géoarchéologique. In: Antiquités africaines, 31, pp 7–51
Clark I, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Cruz JV, Silva MO (2000) Groundwater salinization in Pico Island (Azores, Portugal): origin and mechanisms. Environ Geol 39(10):1181–1189
Custodio E (2010) Coastal aquifers of Europe: an overview. Hydrogeol J 18(1):269–280. doi:10.1007/s10040-009-0496-1
Custodio E, Bruggeman KA (1987) Groundwater problems in coastal areas, UNESCO. Stud Repo Hydrol 45:596
David CA, William BF (1997) Use of bromide:chloride ratios to differentiate potential sources of chloride in a shallow, unconfined aquifer affected by brackish-water intrusion. Hydrogeol J 5(2):17–26
Fedrigoni L, Krimissa M, Zouari K, Maliki A, Zuppi GM (2001) Origine de la minéralisation et comportement hydrogéochimique d’une nappe phréatique soumise à des contraintes naturelles et anthropiques sévères: exemple de la nappe de Djebeniana (Tunisie). C R Acad Sci 332:665–671
Freeman JT (2007) The use of bromide and chloride mass ratios to differentiate salt-dissolution and formation brines in shallow groundwaters of the western Canadian sedimentary basin. Hydrogeol J 15:1377–1385
Freeze RA, Cherry JA (1979) Groundwater. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, p 604
Fukada T, Hiscock KM, Dennis PF (2004) A dual-isotope approach to the nitrogen hydrochemistry of an urban aquifer. Appl Geochem 19:709–719
Gourcy L, Baran N, Vittecoq B (2009) Improving the knowledge of pesticide and nitrate transfer processes using age-dating tools (CFC, SF, H) in a volcanic island (Martinique, French West Indies). J Contam Hydrol 108:107–117
Grassi S, Cortecci G (2005) Hydrogeology and geochemistry of the multilayered confined aquifer of the Pisa Plain (Tuscany–Central Italy). Appl Geochem 20:41–54
Grassi S, Cortecci G, Squarci P (2007) Groundwater resource degradation in coastal plains: the example of the Cecina area (Tuscany–Central Italy). Appl Geochem 22:2273–2289
Hem JD (1992) Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural water (3rd ed): US Geological Survey Water Supply. Paper, 2254, p 263
Hill AR (1982) Nitrate distribution in the groundwater at the Alliston region of Ontario, Canada. Ground Water 20:696–702
IAEA (1995) Reference and intercomparison materials for stable isotopes of light elements. In: Proceedings of a consultants meeting held in Vienna, 1–3/10/1993, IAEA, Vienna, TECDOC-825, p 165
IAEA/GNIP data. http://www-naweb.iaea.org/napc/ih/IHS_resources_gnip.html
Johnston CT, Cook PG, Frape SK, Plummer LN, Busenberg E, Blackport RJ (1998) Ground water age and nitrate distribution within a glacial aquifer beneath a thick unsaturated zone. Ground Water 36:171–180
Kass A, Gavrieli I, Echieli Y, Vengosh A, Starinksy A (2005) The impact of freshwater and wastewater irrigation on the chemistry of shallow groundwater: a case study from the Israeli coastal aquifer. J Hydrol 300:314–331
Knuth M, Jackson JL, Whittemore DO (1990) An integrated approach to identifying the salinity source contaminating a groundwater supply. Ground Water 28:207–214
Kouzana L, Ben Mammou A, Sfar Felfoul M (2009) Seawater intrusion and associated processes: case of the Korba aquifer (Cap-Bon, Tunisia). C R Geosci 341:21–35
Ma F, Yang YS, Yuan R, CaiS Z, Pan S (2007) Study of shallow groundwater quality evolution under saline intrusion with environmental isotopes and geochemistry. Environ Geol 51:1009–1017
Mejri L (2012) Tectonique quaternaire, paléosismicité et sources sismogéniques en Tunisie nord-orientale: Etude de la faille d’Utique. PhD Thesis: Univ. Toulouse, p 184
Mejri L, Regard V, Carretier S, Brusset S, Dlala M (2010) Evidence of Quaternary active folding near Utique (Northeast Tunisia) from tectonic observations and a seismic profile. C R Geosci 342:864–872
Melki F, Zouaghi T, Harrab S, Casas Sainz A, Bedir M, Zargouni F (2011) Structuring and evolution of Neogene transcurrent basins in the Tellian foreland domain, north-eastern Tunisia. J Geodyn 52:57–69
Oueslati A, Charfi F, Baccar F (2006) Presentation of the tunisian site: la basse vallée de oued Mejerda et la lagune de Ghar el Melah. Fifth International Meeting INCO-CT-2005-015226, p 26
Re V, Zuppi GM (2011) Influence of precipitation and deep saline groundwater on the hydrological systems of Mediterranean coastal plains: a general overview. Hydrol Sci J 56(6):966–980
Stigter TY, Van Ooijen SPJ, Post VEA, Appelo CAJ, Carvalho Dill AMM (1998) A hydrogeological and hydrochemical explanation of the groundwater composition under irrigated land in a Mediterranean environment, Algarve, Portugal. J Hydrol 208:262–279
Trabelsi R, Zairi M, Ben Dhia H (2007) Groundwater salinization of the Sfax superficial aquifer, Tunisia. Hydrogeol J 15:1341–1355
Vengosh A, Spivack AJ, Artzi Y, Ayalon A (1999) Geochemical and Boron, strontium and oxygen isotopic and geochemical constraints for the origin of the salinity in groundwater from the Mediterranean coast of Israel. Water Resour Res 35:1877–1894
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ben Ammar, S., Taupin, JD., Zouari, K. et al. Identifying recharge and salinization sources of groundwater in the Oussja Ghar el Melah plain (northeast Tunisia) using geochemical tools and environmental isotopes. Environ Earth Sci 75, 606 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5431-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5431-x