Abstract
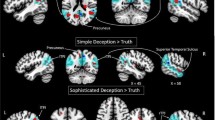
While deception is a conscious cognitive effort and self-deception is an unconscious cognitive effort. Such effort possibly shapes the working memory and generates a neural activation pattern in self-deception. Little attempt was made to identify activation pattern in self-deception. The present study investigated the phenomenon of self-deception by increasing the working memory functions using a boxcar design. functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) revealed more activation in bilateral inferior parietal lobule (BA 40), superior parietal lobule (BA 7), middle frontal gyrus (BA 9), medial frontal gyrus (BA 6), thalamus and cerebellum. Activated areas in frontal and parietal cortex suggest significant role of working memory during self-deception.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashburner J & Friston KJ (1999). Nonlinear spatial normalization using basis functions. Human Brain Mapping, 7:254–266.
Barrios V, Kwan VS, Ganis G, Gorman J, Romanowski J & Keenan JP (2008). Elucidating the neural correlates of egoistic and moralistic self-enhancement. Consciousness and Cognition, 17:451–456.
Birn RM, Cox RW & Bandettini PA (2002). Detection versus estimation in ebent related fMRI: Choosing the optimal stimulus timing. Neuroimage, 15:252–264.
Craik FIM, Moroz TM, Moscovitch M, Stuss DT, Wincour G, Tulving E & Kapur S (1999). In Search of the self: A positron emission tomography study. Psychol Sci, 10:26–34.
Duncan J & Owen AM (2000). Common regions of the human frontal lobe recruited by diverse cognitive demands. Trends Neurosciences, 23:475–483.
Fletcher PC & Henson RN (2001). Frontal lobes and human memory: insights from functional neuroimaging. Brain, 124:849–881.
Fossati P, Hevenor SJ & Graham SJ (2003). In Search of the emotional self: An fMRI study using positive and negative emotional words. Am J Psychiatry, 160:1938–1945.
Friston KJ, et al. (1995). Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: A general linear approach. Human Brain Mapping, 2:189–210.
Ganis G, Kosslyn SM, Stose S, Thompson WL & Yurgelun-Todd DA (2003). Neural correlates of different types of deception: an fMRI investigation. Cerebral Cortex, 13:830–836.
Greenwald AG & Banaji MR (1995). Implicit social cognition: Attitudes, self-esteem and stereotypes. Psychological Review, 102:4–27.
Gur RC & Sackeim HA (1979). Self-deception: A concept in search of phenomena. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 37:147–169.
Jezzard P, Matthews PM & Smith SM (2001). Functional MRI: An Introduction to Methods. Oxford University Press.
Johnson SC, Baxter LC, Wilder LS, Pipe JG, Heiserman JE & Prigatano GP (2002). Neural correlates of self-reflection. Brain, 125:1808–1814.
Kant I (1996). The Metaphysics of Morals. Translated and edited by Mary Gregor. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Koechlin E, Basso G, Pietrini P, Panzer S & Granfman J (1999). The role of the anterior prefrontal cortex in human cognition. Nature, 399:148–151.
Kwan VS, Barrios V, Ganis G, Gorman J, Lange C, Kumar M, Shepard A & Keenan JP (2007). Assessing the neural correlates of self-enhancement bias: a transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Exp Brain Res, 182:379–385.
Langleben DD, et al. (2002). Brain activity during simulated deception: an event-related functional magnetic resonance study. Neuroimage, 15:727–732.
Lee TMC, et al. (2002). Lie detection by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Human Brain Mapping, 15:157–164.
Levy N (2004). Self-deception and moral responsibility. Ratio, 3:294–311.
Lou HC, Luber B, Crupain M, Keenan JP, Nowak M, Kjaer TW, Sackeim HA & Lisanby SH (2004). Parietal cortex and representation of the mental self. Proc Natl Acad Sci, 101:6827–6832.
Nachson I (1997). The mythomanias: The nature of deception and self-deception.
Ochsner KN, Beer JS, Robertson ER, Cooper JC, Gabrieli JDE, Kihsltrom JF & D’Esposito M (2005). The neural correlates of direct and reflected self-knowledge. Neuroimage, 28: 797–814.
Okado Y, Stark C (2003). Neural processing associated with true and false memory retrieval. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci, 3:323–334.
Prabhakaran V, Narayanan Z, Zhao Z & Gabrieli JDE (2000). Integration of diverse information in working memory within the frontal lobe. Nature Neurosciences, 3:85–90.
Slotnick SD, Schacter D (2004). A sensory signature that distinguishes true from false memories. Nat Neurosci, 6: 664–672.
Smith EE & Jonides J (1998). Neuroimaging analyses of human working memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 95:12061–12068.
Spence SA, et al. (2001). Behavioural and functional anatomical correlates of deception in humans. Neuroreport, 12: 2849–2853.
Talairach J & Tournox P (1988). Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain: 3-D proportional system: An approach to cerebral imaging. Stuttgart: Thieme.
Tulving E (1972). Episodic and semantic memory. In E Tulving & W Donaldson (Eds.), Organisation of memory. New York: Academic Press.
Worsley KJ, et al. (1996). A unified statistical approach or determining significant signals in images of cerebral activation. Human Brain Mapping, 4:58–73.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, M., Modi, S., Khushu, S. et al. Neural activation pattern in self-deceivers. Psychol Stud 55, 71–76 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12646-010-0008-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12646-010-0008-3