Abstract
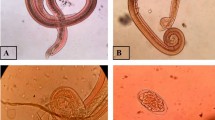
Angiostrongyliasis is a parasitic disease and a leading cause of human eosinophilic meningoencephalitis caused by rat lungworm Angiostrongylus cantonensis. This parasite infects a wide range of animal hosts, including snails and rats, which plays a significant role in zoonotic transmission. The study was conducted to determine the prevalence of A. cantonensis infection in freshwater snails and definitive rat hosts in the agricultural area in Ampayon, Butuan City, Philippines. A total of 54 rat samples and 719 snail individuals were collected in June and July 2020. An overall 2.36% prevalence rate of A. cantonensis snail infection was recorded, consisting of Pomacea canaliculata and Melanoides tuberculata, with a prevalence rate of 4.05% and 1.38%, respectively. Results revealed an overall prevalence of 38.9% in rat infection. Rattus tanezumi (48.48%) showed a higher infection than Rattus norvegicus (23.80%). Higher infection rates were found in rice field environments than residential houses, with 44.12% and 30% prevalence rates, respectively. Moreover, male rats showed higher infection rates (50%) than female rats (26.92%). Among age classes, adult rats had significantly higher infection rates (48.57%) than juvenile rats (21.05%). Correlation analysis showed a significant positive correlation between A. cantonensis infection intensity to the body length (r = 0.603; p = 0.001) and body weight (r = 0.715; p = 0.000) of rats. The study exemplifies the critical role of intermediate and definitive hosts for angiostrongyliasis. Infected freshwater snails and rats in rice fields make these agricultural areas a venue for A. cantonensis emergence. Integrated actions, health education campaigns, surveillance, hygiene, and good farming practices will help prevent the potential risk of the transmission of angiostrongyliasis in the area.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alto W (2001) Human infections with Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Pac Health Dialog 8(1):176–182 (PMID: 12017820)
Bayless DW, Darling JS, Stout WJ, Daniel JM (2012) Sex differences in attentional processes in adult rats as measured by performance on the 5-choice serial reaction time task. Behav Brain Res 235(1):48–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2012.07.028
Bayless DW, Darling JS, Daniel JM (2013) Mechanisms by which neonatal testosterone exposure mediates sex differences in impulsivity in prepubertal rats. Hor Behav 64(5):764–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2013.10.003
Castillo DSC, Paller VGV (2018) Occurrence of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in rodents from the rice granary of the Philippines and associated risk factors for zoonotic transmission. J Paras Dis 42(3):350–356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-018-1005-z
Cawas JR, Quisao CJT, Castillo DSC, Pornobi KO (2020) Prevalence of Angiostrongylus cantonensis among different species of snails in the village of Bagong Sikat Munoz, Nueva Ecija, Philippines and its associated risk factors for zoonotic transmission. J Paras Dis 44(2):388–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-020-01200-0
Constantino-Santos DMA, Basiao ZU, Wade CM, Santos BS, Fontanilla IKC (2014) Identification of Angiostrongylus cantonensis and other nematodes using the SSU rDNA in Achatina fulica populations of Metro Manila. Trop Biomed 31(2):327–335 (PMID: 25134902)
Deng ZH, Zhang QM, Lin RX, Huang S, Zhang Y, Lv S, Liu H, Hu L, Pei F, Wang J, Ruan C (2008) Survey on the natural focus of angiostrongyliasis in Guandong province. S Chi J Prev Med 34:42–45 (PMID: 20411741)
Estaño LA, Bordado AMD, Paller VGV (2020) Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection of non-native rats in Mount Makiling Forest reserve, the Philippines. Parasitology 148(2):143–148. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182020001511
Graeff-Teixeira C, da Silva ACA, Yoshimura K (2009) Update on eosinophilic meningoencephalitis and its clinical relevance. Clin Micro Rev 22(2):322–348
Harper GA, Bunbury N (2015) Invasive rats on tropical islands: their population biology and impacts on native species. Glob Eco Conserv 3:607–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2015.02.010
Heaney LR, Balete DS, Rickart EA, Utzurrum RCB, Gonzales PC (1999) Mammalian diversity on Mount Isarog, a threatened center of endemism on Southern Island, Philippines. Field Zoo New Ser 95:1–58
Heaney LRM, Dolar ML, Balete DS, Esselstyn JA, Rickart EA, Sedlock JL (2010) Field Museum website, http://www.fieldmuseum.org/philippine_mammals/.
Hochberg NS, Park SY, Blackburn BG, Sejvar JJ, Gaynor K, Chung H, Effler PV (2007) Distribution of eosinophilic meningitis cases attributable to Angiostrongylus cantonensis. Hawaii Emerg Infect Dis 13:1675–1680. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1311.070367
Hollingsworth RG, Kaneta R, Sullivan JJ, Bishop HS, Qvarnstrom Y, Da Silva AJ, Robinson DG (2007) Distribution of Parmarion cf martensi (Pulmonata: Helicarionidae), a New Semi-Slug Pest on Hawai ‘i Island, and Its Potential as a Vector for Human Angiostrongyliasis1. Pac Sci 61(4):457–467. https://doi.org/10.2984/1534-6188(2007)61[457:DOPCMP]2.0.CO;2
Jacob J, Tan G, Lange I, Saeed H, Date A, Jarvi S (2021) In vitro efficacy of anthelmintics on Angiostrongylus cantonensis L3 larvae. Parasitology 148(2):240–250. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182020001146
Jarvi S, Prociv P (2020) Angiostrongylus cantonensis and neuroangiostrongyliasis (rat lungworm disease). Parasitology 148(2):129–132. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003118202000236X
Jumawan JC, Estaño LA (2021) Prevalence of Schistosoma japonicum in bovines and Oncomelania hupensis quadrasi from ricefifields surrounding Lake Mainit, Philippines. J Paras Dis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-021-01372-3
Lv S, Zhang QM, Steinmann P, Deng ZH, Lin RX, Huang S, Zhang Y, Liu H, Hu L, Pei F, Wang J, Ruan C (2011) The emergence of angiostrongyliasis in the People’s Republic of China: the interplay between invasive snails, climate change and transmission dynamics. Freshwat Bio 56(4):717–734. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2011.02579.x
Ma M, Zhang M, Qiu Z (2018) Eosinophilic meningitis caused by Angiostrongylus cantonensis in an infant: a case report. Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000010975
Modrý D, Fecková B, Putnová B, Manalo S, Otranto D (2021) Alternative pathways in Angiostrongylus cantonensis (Metastrongyloidea: Angiostrongylidae) transmission. Parasitology 148(2):167–173. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182020001857
Niebuhr CN, Siers SR, Leinbach IL, Kaluna LM, Jarvi SI (2021) Variation in Angiostrongylus cantonensis infection in definitive and intermediate hosts in Hawaiʻi, a global hotspot of rat lungworm disease. Parasitology 148(2):133–142. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003118202000164X
Paller VG, Macaraig JRM, Verona RT, Estaño LA (2019) Cercarial fauna of freshwater snails in selected agricultural areas in Laguna, Philippines. Helminthologia 56(1):81–86. https://doi.org/10.2478/helm-2018-0040
Perrin N, Christe P, Richner H (1996) On host life-history response to parasitism. Oikos 75:317–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1286-4579(00)00389-0
Quilla MHD, Paller VGV (2020) Histopathological features and prevalence of Capillaria hepatica infection in Rattus spp. in Philippine Mount Makiling forest reserve and its adjacent areas. J Paras Dis 44(2):338–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-019-01189-1
Schwanz LE (2008) Chronic parasitic infection alters reproductive output in deer mice. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 62(8):1351–1358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-008-0563-y
Singleton GR, Belmain S, Brown PR, Aplin K, Htwe NM (2010) Impacts of rodent outbreaks on food security in Asia. Wildl Res 37(5):355–359. https://doi.org/10.1071/WR10084
Soliman S, Marzouk AS, Main AJ, Montasser AA (2001) Effect of sex, size, and age of commensal rat hosts on the infestation parameters of their ectoparasites in a rural area of Egypt. J Parasitol 87(6):1308–1316. https://doi.org/10.1645/0022-3395(2001)087[1308:EOSSAA]2.0.CO;2
Steel A, Jacob J, Klasner I, Howe K, Jacquier S, Pitt W, Hollingsworth R, Jarvi S (2021) In vitro comparison of treatments and commercially available solutions on mortality of Angiostrongylus cantonensis third-stage larvae. Parasitology 148(2):212–220. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182020001730
Tew TE, Macdonald DW (1994) Dynamics of space use and male vigour amongst wood mice, Apodemus sylvaticus, in the cereal ecosystem. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 34(5):337–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00197004
Tseng M, Myers JH (2014) The relationship between parasite fitness and host condition in an insect-virus system. PLoS One 9(9):e106401. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0106401
Tujan MA, Fontanilla IKC, Paller VGV (2016) Vectors and Spatial patterns of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in selected rice-farming villages of Muñoz, Nueva Ecija, Philippines. J Parasitol Res 2:1–7
Wang QP, Lai DH, Zhu XQ, Chen XG, Lun ZR (2008) Human angiostrongyliasis. Lancet Infect Dis 8(10):621–630
Acknowledgements
The author would like to express the most profound appreciation and gratitude to the locals of Ampayon, Butuan City, for assistance during the collection of samples and to the Department of Biology, College of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Caraga State University, for allowing the researcher to conduct the processing of samples and laboratory analysis. To: Celestial, H., Aro, K.L., Casindac, K.I., Andress, P.K., and Sevandal, E.B., for assistance collecting samples. The 6th International Angiostrongyliasis and Angiostrongylus workshop for the available information and data presentations to make this study attainable. Paller, V.G., for the completed research works in Angiostrongylus in Northern Philippines and information integration for this study conducted in Southern Philippines.
Funding
This work was supported by the Philippine Commission of Higher Education (CHED) for the research fund granted to L.A. Estaño.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed sampling: LAE performed the collection of samples and laboratory analysis as well as the writing of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Estaño, L.A. Prevalence of Angiostrongylus cantonensis in definitive and intermediate hosts collected from agricultural areas in Ampayon, Butuan City, Southern Philippines. J Parasit Dis 47, 807–814 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-023-01626-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-023-01626-2