Abstract
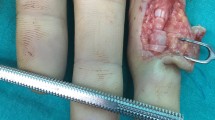
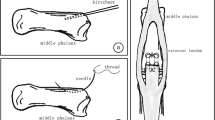
Flexor tendon laceration is a common hand injury. Timely and correct diagnosis of this defect is an important factor for restoring hand function. Post-operative adhesion is a frequent problem after tendon repair and its prevention is difficult in some types of tendon lacerations. There have been some controversial studies on the positive effect of some materials and substances on prevention of these adhesions. This study aims to evaluate effects of the Heparin in postoperative tendon adhesions. In this clinical trial, 100 patients with laceration of flexor tendons in zone II of the hand were enrolled. The patients were randomly divided into two groups. In the first group, 0.5 cc Heparin (5000 IU/cc) was injected into each tendon ends before tendon repair. In the control group, repair was carried out without any heparin injection. After 3 months the total active range of motion (TAROM), mean extension gap (MEG) and mean flexion gap (MFG) were measured and compared between these two groups. The TAROM and MEGs were not significantly different between two groups; but MFGs were significantly better in Heparin treated group (P < 0.02). However rupture rate was significantly higher in heparin treated group (P = 0.003). Heparin may improve the tendons function and reduce the postoperative adhesions in zone II of the hand; however there is a significant risk of tendon rupture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trumble TE, Vedder NB, Seiler JG 3rd, Hanel DP, Diao E, Pettrone S (2010) Zone-II flexor tendon repair: a randomized prospective trial of active place-and-hold therapy compared with passive motion therapy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92(6):1381–9
Richard HJ (1980) factors affecting the healing and return of function on the repaired digital flexor tendon. AUST N Z J Surg 50:258–263
Kleinert HE, Spokevicius S, Papas NH (1995) History of Flexor tendon repair. J Hand Surg [Am] 20(pt2):s46–s52
Strickland JW (2000) Developing of flexor tendon surgery: twenty five years of progress. J Hand Surg [Am] 20:241–235
Williamson DJ, Richards RS. FRCSC (2006) Flexor tendon injury and reconstruction. Mathes S.J, McCarthy MD. Plastic Surgery. 2nd ed, Philadelphia: Sunders. p.356
Williamson DJ,Richards RS, FRCSC (2006) Flexor tendon injury and reconstruction. Mathes S.J, McCarthy MD. Plastic Surgery 2nd ed, Philadelphia : Sunders. P. 358
Tan V, Nourbakhsh A, Capo J, Cottrell JA, Meyenhofer M, O’Connor JP (2010) Effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on flexor tendon adhesion. J Hand Surg [Am] 35(6):941–7
Kapetanos G (1982) The effect of the local corticosteroids on the healing and biomechanical properties of the partially injured tendon. Clin Orthop Relat Res 163:170–9
Zakrzewska M, Wiedlocha A, Szlachcic A, Krowarsch D, Otlewski J, Olsnes S (2009) Increased Protein stability of FGF1 can compensate for the reduced affinity for heparin. J Biol Chem 284(37):25388–25403
Tayyar M, Başbuğ M (1999) The effects of intraperitoneal piroxicam and low molecular weight heparin in prevention of adhesion reformation in rat uterine horn. Res Exp Med (Berl) 198(5):269–75
Moran SL, Ryan CK, Orlando GS, Pratt CE, Michalko KB (2000) Effects of 5- fluorouracil on flexor tendon repair. J Hand Surg [Am] 25(2):242–51
Demirkan F, Colakoglu N, Herek O, Erkula G (2002) The use of amniotic membrane in flexor tendon repair: an experimental model. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 122(7):396–9
Darmani H, Crossan J, Curtis A (2004) Single dose of Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor induces prolonged inflammatory cell accumulation and fibrosis around injured tendon and synovium. Mediat Inflamm 13(3):157–64
Ferguson RE, Rinker B (2006) The use of a hydrogel sealant on flexor tendon repairs to prevent adhesion formation. Ann Plast Surg 56(1):54–8
Tanaka T, Zhao C, Sun YL, Zobitz ME, An KN, Amadio PC (2007) The effect of carbodiimide – derivatized hyaluronic acid and gelatin surface modification on peroneus longus tendon graft in a short – term canine model in vivo. J Hand Surg [Am] 32(6):876–81
Esen E, Cila E, Ozoğul C, Taşçi AG, Sipahioğlu S, Gemalmaz HC et al (2009) The effect of low-molecular-weight heparin on rat tendon healing. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 43(1):54–61
Virchenko O, Aspenberg P, Lindahl TL (2008) Low molecular weight heparin impairs tendon repair. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 90(3):388–92
Khanna A, Friel M, Gougoulias N, Longo UG, Maffulli N (2009) Prevention of adhesions in surgery of the flexor tendons of the hand: what is the evidence? Br Med Bull 90:85–109
Compliance with Ethical Standards
Funding
This study was not funded by any institutes or organizations.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee of the Iran University of Medical Sciences and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of Interest
All Authors indicate that they do not have any conflict of interest in this study and they have not received research grants from any Company, Institute or organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akbari, H., Rahimi, A.A.K., Ghavami, Y. et al. Effect of Heparin on Post-Operative Adhesion in Flexor Tendon Surgery of the Hand. J Hand Microsurg 7, 244–249 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12593-015-0192-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12593-015-0192-4