Abstract
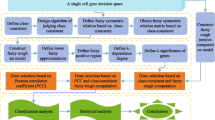
If the samples, features and information values in a real-valued information system are cells, genes and gene expression values, respectively, then for convenience, this system is said to be a single cell gene space. In the era of big data, people are faced with high dimensional gene expression data with redundancy and noise causing its strong uncertainty. D–S evidence theory excels at tackling the problem of uncertainty, and its conditions to be met are weaker than Bayesian probability theory. Therefore, this paper studies the gene selection in a single cell gene space to remove noise and redundancy with D–S evidence theory. The distance between two cells in each gene is first defined. Then, the tolerance relation is established according to the defined distance. In addition, the belief and plausibility functions to grasp the uncertainty of a single cell gene space are introduced on the basis of the tolerance classes. Statistical analysis shows that they can effectively measure the uncertainty of a single cell gene space. Furthermore, several gene selection algorithms in a single cell gene space are presented using the proposed belief and plausibility. Finally, the performance of the proposed algorithm is compared to other algorithms on some published single-cell data sets. Experimental results and statistical tests show that the classification and clustering performance of the presented algorithm not only exceeds the other three state-of-the-art algorithms, but also its gene reduction rate is very high.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
25 May 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-022-00527-x
References
Calinski T, Harabasz J (1974) A dendrite method for cluster analysis. Commun Stat 3:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610917408548446
Cornelis C, Jensen R, Martin GH, Slezak D (2010) Attribute selection with fuzzy decision reducts. Inf Sci 180:209–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2009.09.008
Dempster AP (1967) Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multivalued mapping. Ann Math Stat 38:325–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-44792-4_3
Davies DL, Bouldin DW (1979) A cluster separation measure. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 1:224–227. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.1979.4766909
Demsar J (2006) Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. J Mach Learn Res 7:1–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-005-9016-2
Deng Y, Shi WK, Zhu ZF, Liu Q (2005) Combining belief functions based on distance of evidence. Decis Support Syst 38:489–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2004.04.015
Dai JH, Xu Q (2013) Attribute selection based on information gain ratio in fuzzy rough set theory with application to tumor classification. Appl Soft Comput 13:211–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2012.07.029
Dai JH, Xu Q, Wang WT, Tian HW (2012) Conditional entropy for incomplete decision systems and its application in data mining. Int J Gen Syst 41:713–728. https://doi.org/10.1080/03081079.2012.685471
Farouq MW, Boulila W, Abdel-Aal M, Hussain A, Salem AB, Farouq MW, Boulila W, Abdel-Aal M, Hussain A, Salem AB (2019) A novel multi-stage fusion based approach for gene expression profiling in non-small cell lung cancer. IEEE Access 7:37141–37150. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2898897
Hempelmann CF, Sakoglu U, Gurupur VP, Jampana S (2016) An entropy-based evaluation method for knowledge bases of medical information systems. Expert Syst Appl 46:262–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.10.023
Jaddi NS, Abadeh MS (2022) Cell separation algorithm with enhanced search behaviour in miRNA feature selection for cancer diagnosis. Inf Syst 104:101906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.is.2021.101906
Jia XY, Rao Y, Shang L, Li TJ (2020) Similarity-based attribute reduction in rough set theory: a clustering perspective. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 11:1047–1060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-019-00959-w
Kolodziejczyk AA, Kim JK, Tsang JC, Ilicic T, Henriksson J, Natarajan KN, Tuck AC, Gao X, Buhler M, Liu P, Marioni JC, Teichmann SA (2015) Single cell RNA-sequencing of pluripotent states unlocks modular transcriptional variation. Cell Stem Cell 17:471–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2015.09.011
Li ZW, Qu LD, Zhang GQ, Xie NX (2021) Attribute selection for heterogeneous data based on information entropy. Int J Gen Syst 50(5):548–566. https://doi.org/10.1080/03081079.2021.1919101
Li L, Mu X, Li S, Peng H (2020) A review of face recognition technology. IEEE Access 8:139110–139120. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3011028
Liang JY, Shi ZZ (2006) The information entropy, rough entropy and knowledge granulation in rough set theory. Int J Uncertain Fuzziness Knowl Based Syst 12:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/03081070600687668
Navarrete J, Viejo D, Cazorla M (2016) Color smoothing for RGB-D data using entropy information. Appl Soft Comput 46:361–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.05.019
Pawlak Z (1982) Rough sets. Int J Comput Inf Sci 11:341–356. https://doi.org/10.1145/219717.219791
Patel AP, Tirosh I, Trombetta JJ, Shalek AK, Gillespie SM, Wakimoto H, Cahill DP, Nahed BV, Curry WT, Martuza RL, Louis DN, Rozenblatt O, Suva ML, Regev A, Bernstein BE (2014) Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intratumoral heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma. Science 344:1396–1401. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1254257
Pollen AA, Nowakowski TJ, Shuga J, Wang XH, Leyrat AA, Lui JH, Li N, Szpankowski L, Fowler B, Chen P, Ramalingam N, Sun G, Thu M, Norris M, Lebofsky R, Toppani D, Kemp DW, Wong M, Clerkson B, Jones BN, Wu S, Knutsson L, Alvarado B, Wang J, Weaver LS, May AP, Jones RC, Unger MA, Kriegstein AR, West JA (2014) Low-coverage single-cell mRNA sequencing reveals cellular heterogeneity and activated signaling pathways in developing cerebral cortex. Nat Biotechnol 32:1053–1058. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2967
Peng YC, Zhang QL (2021) Feature selection for interval-valued data based on DS evidence theory. IEEE Access 9:122754–122765. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3109013
Rouseeuw PJ (1987) Silhouettes: a graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J Comput Appl Math 20:53–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-0427(87)90125-7
Shannon C (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst Tech J 27:379–423. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb00917.x
Shafer G (1976) A mathematical theory of evidence. Princeton University Press, Princeton. https://doi.org/10.1515/9780691214696
https://scanpy.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
Shukla AK (2022) Chaos teaching learning based algorithm for large-scale global optimization problem and its application. Concurr Comput Pract Experience 34:e6514. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.6514
Swiniarski RW, Skowron A (2003) Rough set methods in feature selection and recognition. Pattern Recognit Lett 24:833–849. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8655(02)00196-4
Saqlain SM, Sher M, Shah FA, Khan I, Ashraf MU, Awais M, Ghani A (2019) Fisher score and Matthews correlation coefficient-based feature subset selection for heart disease diagnosis using support vector machines. Knowl Inf Syst 58:139–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8655(02)00196-4
Singh S, Shreevastava S, Som T, Somani G (2020) A fuzzy similarity-based rough set approach for attribute selection in set-valued information systems. Soft Comput 24:4675–4691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04228-4
Tibshirani R (1996) Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J R Stat Soc (Ser B) 58:267–288. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9868.2011.00771.x
Traag V, Waltman L, Eck N (2019) From Louvain to Leiden: guaranteeing well-connected communities. Sci Rep 9:5233. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-41695-z
Tan AH, Wu WZ, Tao YZ (2018) A unified framework for characterizing rough sets with evidence theory in various approximation spaces. Inf Sci 454(455):144–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2018.04.073
Usoskin D, Furlan A, Islam S, Abdo H, Lnnerberg P, Lou D, Hjerling J, Haeggstrm J, Kharchenko O, Kharchenko PV, Linnarsson S, Ernfors P (2015) Unbiased classification of sensory neuron types by large-scale single-cell RNA sequencing. Nat Neurosci 18:145–153. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3881
Wu WZ (2008) Attribute reduction based on evidence theory in incomplete decision systems. Inf Sci 178:1355–1371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2007.10.006
Wu WZ, Leung Y, Zhang WX (2002) Connections between rough set theory and Dempster–Shafer theory of evidence. Int J Gen Syst 31:405–430. https://doi.org/10.1080/0308107021000013626
Wang CZ, Wang Y, Shao MW, Qian YH, Chen DG (2020) Fuzzy rough attribute reduction for categorical data. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 28:818–830. https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2949765
Wang YB, Chen XJ, Dong K (2019) Attribute reduction via local conditional entropy. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 10(12):3619–3634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-019-00948-z
Wang CZ, Huang Y, Shao MW, Chen DG (2019) Uncertainty measures for general fuzzy relations. Fuzzy Sets Syst 360:82–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2018.07.006
Wu X, Kumar V, Quinlan JR, Ghosh J, Yang Q, Motoda H, McLachlan GJ, Ng A, Liu B, Philip SY, Zhou ZH (2008) Top 10 algorithms in data mining. Knowl Inf Syst 14:1–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-007-0114-2
Wang P, Zhang PF, Li ZW (2019) A three-way decision method based on Gaussian kernel in a hybrid information system with images: An application in medical diagnosis. Appl Soft Comput 77:734–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.01.031
Wu Y, Zhang K (2020) Tools for the analysis of high-dimensional single-cell RNA sequencing data. Nat Rev Nephrol 16:408–421. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-020-0262-0
Yao YY (2001) Information granulation and rough set approximation. Int J Intell Syst 16:87–104
Yang Y, Huh R, Houston WC, Lin Y, Michael IL, Li Y (2019) SAFE-clustering: single-cell aggregated (from Ensemble) clustering for single-cell RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 35:1269–1277. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty793
Zhang QL, Chen YY, Zhang GQ, Li ZW, Chen LJ, Wen CF (2021) New uncertainty measurement for categorical data based on fuzzy information structures: an application in attribute reduction. Inf Sci 580:541–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.08.089
Zeng AP, Li TR, Liu D, Zhang JB, Chen HM (2015) A fuzzy rough set approach for incremental feature selection on hybrid information systems. Fuzzy Sets Syst 258:39–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fss.2014.08.014
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to the reviewers and editors for their valuable comments and suggestions, which have helped us greatly improve the quality of the paper.
Funding
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (11971420) and Doctoral research start project (CZ2021YJRC01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
In the Original Publication, The affiliation of the author Ching-Feng Wen has been replaced as “Key Laboratory of Complex System Optimization and Big Data Processing in Department of Guangxi Education, Yulin Normal University, Yulin 537000, Guangxi, People’s Republic of China”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Zhang, Q., Wang, P. et al. Gene Selection in a Single Cell Gene Space Based on D–S Evidence Theory. Interdiscip Sci Comput Life Sci 14, 722–744 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-022-00518-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-022-00518-y