Abstract
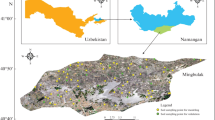
Soil salinity, is an environmental problem that threatens lands mainly in arid regions. Traditionally, monitoring of salty soils has been a hard task, due to the high expenses of soil samples analysis. Recently, remote sensing techniques provide new alternative to assess and monitor salt affected soil rapidly and over larger areas. The investigation area is a semi-arid region located in southern Tunisia. This study aims to identify classes of soil salinity, explore the potential of multispectral data to discern soil features and patterns of saline soil and predict soil salinity. For this purpose, Landsat 8 data were used to generate nineteen spectral indices. Correlations between reflectance indices and Electrical Conductivity (EC) measured on laboratory, showed that the Short Wave Infrared (SWIR) offers the best correlation with -57 %. Three salinity classes were obtained from image classification, with an overall accuracy 73%. Partial Least Square Regression (PLSR) method was applied to estimate soil salinity. The calibration model gives a moderate coefficient of determination R² =52 % and a RMSE=0.66 dS/m.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas A, Khan S (2007) Remote sensing based modelling applications in land and water management: using remote sensing techniques for appraisal of irrigated soil salinity. International Congress on Modelling and Simulation (MODSIM), Modelling and Simulation Society of Australia and New Zealand Brighton 2632-2638
Agoubi B, Kharroubi A, Abida H (2011) Hydrochemistry of groundwater and its assessment for irrigation purpose in coastal Jeffara Aquifer, southeastern Tunisia. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-011-0409-1
Allbed A, Kumar L (2013) Soil salinity mapping and monitoring in arid and semi-arid regions using remote sensing technology: a review. ARS 2:373–385
Aldakheel Y (2011) Assessing NDVI spatial pattern as related to irrigation and soil salinity management in Al-hassa oasis. Indian J Soc Remote Sens 39(2):171–180
Alexakis D, Gotsis D, Giakoumakis S (2014) Evaluation of soil salinization in a Mediterranean site (Agoulinitsa district- West Greece). Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-0141279-0
Bannari A, Guedon AM, El-Harti A, Cherkaoui F, El-Ghmari A (2008) Characterization of slightly and moderately saline and sodic soils in irrigated agriculture land using simulated data of advanced land imaging (E0-1) sensor. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 39:2795–2281. doi:10.1080/00103620802432717
Benchallal A, Oukil A, Belhadj-Aissa A (2009) Identification et détection par imagerie de la dégradation des sols par la salinité dans la cuvette de Ouargla, Sud de l’Algérie. Journées d’Animation Scientifique (JAS09) de l’AUF Alger
Berthier L, Pitres JC, Vaudour E (2008) Prediction spatiale des teneurs en carbone organique des sols par spectroscopie de terrain visible-proche infrarouge et imagerie satellitale SPOT. Etud Gest Sols 15(4):213–224
Bouaziz M, Matschullat J, Gloaguen R (2011) Improved remote sensing detection of soil salinity from a semi-arid climate in Northeast Brazil. Compt Rendus Geosci 343:795–803. doi:10.1016/j.crte.2011.09.003
Cloutis EA (1996) Hyperspectral geological remote sensing: evaluation of analytical techniques. Int J Remote Sens 17:2215–2242
Csillag F, Pasztor L, Biehl LL (1993) Spectral band selection for the characterization of salinity status of soils. Remote Sens Environ 43:231–242
Deering D, Rouse J (1975) Measuring ‘forage production’ of grazing units from Landsat MSS data, 10th International symposium on remote sensing of environment, ERIM, Ann Arbor 1169-1178
Douaoui A, Lépinard P (2010) SIG Cartographie de la salinité des sols de la plaine algerienne du Bas-Chéllif Géomatique Expert 76
FAO (2007) Extent and causes of salt-affected soils in participating countries. AGL: Global network on integrated soil management for sustainable use of salt-affected soils, http://www.fao.org/ag/agl/agll/spush/topic2.htm
Farifteh J, Farshad A, George RJ (2006) Assessing salt-affected soils using remote sensing, solute modeling and geophysics. Geoderma 130(3-4):191–206
Farifteh J, Van der Meer F, Carranza EJM (2007) Similarity measures for spectral discrimination of salt-affected soils. Int J Remote Sen 28(3):5273–5293. doi:10.1080/0143116070122704
Furby S L, Wallace J F, Caccetta P, Wheaton G A (1995) Detecting and monitoring salt-affected land: a report from the LWRRDC projectdetecting and monitoring changes in land condition through time using remotely sensed data, CSIRO Division of Mathematics and statistics
Hachicha M (2007) Les sols salés et leurs mises en valeur en Tunisie. Sécheresse 18(1):45–50. doi:10.1684/sec.2007.0063
Huete AR (1988) A soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI). Remote Sens Environ 25:295–309
IDNP. Indo-Dutch Network Project (2002) A methodology for identification of waterlogging and soil salinity conditions using remote sensing. Central Soil Salinity Research Institute, Karnal, India
Janik LJ, Merry RH, Skjemstad JO (1998) Can mid infra-red diffuse reflectance analysis replace soil extractions? Aust J Exp Agric 38(7):681–696
Lee WS, Sanchez JF, Mylavapu RS, Choe JS (2003) Estimating chemical properties of Florida soils using spectral reflectance. ASAE 46:1443–1453 ISSN:0001-2351
Mathieu C, Pieltain F (2003) Analyse chimique des sols. Ed TEC et doc. Lavoisier, Paris, p. 292
Matinfar HR, Panah SKA, Zand F, Khodaei K (2011) Detection of soil salinity changes and mapping land cover types based upon remotely sensed data. Arab J Geosci 6:913–919
Metternicht GI, Zinck JA (1997) Spatial discrimination of salt and sodium affected soil surfaces. Int J Remote Sens 18:2571–2586
Metternicht GI, Zinck JA (2003) Remote sensing of soil salinity: potentials and constraints. Remote Sens Environ 85:1–20
Mougenot B (1993) Effet des sels sur la réflectance et télédetection des sols salés. Cah. Orstom, sér.pédol 18: 45-54
Mtimet A (2001) Soils in Tunisia. In Zdruli P, Steduto P, Lacirigola C, Montanarella L (ed) Soil resources of southern and eastern Mediterranean countries. Options Méditerranéennes: Serie B Eetudes et Rrecherche 34:243-262
Nawar S, Buddenbaum H, Hill J (2014) Estimation of soil salinity using three quantitative methods based on visible and near infra reflectance spectroscopy: a case study from Egypt. Arab J Geosci. doi:10.1007/s12517-014-1580-y
UNEP (1991) United Nations Environment Program. Status of desertification and implementation of the United Nations Plans of Action to Combat Desertification. UNEP, Nairobi
Zribi M, Baghdadi N, Nolin M (2011) Remote sensing of soil. Appl Environ Soil Sci 1-2:ID 904561. doi:10.1155/2011/904561
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the DAAD project: German Academic Exchange Service for their financial support. The authors thank the United States Geological Survey (USGS) for the provided datasets. We are grateful to the National Engineering School of Sfax and Technische Universität in Dresden for their help and assistance in proceeding of this study. The corresponding author thanks Stefanie Eisold for her help in field survey and Landsat 8 data preprocessing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Triki Fourati, H., Bouaziz, M., Benzina, M. et al. Modeling of soil salinity within a semi-arid region using spectral analysis. Arab J Geosci 8, 11175–11182 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2004-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2004-3