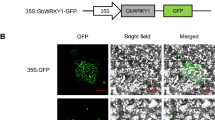
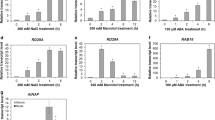
Abstract
Osmotic stress is induced by several environmental stresses such as drought, cold and salinity. Osmotic stress may finally leads to oxidative damage, ionic imbalance and growth inhibition in plants. Gene expression analyses indicated that ZAT10 transcription factor, a novel substrate of Arabidopsis MPKs, could be induced by environmental stresses that result in osmotic stress. As previously reported, ZAT10 overexpressing transgenic plants showed enhanced tolerance to osmotic stress. However, in contrast to previous report, a zat10 knockout mutant showed an osmotic stress sensitive phenotype. To determine the biological function of EAR domain and phosphorylation sites of ZAT10, we constructed two transgenic plants expressing two ZAT10 mutant proteins having EAR domain mutations (ZAT10EAR) and phosphorylation site mutations (ZAT10AA). The phenotype of zat10 was complemented by the expression of ZAT10EAR mutant, however not by the expression of ZAT10AA mutant, indicating that the phosphorylation sites in ZAT10 by MPKs are involved in stress tolerance but the EAR domain is not. In this report, we suggest that ZAT10 function as a positive regulator in osmotic stress tolerance and the phosphorylation of ZAT10 is required for its function in Arabidopsis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray EA (2004) Genes commonly regulated by water-deficit stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 55:2331–2341
Ciftci-Yilmaz S, Mittler R (2008) The zinc finger network of plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:1150–1160
Ciftci-Yilmaz S, Morsy MR, Song L, Coutu A, Krizek BA, Lewis MW, Warren D, Cushman J, Connolly EL, Mittler R (2007) The EAR-motif of the Cys2/His2-type zinc finger protein Zat7 plays a key role in the defense response of Arabidopsis to salinity stress. J Biol Chem 282:9260–9268
Colcombet J, Hirt H (2008) Arabidopsis MAPKs: a complex signaling network involved in multiple biological processes. Biochem J 413:217–226
Davletova S, Rizhsky L, Liang H, Shengqiang Z, Oliver DJ, Coutu J, Shulaey V, Schlauch K, Mittler R (2005) Cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase 1 is a central component of the reactive oxygen gene network of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:268–281
Droillard M, Boudsocq M, Barbier-Brygoo H, Lauriere C (2002) Different protein kinase families are activated by osmotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana cell suspensions. Involvement of the MAP kinases AtMPK3 and AtMPK6. FEBS Lett 527:43–50
Droillard MJ, Boudsocq M, Barbier-Brygoo H, Lauriere C (2004) Involvement of MPK4 in osmotic stress response pathways in cell suspensions and plantlets of Arabidopsis thaliana: activation by hypoosmolarity and negative role in hyperosmolarity tolerance. FEBS Lett 574:42–48
Englbrecht CC, Schoof H, Bohm S (2004) Conservation, diversification and expansion of C2H2 zinc finger proteins in the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. BMC Genomics 5(1):39
Hamilton DW, Hills A, Kohler B, Blatt MR (2000) Ca2+ channels at the plasma membrane of stomatal guard cells are activated by hyperpolarization and abscisic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4967–4972
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant Cellular and Molecular Responses to High Salinity. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499
Hiratsu K, Matsui K, Koyama T, Ohme-Takagi M (2003) Dominant repression of target genes by chimeric repressors that include the EAR motif, a repression domain, in Arabidopsis. Plant J 34:733–739
Kilian J, Whitehead D, Horak J, Wanke D, Weinl S, Batistic O, D'Angelo C, Bornberg-Bauer E, Kudla J, Harter K (2007) The AtGenExpress global stress expression data set: protocols, evaluation and model data analysis of UV-B light, drought and cold stress responses. Plant J 50:347–363
Kreps JA, Wu Y, Chang HS, Zhu T, Wang X, Harper JF (2002) Transcriptome changes for Arabidopsis in response to salt, osmotic, and cold stress. Plant Physiol 130:2129–2141
Lippuner V, Cyert MS, Gasser CS (1996) Two classes of plant cDNA clones differentially complement yeast calcineurin mutants and increase salt tolerance of wild-type yeast. J Biol Chem 271: 12859–12866
Meissner R, Michael AJ (1997) Isolation and characterisation of a diverse family of Arabidopsis two and three-fingered C2H2 zinc finger protein genes and cDNAs. Plant Mol Biol 33:615–624
Mittler R, Kim Y, Song L, Coutu J, Coutu A, Ciftci-Yilmaz S, Lee H, Stevenson B, Zhu JK (2006) Gain-and loss-of-function mutations in Zat10 enhance the tolerance of plants to abiotic stress. FEBS Lett 580:6537–6542
Nguyen XC, Lee K, Kim KE, Liu X-M, Han HJ, Hoang MHT, Lee SW, Hong JC, Moon YH, Chung WS (2012) Identification of a C2H2-type zinc finger transcription factor (ZAT10) from Arabidopsis as a substrate of MAP kinase. Plant Cell Rep 31:737–745
Ohta M, Matsui K, Hiratsu K, Shinshi H, Ohme-Takagi M (2001) Repression domains of class II ERF transcriptional repressors share an essential motif for active repression. Plant Cell 13:1959–1968
Pei ZM, Murata Y, Benning G, Thomine S, Klusener B, Allen GJ, Grill E, Schroeder JI (2000) Calcium channels activated by hydrogen peroxide mediate abscisic acid signalling in guard cells. Nature 406:731–734
Rodriguez MC, Petersen M, Mundy J (2010) Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:621–649
Rossel JB, Wilson PB, Hussain D, Woo NS, Gordon MJ, Mewett OP, Howell KA, Whelan J, Kazan K, Pogson BJ (2007) Systemic and intracellular responses to photooxidative stress in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:4091–4110
Sakamoto H, Araki T, Meshi T, Iwabuchi M (2000) Expression of a subset of the Arabidopsis Cys(2)/His(2)-type zinc-finger protein gene family under water stress. Gene 248:23–32
Sakamoto H, Maruyama K, Sakuma Y, Meshi T, Iwabuchi M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2004) Arabidopsis Cys2/His2-type zinc-finger proteins function as transcription repressors under drought, cold, and high-salinity stress conditions. Plant Physiol 136:2734–2746
Seki M, Kamei A, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2003) Molecular responses to drought, salinity and frost: common and different paths for plant protection. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14:194–199
Seki M, Narusaka M, Ishida J, Nanjo T, Fujita M, Oono Y, Kamiya A, Nakajima M, Enju A, Sakurai T, Satou M, Akiyama K, Taji T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Carninci P, Kawai J, Hayashizaki Y, Shinozaki K (2002) Monitoring the expression profiles of 7000 Arabidopsis genes under drought, cold and high-salinity stresses using a full-length cDNA microarray. Plant J 31:279–292
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Seki M (2003) Regulatory network of gene expression in the drought and cold stress responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:410–417
Vogel JT, Zarka DG, Van Buskirk HA, Fowler SG, Thomashow MF (2005) Roles of the CBF2 and ZAT12 transcription factors in configuring the low temperature transcriptome of Arabidopsis. Plant J 41:195–211
Xiong L, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2002) Cell signaling during cold, drought, and salt stress. Plant Cell 14 Suppl:S165–183
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:781–803
Zhang X, Zhang L, Dong F, Gao J, Galbraith DW, Song CP (2001) Hydrogen peroxide is involved in abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure in Vicia faba. Plant Physiol 126:1438–1448
Zhu JK (2002) Salt and drought stress signal transduction in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 53:247–273
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, X.C., Kim, S.H., Hussain, S. et al. A positive transcription factor in osmotic stress tolerance, ZAT10, is regulated by MAP kinases in Arabidopsis. J. Plant Biol. 59, 55–61 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-016-0442-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-016-0442-4