Abstract
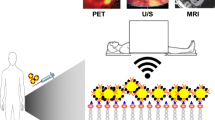
Molecular probes provide imaging signal and contrast for the visualization, characterization, and measurement of biological processes at the molecular level. These probes can be designed to target the cell or tissue of interest and must be retained at the imaging site until they can be detected by the appropriate imaging modality. In this article, we will discuss the basic design of molecular probes, differences among the various types of probes, and general strategies for their evaluation of cardiovascular disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- 18F-FDG:
-
18 F-Fluorodeoxyglucose
- HMPAO:
-
Hexamethylpropyleneamine oxime
- HSV-TK:
-
Herpes simplex virus type I thymidine kinase
- MR:
-
Magnetic resonance
- PET:
-
Positron emission tomography
- SPECT:
-
Single photon emission tomography
- SPIO:
-
Superparamagnetic iron oxide particles
- 99mTc:
-
Technetium 99 M
- VCAM-1:
-
Vascular adhesion molecule-1
References
Nolting DD, Nickels ML, Guo N, Pham W. Molecular imaging probe development: A chemistry perspective. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2012;2:273-306.
Jokerst JV, Pohling C, Gambhir SS. Molecular imaging with surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy nanoparticle reporters. MRS Bull 2013;38:625-30.
Villanueva FS. Molecular imaging of cardiovascular disease using ultrasound. J Nucl Cardiol 2008;15:576-86.
Chen IY, Wu JC. Cardiovascular molecular imaging: Focus on clinical translation. Circulation 2011;123:425-43.
Nguyen PK, Riegler J, Wu JC. Stem cell imaging: From bench to bedside. Cell Stem Cell 2014;14:431-44.
Pu K, Shuhendler AJ, Jokerst JV, Mei J, Gambhir SS, Bao Z, et al. Semiconducting polymer nanoparticles as photoacoustic molecular imaging probes in living mice. Nat Nanotechnol 2014;9:233-9.
Osborn EA, Jaffer FA. The advancing clinical impact of molecular imaging in CVD. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2013;6:1327-41.
Shaw SY. Molecular imaging in cardiovascular disease: Targets and opportunities. Nat Rev Cardiol 2009;6:569-79.
Nguyen PK, Lan F, Wang Y, Wu JC. Imaging: Guiding the clinical translation of cardiac stem cell therapy. Circ Res 2011;109:962-79.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Ian Chen, MD, PhD and Joseph Wu, MD, PhD for their assistance in editing this manuscript. We would like to thank Amy Morris for her contribution to the figures. We would also like to thank the Stanford Cardiovascular Institute, American Heart Association, and the Veterans Affairs for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, G., Nguyen, P.K. Molecular probes for cardiovascular imaging. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 23, 783–789 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-016-0501-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-016-0501-8