Abstract
Introduction
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations are observed in approximately 15% of patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in the USA. Little is known about treatment patterns in EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC following progression on or after first-line (1L) treatment with first- or second-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs). Osimertinib, a third-generation EGFR-TKI, is a treatment option for patients with EGFR T790M-positive NSCLC following progression on 1L EGFR-TKIs. This study analyzed real-world treatment sequencing of EGFR-TKIs, EGFR T790M testing rates, and disposition of patients with EGFR mutations after 1L EGFR-TKI post-FDA approval of osimertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC.
Methods
Adult patients with stage IV NSCLC and documented EGFR mutation-positive status were identified between December 1, 2015 and May 31, 2017 from the US Oncology Network iKnowMed™ electronic health record (EHR). Data were abstracted from the EHR database and supplemented by chart review.
Results
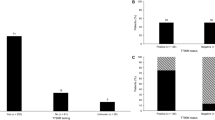
Of 308 patients, 302 (98%) received an EGFR-TKI overall, and 246 patients (80%) received a 1L EGFR-TKI. The most common 1L EGFR-TKI was erlotinib (66%); the remaining 1L regimens were predominantly combination chemotherapies with or without an EGFR-TKI. Only 80 patients (26%) received any 2L therapy. The most common EGFR-TKIs used as 2L monotherapy in patients who received 1L EGFR-TKI were afatinib and osimertinib (n = 7 for both). Among all patients treated with 1L EGFR-TKI (n = 246), 47 (19%) were tested for EGFR T790M [16 patients (34%) were positive], 48 (20%) remained on 1L EGFR-TKI, 29 (12%) received subsequent therapy, 38 (15%) had died on or after their 1L EGFR-TKI therapy, and 131 (53%) stopped their EGFR-TKI with no recorded evidence of having received subsequent therapy at follow-up end.
Conclusion
Following 1L EGFR-TKI treatment, 19% of patients were tested for EGFR T790M, and most (69%) had no record of receiving any subsequent therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7–34.
Hanna N, Johnson D, Temin S, et al. Systemic therapy for stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Update. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(30):3484–515.
Shigematsu H, Lin L, Takahashi T, et al. Clinical and biological features associated with epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations in lung cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(5):339–46.
Khozin S, Blumenthal GM, Jiang X, et al. U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval summary: erlotinib for the first-line treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor exon 19 deletions or exon 21 (L858R) substitution mutations. Oncologist. 2014;19(7):774–9.
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(3):169–81.
Zhang YL, Yuan JQ, Wang KF, et al. The prevalence of EGFR mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2016;7(48):78985–93.
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(10):947–57.
Arcila ME, Oxnard GR, Nafa K, et al. Rebiopsy of lung cancer patients with acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors and enhanced detection of the T790M mutation using a locked nucleic acid-based assay. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(5):1169–80.
Sun JM, Ahn MJ, Choi YL, Ahn JS, Park K. Clinical implications of T790M mutation in patients with acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Lung Cancer. 2013;82(2):294–8.
Kuiper JL, Heideman DA, Thunnissen E, et al. Incidence of T790M mutation in (sequential) rebiopsies in EGFR-mutated NSCLC-patients. Lung Cancer. 2014;85(1):19–24.
Li W, Ren S, Li J, et al. T790M mutation is associated with better efficacy of treatment beyond progression with EGFR-TKI in advanced NSCLC patients. Lung Cancer. 2014;84(3):295–300.
Akamatsu H, Delmonte A, John T, et al. 421P EGFR mutation analysis for prospective patient (pt) selection in AURA3 phase III trial of osimertinib vs platinum-pemetrexed (plt-pem) in pts with EGFR T790M positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann Oncol. 2017;28(suppl_10):mdx671.010.
Zhang H. Three generations of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors developed to revolutionize the therapy of lung cancer. Drug Des Dev Ther. 2016;10:3867–72.
Jänne PA, Yang JC, Kim DW, et al. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(18):1689–99.
Cross DA, Ashton SE, Ghiorghiu S, et al. AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014;4(9):1046–61.
Mok TS, Wu Y-L, Ahn M-J, et al. Osimertinib or platinum-pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(7):629–40.
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(2):113–25.
Wu YL, Ahn MJ, Garassino MC, et al. CNS efficacy of osimertinib in patients with T790M-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: data from a randomized phase III trial (AURA3). J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(26):2702–9.
Reungwetwattana T, Nakagawa K, Cho BC, et al. CNS response to osimertinib versus standard epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(33):3290–7.
Roeper J, Falk M, Tiemann M, et al. Risk of not receiving 2nd line therapy is high in EGFR mt + pts: real world data of certified lung cancer centers on treatment sequence in EGFR mt + pts. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(15_suppl):e21220-e.
Chiang A, Fernandes A, Pavilack M, et al. MA15.11 real world biomarker testing and treatment patterns in patients with advanced NSCLC receiving EGFR-TKIs. J Thorac Oncol. 2018;13(10):S410–1.
Jenkins S, Yang JC, Ramalingam SS, et al. Plasma ctDNA analysis for detection of the EGFR T790M mutation in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12(7):1061–70.
Lee DH. Treatments for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): the road to a success, paved with failures. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;174:1–21.
Ramalingam S, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, et al. LBA2_PR osimertinib vs standard of care (SoC) EGFR-TKI as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with EGFRm advanced NSCLC: FLAURA. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(suppl_5):v605–49.
Ramalingam S, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard D, et al. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1913662.
Planchard D, Popat S, Kerr K, et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(Supplement_4):iv192–237.
Acknowledgements
Funding
Sponsorship for this study and the journal’s Rapid Service Fee were funded by AstraZeneca. All authors had full access to all of the data in this study and take complete responsibility for the integrity of the data and accuracy of the data analysis.
Medical Writing and Editorial Assistance
The authors would like to acknowledge Robert Harrison, PhD, of iMed Comms, Macclesfield, UK, an Ashfield Company, part of UDG Healthcare plc, for technical editing support that was funded by AstraZeneca in accordance with Good Publications Practice (GPP3) guidelines (http://www.ismpp.org/gpp3).
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Disclosures
Eric Nadler reports a consulting or advisory role for Merck, and participation in speaker bureaus for Merck, Genentech and AstraZeneca. Melissa Pavilack and Ancilla Fernandes are AstraZeneca employees and shareholders. Janet Espirito and Jamyia Clark are McKesson employees and shareholders.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Institutional Review Board approval and waiver of authorization was obtained for the study.
Data Availability
Data underlying the findings described in this manuscript may be obtained in accordance with AstraZeneca’s data sharing policy described at https://astrazenecagrouptrials.pharmacm.com/ST/Submission/Disclosure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced Digital Features
To view enhanced digital features for this article go to https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.11494233.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nadler, E., Pavilack, M., Espirito, J.L. et al. Observational Study of Treatment Patterns in Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer After First-Line EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Adv Ther 37, 946–954 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-020-01221-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-020-01221-4