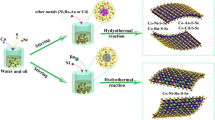
Abstract
The dimensional confinement endows ultrathin nanosheets with unique physical and chemical properties, which have been widely studied for the purpose of developing active electrocatalysts for water splitting. Ultrathin nanosheets are generally synthesized by chemical vapor deposition, exfoliation, or surfactant-assisted synthesis, which either require special equipment and reaction conditions, or is limited by the low yields and the difficulty in controlling the lateral size and structure of the nanosheets. In addition, achieving a high loading of ultrathin nanosheets on the electrodes without compromising their catalytic activity still remains a challenge. Herein, we report a simple electrodeposition method for preparing Co3O4 and Co(OH)2 ultrathin nanosheet arrays (UNA) without using templates or surfactants. The obtained arrays exhibit high activity for oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions, in both alkaline and neutral media. The electrolyzer based on Co3O4 and Co(OH)2 UNA shows superior activity and stability than that based on IrO2 and Pt/C, which demonstrates the potential of the present electrodeposition method for developing active and stable electrocatalysts for water splitting.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thoi, V. S.; Sun, Y. J.; Long, J. R.; Chang, C. J. Complexes of earth-abundant metals for catalytic electrochemical hydrogen generation under aqueous conditions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2388–2400.
Nocera, D. G. The artificial leaf. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 767–776.
Joya, K. S.; Joya, Y. F.; Ocakoglu, K.; Van de Krol, R. Water-splitting catalysis and solar fuel devices: Artificial leaves on the move. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10426–10437.
Jiao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S. Z. Design of electrocatalysts for oxygen- and hydrogen-involving energy conversion reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2060–2086.
Greeley, J.; Jaramillo, T. F.; Bonde, J.; Chorkendorff, I. B.; Nørskov, J. K. Computational high-throughput screening of electrocatalytic materials for hydrogen evolution. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 909–913.
Frame, F. A.; Townsend, T. K.; Chamousis, R. L.; Sabio, E. M.; Dittrich, T.; Browning, N. D.; Osterloh, F. E. Photocatalytic water oxidation with nonsensitized IrO2 nanocrystals under visible and UV light. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 7264–7267.
Kong, D. S.; Cha, J. J.; Wang, H. T.; Lee, H. R.; Cui, Y. First-row transition metal dichalcogenide catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3553–3558.
Zhao, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, X. P.; Xu, C. Y.; Zhang, Z. P.; Shi, G. Q.; Qu, L. T. Graphitic carbon nitride nanoribbons: Graphene-assisted formation and synergic function for highly efficient hydrogen evolution. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13934–13939.
Liu, Z. Y.; Zhang, G. X.; Lu, Z. Y.; Jin, X. Y.; Chang, Z.; Sun, X. M. One-step scalable preparation of N-doped nanoporous carbon as a high-performance electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Nano Res. 2013, 6, 293–301.
Liang, L.; Cheng, H.; Lei, F. C.; Han, J.; Gao, S.; Wang, C. M.; Sun, Y. F.; Qamar, S.; Wei, S. Q.; Xie, Y. Metallic singleunit- cell orthorhombic cobalt diselenide atomic layers: Robust water-electrolysis catalysts. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12004–12008.
Liang, Y. Y.; Li, Y. G.; Wang, H. L.; Zhou, J. G.; Wang, J.; Regier, T.; Dai, H. J. Co3O4 nanocrystals on graphene as a synergistic catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 780–786.
Huang, J. H.; Chen, J. T.; Yao, T.; He, J. F.; Jiang, S.; Sun, Z. H.; Liu, Q. H.; Cheng, W. R.; Hu, F. C.; Jiang, Y. et al. CoOOH nanosheets with high mass activity for water oxidation. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8722–8727.
Bajdich, M.; García-Mota, M.; Vojvodic, A.; Nørskov, J. K.; Bell, A. T. Theoretical investigation of the activity of cobalt oxides for the electrochemical oxidation of water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13521–13530.
Liu, B. R.; Zhang, L.; Xiong, W. L.; Ma, M. M. Cobaltnanocrystal-assembled hollow nanoparticles for electrocatalytic hydrogen generation from neutral-pH water. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6725–6729.
Popczun, E. J.; Read, C. G.; Roske, C. W.; Lewis, N. S.; Schaak, R. E. Highly active electrocatalysis of the hydrogen evolution reaction by cobalt phosphide nanoparticles. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 5427–5430.
Tian, J. Q.; Liu, Q.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. Self-supported nanoporous cobalt phosphide nanowire arrays: An efficient 3D hydrogen-evolving cathode over the wide range of pH 0–14. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7587–7590.
Faber, M. S.; Dziedzic, R.; Lukowski, M. A.; Kaiser, N. S.; Ding, Q.; Jin, S. High-performance electrocatalysis using metallic cobalt pyrite (CoS2) micro-and nanostructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10053–10061.
Peng, S. J.; Li, L. L.; Han, X. P.; Sun, W. P.; Srinivasan, M.; Mhaisalkar, S. G.; Cheng, F. Y.; Yan, Q. Y.; Chen, J.; Ramakrishna, S. Cobalt sulfide nanosheet/graphene/carbon nanotube nanocomposites as flexible electrodes for hydrogen evolution. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12594–12599.
Sun, Y. J.; Liu, C.; Grauer, D. C.; Yano, J.; Long, J. R.; Yang, P. D.; Chang, C. J. Electrodeposited cobalt-sulfide catalyst for electrochemical and photoelectrochemical hydrogen generation from water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17699–17702.
Gao, M. R.; Liang, J. X.; Zheng, Y. R.; Xu, Y. F.; Jiang, J.; Gao, Q.; Li, J.; Yu, S. H. An efficient molybdenum disulfide/cobalt diselenide hybrid catalyst for electrochemical hydrogen generation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 5982.
Jiang, N.; You, B.; Sheng, M. L.; Sun, Y. J. Electrodeposited cobalt-phosphorous-derived films as competent bifunctional catalysts for overall water splitting. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 6251–6254.
Zhu, Y. P.; Liu, Y. P.; Ren, T. Z.; Yuan, Z. Y. Selfsupported cobalt phosphide mesoporous nanorod arrays: A flexible and bifunctional electrode for highly active electrocatalytic water reduction and oxidation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 7337–7347.
Li, Y. J.; Zhang, H. C.; Jiang, M.; Kuang, Y.; Sun, X. M.; Duan, X. Ternary NiCoP nanosheet arrays: An excellent bifunctional catalyst for alkaline overall water splitting. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 2251–2259.
Wang, J. H.; Cui, W.; Liu, Q.; Xing, Z. C.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. Recent progress in cobalt-based heterogeneous catalysts for electrochemical water splitting. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 215–230.
Pu, Z. H.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, P.; Asiri, A. M.; Obaid, A. Y.; Sun, X. P. CoP nanosheet arrays supported on a Ti plate: An efficient cathode for electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 4326–4329.
Liu, Y. W.; Cheng, H.; Lyu, M. J.; Fan, S. J.; Liu, Q. H.; Zhang, W. S.; Zhi, Y. D.; Wang, C. M.; Xiao, C.; Wei, S. Q. et al. Low overpotential in vacancy-rich ultrathin CoSe2 nanosheets for water oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15670–15675.
Wu, J.; Ren, Z. Y.; Du, S. C.; Kong, L. J.; Liu, B. W.; Xi, W.; Zhu, J. Q.; Fu, H. G. A highly active oxygen evolution electrocatalyst: Ultrathin CoNi double hydroxide/CoO nanosheets synthesized via interface-directed assembly. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 713–725.
Liu, Y. W.; Xiao, C.; Lyu, M. J.; Lin, Y.; Cai, W. Z.; Huang, P. C.; Tong, W.; Zou, Y. M.; Xie, Y. Ultrathin Co3S4 nanosheets that synergistically engineer spin states and exposed polyhedra that promote water oxidation under neutral conditions. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11231–11235.
Tan, C. L.; Zhang, H. Wet-chemical synthesis and applications of non-layer structured two-dimensional nanomaterials. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7873.
Morales-Guio, C. G.; Liardet, L.; Hu, X. L. Oxidatively electrodeposited thin-film transition metal (oxy) hydroxides as oxygen evolution catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8946–8957.
Chen, P. Z.; Xu, K.; Fang, Z. W.; Tong, Y.; Wu, J. C.; Lu, X. L.; Peng, X.; Ding, H.; Wu, C. Z.; Xie, Y. Metallic Co4N porous nanowire arrays activated by surface oxidation as electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14710–14714.
Jiang, P.; Liu, Q.; Liang, Y. H.; Tian, J. Q.; Asiri, A. M.; Sun, X. P. A cost-effective 3D hydrogen evolution cathode with high catalytic activity: FeP nanowire array as the active phase. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12855–12859.
Huang, Y. C.; Ye, K. H.; Li, H. B.; Fan, W. J.; Zhao, F. Y.; Zhang, Y. M.; Ji, H. B. A highly durable catalyst based on CoxMn3–x O4 nanosheets for low-temperature formaldehyde oxidation. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 3881–3892.
Li, Z. H.; Shao, M. F.; An, H. L.; Wang, Z. X.; Xu, S. M.; Wei, M.; Evans, D. G.; Duan, X. Fast electrosynthesis of Fe-containing layered double hydroxide arrays toward highly efficient electrocatalytic oxidation reactions. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 6624–6631.
Yuan, C. Z.; Yang, L.; Hou, L. R.; Shen, L. F.; Zhang, X. G.; Lou, X. W. Growth of ultrathin mesoporous Co3O4 nanosheet arrays on Ni foam for high-performance electrochemical capacitors. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7883–7887.
Fan, Y. Q.; Shao, H. B.; Wang, J. M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J. Q.; Cao, C. N. Synthesis of foam-like freestanding Co3O4 nanosheets with enhanced electrochemical activities. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 3469–3471.
You, Y. X.; Zheng, M. J.; Ma, L. G.; Yuan, X. L.; Zhang, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, F. Z.; Song, J. N.; Jiang, D. K.; Liu, P. J. et al. Galvanic displacement assembly of ultrathin Co3O4 nanosheet arrays on nickel foam for a high-performance supercapacitor. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 105604.
O’sullivan, J. P.; Wood, G. C. The morphology and mechanism of formation of porous anodic films on aluminium. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 1970, 317, 511–543.
Gong, F.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Z. S. In situ growth of Co0.85Se and Ni0.85Se on conductive substrates as high-performance counter electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10953–10958.
Hou, Y.; Lohe, M. R.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S. H.; Zhuang, X. D.; Feng, X. L. Vertically oriented cobalt selenide/NiFe layereddouble- hydroxide nanosheets supported on exfoliated graphene foil: An efficient 3D electrode for overall water splitting. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 478–483.
Xiong, S. L.; Yuan, C. Z.; Zhang, X. G.; Xi, B. J.; Qian, Y. T. Controllable synthesis of mesoporous Co3O4 nanostructures with tunable morphology for application in supercapacitors. Chem.—Eur. J. 2009, 15, 5320–5326.
Gao, S.; Jiao, X. C.; Sun, Z. T.; Zhang, W. H.; Sun, Y. F.; Wang, C. M.; Hu, Q. T.; Zu, X. L.; Yang, F.; Yang, S. Y. et al. Ultrathin Co3O4 layers realizing optimized CO2 electroreduction to formate. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 698–702.
Merki, D.; Fierro, S.; Vrubel, H.; Hu, X. L. Amorphous molybdenum sulfide films as catalysts for electrochemical hydrogen production in water. Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1262–1267.
Li, H. B.; Yu, M. H.; Lu, X. H.; Liu, P.; Liang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Tong, Y. X.; Yang, G. W. Amorphous cobalt hydroxide with superior pseudocapacitive performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 745–749.
Zhang, Y.; Cui, B.; Qin, Z. T.; Lin, H.; Li, J. B. Hierarchical wreath-like Au–Co(OH)2 microclusters for water oxidation at neutral pH. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 6826–6833.
Zhu, Y. C.; Li, H. L.; Koltypin, Y.; Gedanken, A. Preparation of nanosized cobalt hydroxides and oxyhydroxide assisted by sonication. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 729–733.
Cao, B. F.; Veith, G. M.; Neuefeind, J. C.; Adzic, R. R.; Khalifah, P. G. Mixed close-packed cobalt molybdenum nitrides as non-noble metal electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 19186–19192.
Kuang, Y.; Feng, G.; Li, P. S.; Bi, Y. M.; Li, Y. P.; Sun, X. M. Single-crystalline ultrathin nickel nanosheets array from in situ topotactic reduction for active and stable electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 693–697.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21474094, 81401531) and the Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (No. 1508085QH154).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2017_1634_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Electrosynthesis of Co3O4 and Co(OH)2 ultrathin nanosheet arrays for efficient electrocatalytic water splitting in alkaline and neutral media
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Liu, B., Zhang, N. et al. Electrosynthesis of Co3O4 and Co(OH)2 ultrathin nanosheet arrays for efficient electrocatalytic water splitting in alkaline and neutral media. Nano Res. 11, 323–333 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1634-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1634-z