Abstract
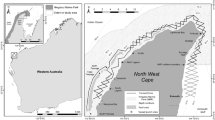
For the Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin, Sousa chinensis, an obligatory shallow water inshore species, the degradation of coastal habitats can have major consequences for population persistence and distribution. Off Taiwan’s west coast (TWC), these animals are predominantly seen in two areas separated by a stretch of coast with only sporadic sightings, suggesting that either (a) only two sectors of TWC offer sufficiently suitable habitat for the dolphins or (b) a recent environmental change limits the population connectivity. We measured the extent of habitat destruction due to land reclamation off TWC since 1972 using a habitat integrity index (HII) and applied general linear models (GLMs) to compare HII with sightings of dolphins per unit effort (SPUE). While early Landsat data reveal extensive continuity and diversity of coastal habitats, by 2013, a total area of over 222 km2 was lost to land reclamation (23 % of dolphin habitat and 40 % of dolphin foraging habitat). GLM analysis showed a significant relationship between HII and SPUE; the lower HII the lower SPUE, indicating that off TWC, the current discontinuous distribution of humpback dolphins is likely due to a different extent of habitat degradation rather than natural patchiness of their environment. We emphasize that the history of coastal habitat alteration must be considered when interpreting cetacean distribution from survey data and formulating habitat management decisions, especially in areas experiencing extensive anthropogenic coastal change.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araújo, C.C., J.Y. Wang, S.K. Hung, B.N. White, and D. Brito. 2014. Viability of the critically endangered eastern Taiwan Strait population of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins, Sousa chinensis. Endangered Species Research 24: 263–271.
Baldwin, R.M., M. Collins, K.V. Waerebeek, and G. Minton. 2004. The Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin of the Arabian region: a status review. Aquatic Mammals 30: 111–124.
Barros, N.B., T.A. Jefferson, and E.C.M. Parsons. 2004. Feeding habits of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins (Sousa chinensis) stranded in Hong Kong. Aquatic Mammals 30: 179–188.
Bates, D., M. Maechler, B. Bolker, and S. Walker. 2015. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software 67: 1–48.
Bearzi, G., D. Holcer, and G.N. Di Sciara. 2004. The role of historical dolphin takes and habitat degradation in shaping the present status of northern Adriatic cetaceans. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 14: 363–379.
Bearzi, G., E. Politi, S. Agazzi, and A. Azzellino. 2006. Prey depletion caused by overfishing and the decline of marine megafauna in eastern Ionian Sea coastal waters (central Mediterranean). Biological Conservation 127: 373–382.
Bearzi, G., S. Agazzi, J. Gonzalvo, M. Costa, S. Bonizzoni, E. Politi, C. Piroddi, and R.R. Reeves. 2008. Overfishing and the disappearance of short-beaked common dolphins from western Greece. Endangered Species Research 5: 1–12.
Castilla, G., K. Larkin, J. Linke, and G.J. Hay. 2009. The impact of thematic resolution on the patch-mosaic model of natural landscapes. Landscape Ecology 24: 15–23.
Chang, W.-L. 2011. Social structure and reproductive parameters of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins (Sousa chinensis) off the west coast of Taiwan. Masters Thesis. National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan.
Chen, Y.L., and H.-Y. Chen. 2006. Seasonal dynamics of primary and new production in the northern South China Sea: The significance of river discharge and nutrient advection. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers 53: 971–986.
Chen, J.-Z., S.-L. Huang, and Y.-S. Han. 2014. Impact of long-term habitat loss on the resource of Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 151: 361–369.
Chen, B., X. Xinrong, T.A. Jefferson, P.A. Olson, Q. Qin, H. Zhang, L. He, and G. Yang. 2016. Conservation status of the Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin (Sousa chinensis) in the northern Beibu Gulf, China. Advances in Marine Biology 73: 119–139.
Chou, L.-S. 2007. The Population Estimation and Habitats of Cetacean in Coastal Waters of Taiwan (I) (in Chinese). Taipei: Fishery Agency, Council of Agriculture, Executive Yuan 63 pp.
Chou, L.-S. 2009. The Confirmation of Status of Endangered Marine Biological Resource and its Biological Characters: Ecology of Sousa chinensis and its Interaction with Fishery in Taiwan (in Chinese). Taipei: Fishery Agency, Council of Agriculture, Executive Yuan 61 pp.
Chou, L.-S., and M.-H. Chen. 2011. Ecological census on the Chinese White Dolphin, Sousa chinensis, along Coastal Yuanlin Waters: Investigation Results between 2009 and 2010. (in Chinese). Taipei: Formosa Plastics Group 123 pp.
Chou, L.-S., and J.-D. Lee. 2010. Habitat Hotspot of Humpback Dolphin, Sousa chinensis, and Master Planning for Conservation Management (in Chinese). Taipei: Forestry Bureau, Council of Agriculture, Executive Yuan 65 pp. http://conservation.forest.gov.tw/public/Attachment/08512385771.pdf.
Chou, L.-S., J.-D. Lee, C.-C. Kao, C.-T. Chuang, C.-F. Chen, W.-C. Yang, P.-F. Lee, K.-T. Shao, M.-H. Chen, R.-C. Wei, and H.-C. Tsai. 2011. Population Ecology, Critical Habitat and Master Planning for Marine Mammal Protected Area of Indo-Pacific Humpback Dolphin, Sousa chinensis (in Chinese). Taipei: Forestry Bureau, Council of Agriculture, Executive Yuan 202 pp. http://conservation.forest.gov.tw/public/Attachment/181616351971.pdf.
Doak, D.F. 1995. Source-sink models and the problem of habitat degradation: general models and applications to the Yellowstone grizzly. Conservation Biology 9: 1370–1379.
ESRI. 2008. ArcMap 9.3. Redlands, California: Environmental Systems Research Institute.
Froese, R., and D. Pauly. 2012. FishBase, World Wide Web electronic publication. http://www.fishbase.org, Version (04/2014), accessed at 22nd/June/2014.
Gowans, S., B. Würsig, and L. Karczmarski. 2008. The social structure and strategies of delphinids: Predictions based on an ecological framework. Advances in Marine Biology 53: 195–294.
Griffen, B.D., and J.M. Drake. 2008. Effects of habitat quality and size on extinction in experimental populations. Proceedings of the Royal Society, Series B: Biological Science 275: 2251–2256.
Huang, S.-L., and L. Karczmarski. 2014. Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins: A demographic perspective of a threatened species. In Primates and Cetaceans: Field Research and Conservation of Complex Mammalian Societies, eds. J. Yamagiwa, and L. Karczmarski., 249–272. Japan: Springer.
Huang, S.-L., Y. Hao, Z. Mei, S.T. Turvey, and D. Wang. 2012a. Common pattern of population decline for freshwater cetacean species in deteriorating habitats. Freshwater Biology 57: 1266–1276.
Huang, S.-L., L. Karczmarski, J. Chen, R. Zhou, W. Lin, H. Zhang, H. Li, and Y. Wu. 2012b. Demography and population trends of the largest population of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins. Biological Conservation 147: 234–242.
Huang, S.-L., M.-Y. Chang, Y.-T. Wang, C.-W. Chang, S.-H. Lin, and W.-N. Tzeng. 2013. Diversity loss of fish fauna due to urbanization in river catchments. In The International Conference on Challenges in Aquatic Sciences. Keelug: National Taiwan Ocean University.
Huang, S.-L., W.-L. Chang, and L. Karczmarski. 2014. Population trend and vulnerability of humpback dolphins Sousa chinensis off the west coast of Taiwan. Endangered Species Research 26: 147–159.
Jefferson, T.A. 2000. Population biology of the Indo-Pacific hump-backed dolphin in Hong Kong waters. Wildlife Monographs 144: 1–65.
Jefferson, T.A., and L. Karczmarski. 2001. Sousa chinensis. Mammalian Species 655: 1–9.
Jefferson, T.A., S.K. Hung, and B. Würsig. 2009. Protecting small cetaceans from coastal development: Impact assessment and mitigation experience in Hong Kong. Marine Policy 33: 305–311.
Karczmarski, L. 1999. Group dynamics of humpback dolphins (Sousa chinensis) in the Algoa Bay region, South Africa. Journal of Zoology 249: 283–293.
Karczmarski, L. 2000. Conservation and management of humpback dolphins: the South African perspective. Oryx 34: 207–216.
Karczmarski, L., V.G. Cockcroft, and A. Mclachlan. 2000. Habitat use and preferences of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins, Sousa chinensis, in Algoa Bay, South Africa. Marine Mammal Science 16: 65–79.
Karczmarski, L., S.-L. Huang, C.K.M. Or, D. Gui, S.C.Y. Chan, W. Lin, L. Porter, W.-H. Wong, R. Zheng, Y.-W. Ho, S.Y.S. Chui, A.J.C. Tiongson, Y. Mo, W.-L. Chang, J.H.W. Kwok, R.W.K. Tang, A.T.L. Lee, S.-W. Yiu, M. Keith, G. Gailey, and Y. Wu. 2016. Humpback dolphins in Hong Kong and the Pearl River Delta: Status, threats, and conservation challenges. Advances in Marine Biology 73: 27–64.
Karczmarski, L., S.-L. Huang, and S.C.Y. Chan. In Press. Threshold of survival of a coastal delphinid in anthropogenically degraded environment: Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins in Pearl River Delta. Scientific Reports.
Kerr, J.T., and M. Ostrovsky. 2003. From space to species: ecological applications for remote sensing. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 18: 299–305.
Ko, M.-C. 2011. The potential competition for prey between Sousa chinensis and the coastal fisheries of western Taiwan. Master Thesis. National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan.
Koper, R.P., L. Karczmarski, D. du Preez, and S. Plön. 2016. Sixteen years later: Occurrence, group size, and habitat use of humpback dolphins (Sousa plumbea) in Algoa Bay, South Africa. Marine Mammal Science 32: 490–507.
Lin, Y.-C. 2012. The long-term variation of the catches on the prey fish of Chinese white dolphins (Sousa chinensis) at western Taiwan. Master Thesis. National Sun-Yet-Sen University, Kaoshiung, Taiwan.
Mattson, K.M., and P.L. Angermeier. 2007. Integrating human impacts and ecological integrity into a risk-based protocol for conservation planning. Environmental Management 39: 125–138.
Merem, E.C., and Y.A. Twumasi. 2008. Using spatial information technologies as monitoring devices in international watershed conservation along the Senegal River Basin of West Africa. International Journal of Environmental Science and Public Health 5: 464–476.
Or, C.K.M. 2016. Socio-spatial ecology of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins (Sousa chinensis) in Hong Kong and Pearl River Estuary. Ph.D. Thesis. The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong S.A.R.
Parra, G.J. 2006. Resource partitioning in sympatric delphinids: space use and habitat preferences of Australian snubfin and Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins. Journal of Animal Ecology 75: 862–874.
Parra, G.J., and D. Cagnazzi. 2016. Conservation status of the Australian humpback dolphin (Sousa sahulensis) using the IUCN Red List Criteria. Advances in Marine Biology 73: 157–192.
Piroddi, C., G. Bearzi, J. Gonzalvo, and V. Christensen. 2011. From common to rare: The case of the Mediterranean common dolphin. Biological Conservation 144: 2490–2498.
Reeves, R. R., M. L. Dalebout, T. A. Jefferson, L. Karczmarski, K. Laidre, G. O’corry-Crowe, L. Rojas-Bracho, E.R. Secchi, E. Slooten, B.D. Smith, J. Y. Wang, and K. Zhou. 2008. Sousa chinensis (Eastern Taiwan Strait subpopulation). In: IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008: e.T133710A3873928. http://www.iucnredlist.org/details/full/133710/0.
Rodriguez, C.A., K.W. Flessa, and D.L. Dettman. 2001. Effects of upstream diversion of Colorado River water on the estuarine bivalve mollusc Mulinia coloradoensis. Conservation Biology 15: 249–258.
Ross, P.S., S.Z. Dungan, S.K. Hung, T.A. Jefferson, C. Macfarquhar, W.F. Perrin, K.N. Riehl, E. Slooten, J. Tsai, J.Y. Wang, B.N. White, B. Würsig, S.C. Yang, and R.R. Reeves. 2010. Averting the baiji syndrome: conserving habitat for critically endangered dolphins in Eastern Taiwan Strait. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 20: 685–694.
Ross, P.S., J. Barlow, T.A. Jefferson, B.E. Hickie, T. Lee, C. Macfarquhar, E.C. Parsons, K.N. Riehl, N.A. Rose, E. Slooten, C.-Y. Tsai, J.Y. Wang, A.J. Wright, and S.C. Yang. 2011. Ten guiding principles for the delineation of priority habitat for endangered small cetaceans. Marine Policy 35: 483–488.
Rowell, K., K.W. Flessa, D.L. Dettman, and M. Román. 2005. The importance of Colorado River flow to nursery habitats of the Gulf corvina (Cynoscion othonopterus). Canadian Journal of Aquatic and Fishery Sciences 62: 2874–2885.
Schupp, C.A., J.E. Mcninch, and J.H. List. 2006. Nearshore shore-oblique bars, gravel outcrops, and their correlation to shoreline change. Marine Geology 233: 63–79.
Slooten, E., Wang J.Y., S.Z. Dungan, K.A. Forney, S.K. Hung, T.A. Jefferson, K.N. Riehl, L. Rojas-Bracho, P.S. Ross, A. Wee, R. Winkler, S.C. Yang, and C.A. Chen. 2013. Impacts of fisheries on the critically endangered humpback dolphin Sousa chinensis population in the eastern Taiwan Strait. Endangered Species Research 22: 99–114.
Turvey, S.T., R.L. Pitman, B.L. Taylor, J. Barlow, T. Akamatsu, L.A. Barrett, X. Zhao, R.R. Reeves, B.S. Stewart, K. Wang, Z. Wei, X. Zhang, L.T. Pusser, M. Richlen, J.R. Brandon, and D. Wang. 2007. First human-caused extinction of a cetacean species? Biology Letters 3: 537–540.
Turvey, S.T., L.A. Barrett, Y. Hao, L. Zhang, X. Zhang, X. Wang, Y. Huang, K. Zhou, T. Hart, and D. Wang. 2010. Rapidly shifting baselines in Yangtze fishing communities and local memory of extinct species. Conservation Biology 24: 778–787.
Wang, K., D. Wang, X. Zhang, A. Pfluger, and L. Barrett. 2006. Range-wide Yangtze freshwater dolphin expedition: The last chance to see Baiji? Environmental Science and Pollution Research 13: 418–424.
Wang, J.Y., S.C. Yang, S.K. Hung, and T.A. Jefferson. 2007. Distribution, abundance and conservation status of the eastern Taiwan Strait population of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins, Sousa chinensis. Mammalia 71: 157–165.
Wang, J.Y., S.C. Yang, P.F. Fruet, F.G. Daura-Jorge, and E.R. Secchi. 2012. Mark-recapture analysis of the critically endangered Eastern Taiwan Strait population of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphins (Sousa chinensis): implications for conservation. Bulletin of Marine Science 88: 885–902.
Wang, J.Y., S.C. Yang, and S.K. Hung. 2015. Diagnosability and description of a new subspecies of Indo-Pacific humpback dolphin, Sousa chinensis (Osbeck, 1765), from the Taiwan Strait. Zoological Studies 54: 36–51.
Weir, C.R., and T. Collins. 2016. A review of the geographical distribution and habitat of the Atlantic humpback dolphin (Sousa teuszii). Advances in Marine Biology 72: 79–117.
Wikramanayake, E.D., E. Dinerstein, J.G. Robinson, U. Karanth, A. Rabinowitz, D. Olson, T. Mathew, P. Hedao, M. Conner, G. Hemley, and D. Bolze. 1998. An ecology-based method for defining priorities for large mammal conservation: the tiger as case study. Conservation Biology 12: 865–878.
Yeh, C.-H. 2011. Distribution Prediction and Ranging Pattern of Indo-Pacific Humpback Dolphins (Sousa chinensis) in Taiwan. Master Thesis. National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan.
Yu, H.-Y., T.-H. Lin, W.-L. Chang, and L.-S. Chou. 2010. Using the mark-recapture method to estimate the population size of Sousa chinensis in Taiwan. in Workshop on Population Connectivity and Conservation of Sousa chinensis off Chinese Coast, Nanjing, China.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Research Grants Council (RGC) of Hong Kong (GRF Grant HKU 17100015M). We acknowledge the important work of Lien-Siang Chou’s research team at the Institute of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, National Taiwan University. L. Karczmarski acknowledges the Professorial Sponsorship Programme of the Ocean Park Conservation Foundation Hong Kong (OPCFHK). We much appreciate the valuable comments provided by James Lovvorn and anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Charles Simenstad
L. Karczmarski, S.-L. Huang, and M. Keith contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karczmarski, L., Huang, SL., Wong, WH. et al. Distribution of a Coastal Delphinid Under the Impact of Long-Term Habitat Loss: Indo-Pacific Humpback Dolphins off Taiwan’s West Coast. Estuaries and Coasts 40, 594–603 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-016-0146-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-016-0146-5