Abstract
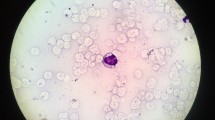
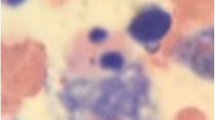
Lysinuric protein intolerance (LPI) (MIM#222700) is a rare autosomal recessive defect in bibasic amino acid transport caused by pathogenic variants in solute carrier family 7 member 7 gene ( SLC7A7). The symptoms begin after weaning from breast milk and include refusal of feeding, vomiting, and consequent failure to thrive. Some metabolic disorders, including LPI, are complicated by hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH); however, the frequency of HLH caused by inborn errors of metabolism is very rare in the HLH cohort. SLC7A7 consists of 11 exons, and has 66 known pathogenic variants. SLC7A7 is associated with HLH. Here, we report the case of a 32-year-old woman who presented with LPI and HLH. Genetic analysis revealed a novel compound heterozygosity in SLC7A7 with two pathogenic variants, c.713C>T (p. Sre238Phe) and c.625+1G>A (splicing acceptor site) inherited from her father and mother, respectively.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LPI:
-
Lysinuric protein intolerance
- SLC7A7 :
-
Solute carrier family 7 member 7 gene
- y+L AT-1:
-
Y+L amino acid transporter-1
- HLH:
-
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
- HGMD:
-
Human genome database
- IEM:
-
Inborn errors of metabolism
- EBV:
-
Epstein–Barr virus
- VCA:
-
Viral capsid antigen
- ANA:
-
Antinuclear antibody
- SS:
-
Sjögren syndrome
- HbA1c :
-
Hemoglobin A1c
- anti-dsDNA:
-
Anti-double stranded DNA
- SLE:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
- COG6:
-
Component of oligomeric Golgi complex 6
References
Torrents D, Mykkänen J, Pineda M, Feliubadaló L, Estévez R, de Cid RD, et al. Identification of SLC7A7, encoding y+LAT-1, as the lysinuric protein intolerance gene. Nat Genet. 1999;21:293–6.
Noguchi A, Takahashi T. Overview of symptoms and treatment for lysinuric protein intolerance. J Hum Genet. 2019;64:849–58.
Yahyaoui R, Pérez-Frías J. Amino acid transport defects in human inherited metabolic disorders. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;21:119.
Carpentieri D, Barnhart MF, Aleck K, Miloh T, deMello D. Lysinuric protein intolerance in a family of Mexican ancestry with a novel SLC7A7 gene deletion. Case report and review of the literature. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2015;2:47–50.
Morimoto A, Nakazawa Y, Ishii E. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Pediatr Int. 2016;58:817–25.
Althonaian N, Alsultan A, Morava E, Alfadhel M. Secondary hemophagocytic syndrome associated with COG6 gene defect: report and review. JIMD Rep. 2018;42:105–11.
Gadoury-Levesque V, Dong L, Su R, Chen J, Zhang K, Risma KA, et al. Frequency and spectrum of disease-causing variants in 1892 patients with suspected genetic HLH disorders. Blood Adv. 2020;4:2578–94.
Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, Egeler RM, Filipovich AH, Imashuku S, et al. HLH-2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007;48:124–31.
Baralle D, Baralle M. Splicing in action: assessing disease causing sequence changes. J Med Genet. 2005;42(10):737–48.
Baronio F, Conti F, Miniaci A, Carfagnini F, Di Natale V, Di Donato G, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of a case of Wolman disease with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2022;30: 100833.
Bartakke S, Nisal A, Bafna V, Valecha A. Secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in an Infant with Wolman Disease. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2021;37(1):191–2.
Alabbas F, Elyamany G, Alanzi T, Ali TB, Albatniji F, Alfaraidi H. Wolman’s disease presenting with secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a case report from Saudi Arabia and literature review. BMC Pediatr. 2021;21(1):1–6.
Gokce M, Unal O, Hismi B, Gumruk F, Coskun T, Balta G, et al. Secondary hemophagocytosis in 3 patients with organic acidemia involving propionate metabolism. Pediatric Hematol Oncol. 2012;29(1):92–8.
Karaman S, Urganci N, Kutluk G, Cetinkaya F. Niemann – Pick disease associated with hemophagocytic syndrome. Turk J Haematol. 2010;27(4):303–7.
Tangye SG, Al-Herz W, Bousfiha A, Chatila T, Cunningham-Rundles C, Etzioni A, et al. Human Inborn Errors of Immunity: 2019 Update on the Classification from the International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee. J Clin Immunol. 2020;40(1):24–64.
Duval M, Fenneteau O, Doireau V, Faye A, Emilie D, Yotnda P, et al. Intermittent hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis is a regular feature of lysinuric protein intolerance. J Pediatr. 1999;134(2):236–9.
Gordon WC, Gibson B, Leach MT, Robinson P. Haemophagocytosis by myeloid precursors in lysinuric protein intolerance. Br J Haematol. 2007;138:1.
Taurisano R, Maiorana A, De Benedetti F, Dionisi-Vici C, Boldrini R, Deodato F. Wolman disease associated with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: attempts for an explanation. Eur J Pediatr. 2014;173:1391–4.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Drs. Mamiko Yamada, Hisato Suzuki, and Toshiki Takeuchi (Center of Medical Genetics, Keio University School of Medicine) for patient genetic analysis. We also thank all the medical staff of Shiga University of Medical Science involved in the treatment of this patient.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YM. and KS. collected and interpreted the data and wrote the manuscript; TT. and YM. designed the study, interpreted the data, wrote the manuscript, and provided medical care for this patient; KK. evaluated the patient and collected data. All authors discussed the results and critically reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Matsukawa, Y., Sakamoto, K., Ikeda, Y. et al. Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis syndrome due to lysinuric protein intolerance: a patient with a novel compound heterozygous pathogenic variant in SLC7A7. Int J Hematol 116, 635–638 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-022-03375-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-022-03375-z