Abstract
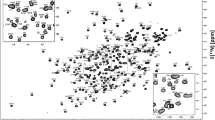
Trappin-2 is a serine protease inhibitor with a very narrow inhibitory spectrum and has significant anti-microbial activities. It is a 10 kDa cationic protein composed of two distinct domains. The N-terminal domain (38 residues) named cementoin is known to be intrinsically disordered when it is not linked to the elafin. The C-terminal domain (57 residues), corresponding to elafin, is a cysteine-rich domain stabilized by four disulfide bridges and is characterized by a flat core and a flexible N-terminal part. To our knowledge, there is no structural data available on trappin-2. We report here the complete 1H, 15N and 13C resonance assignment of the recombinant trappin-2 and the 1H assignments of cementoin and elafin, under the same experimental conditions. This is the first step towards the 3D structure determination of the trappin-2.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baranger K, Zani M-L, Chandenier J et al (2008) The antibacterial and antifungal properties of trappin-2 (pre-elafin) do not depend on its protease inhibitory function. FEBS J 275:2008–2020. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06355.x
Bellemare A, Vernoux N, Morin S et al (2010) Structural and antimicrobial properties of human pre-elafin/trappin-2 and derived peptides against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Microbiol 10:253. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-10-253
Cheung M-S, Maguire ML, Stevens TJ, Broadhurst RW (2010) DANGLE: a Bayesian inferential method for predicting protein backbone dihedral angles and secondary structure. J Magn Reson 202:223–233. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2009.11.008
Efremov RG, Volynsky PE, Dauchez MAM et al (2001) Assessment of conformation and energetics of the N-terminal part of elafin via computer simulations. Theor Chem Acc 106:55–61. doi:10.1007/s002140000237
Francart C, Dauchez M, Alix AJ, Lippens G (1997) Solution structure of R-elafin, a specific inhibitor of elastase. J Mol Biol 268:666–677
Moreau T, Baranger K, Dadé S et al (2008) Multifaceted roles of human elafin and secretory leukocyte proteinase inhibitor (SLPI), two serine proteases inhibitors of the chelonianin family. Biochimie 90:284–295
Pickford AR, O’Leary JM (2004) Isotopic labeling of recombinant proteins from the methylotrophic yeast pichia pastoris. Methods Mol Biol 278:17–33
Vranken WF, Boucher W, Stevens TJ et al (2005) The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: development of a software pipeline. Proteins 59:687–696. doi:10.1002/prot.20449
Zani ML, Nobar SM, Lacour SA et al (2004) Kinetics of the inhibition of neutrophil proteinases by recombinant elafin and pre-elafin (trappin-2) expressed in Pichia pastoris. Eur J Biochem 271:2370–2378. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04156.x
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the committees of the Région Centre-Val de Loire (TRAP2VEC project). We thank Philippe Marceau for support for solid phase peptide synthesis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loth, K., Alami, S.A.I., Habès, C. et al. Complete 1H, 15N and 13C assignment of trappin-2 and 1H assignment of its two domains, elafin and cementoin. Biomol NMR Assign 10, 223–226 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-016-9671-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-016-9671-1